Multi sensor adaptive fusion SLAM method for underground mobile robots in coal mines
-
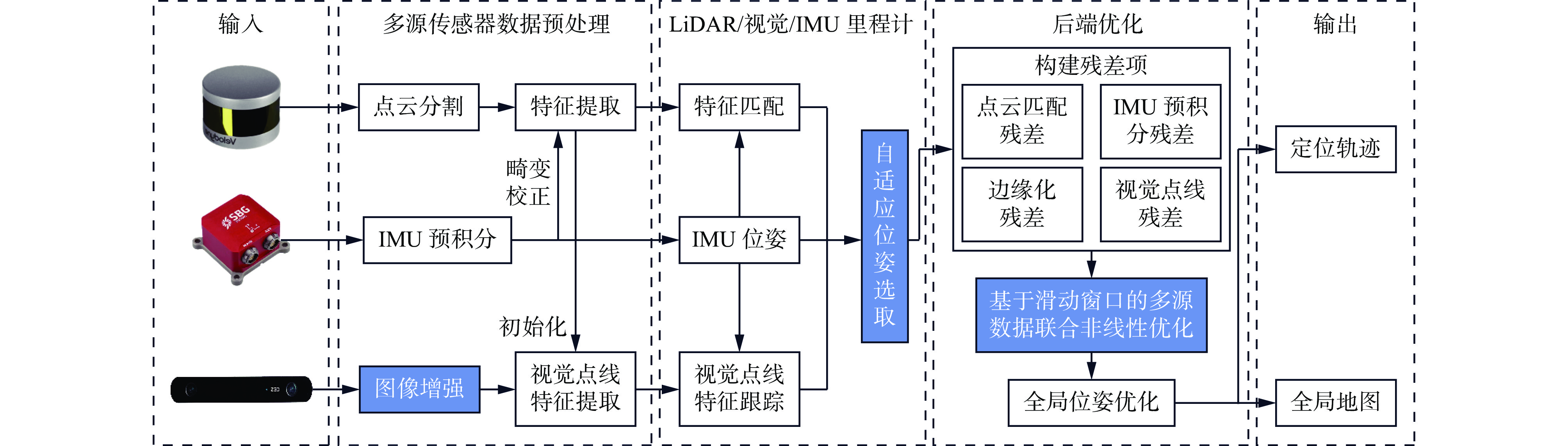
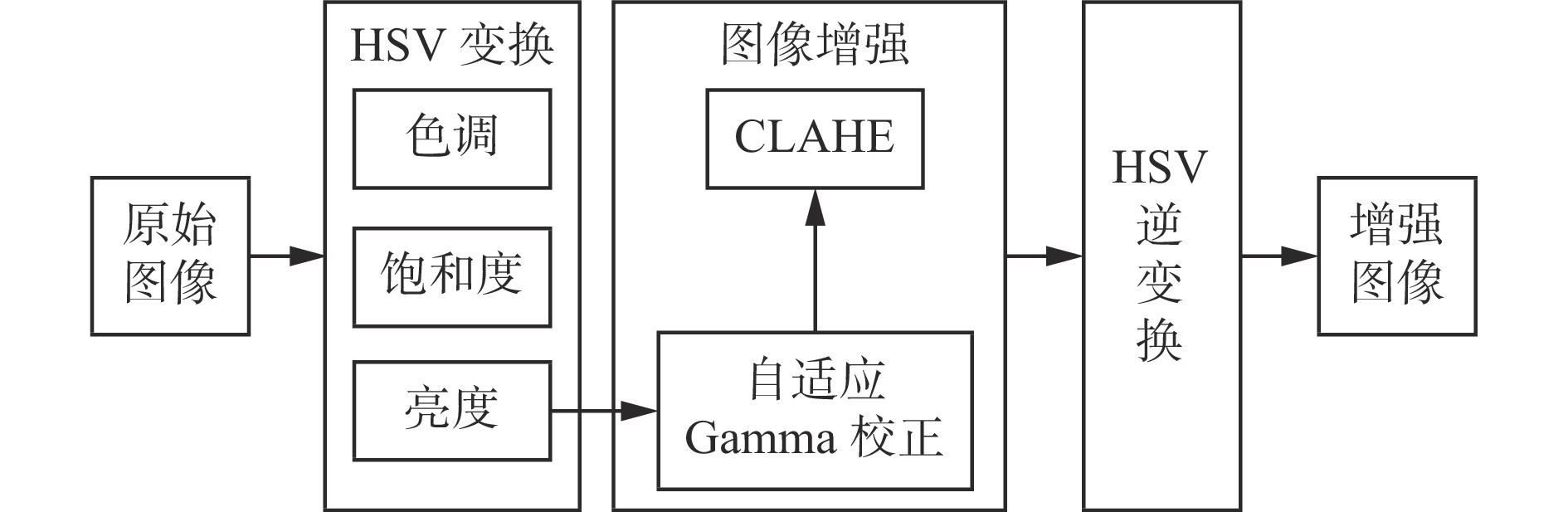
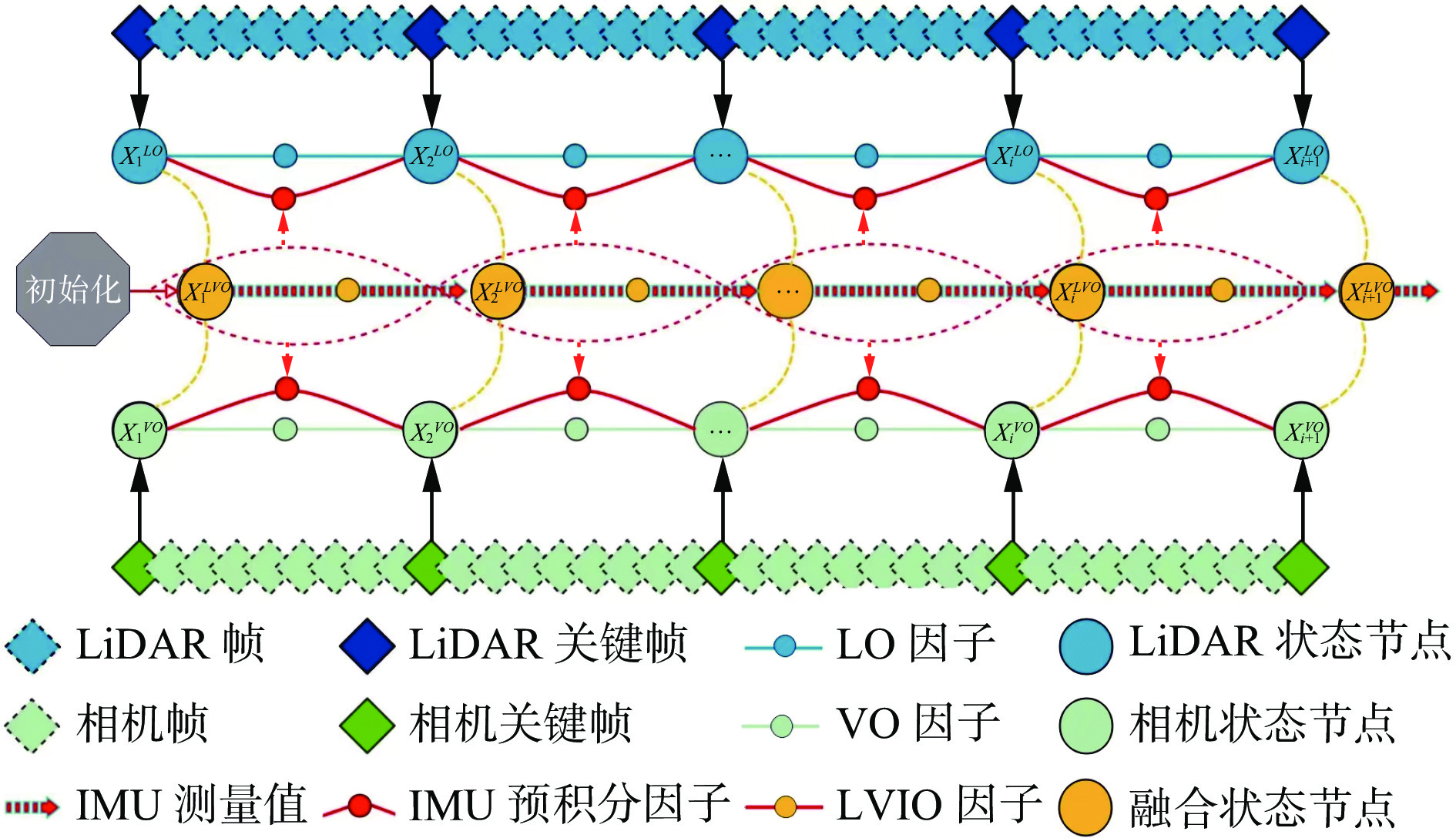
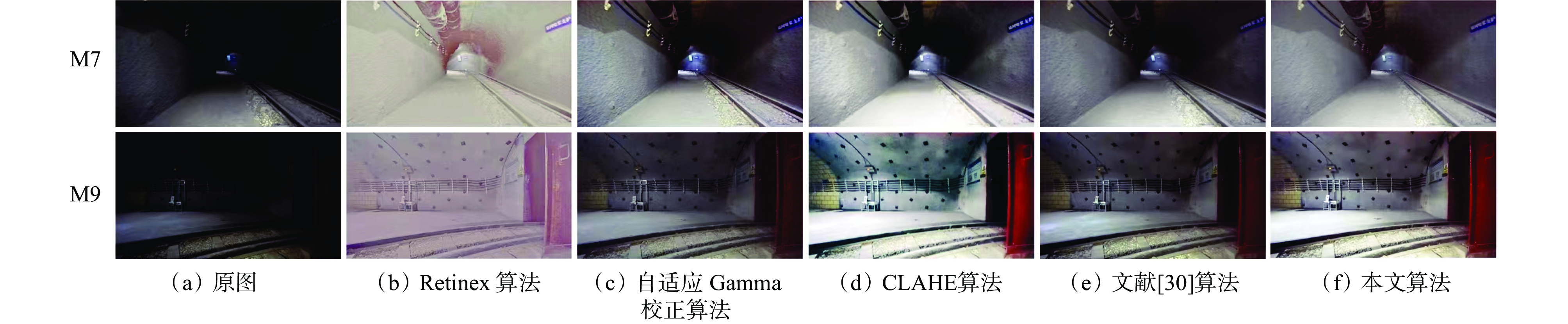
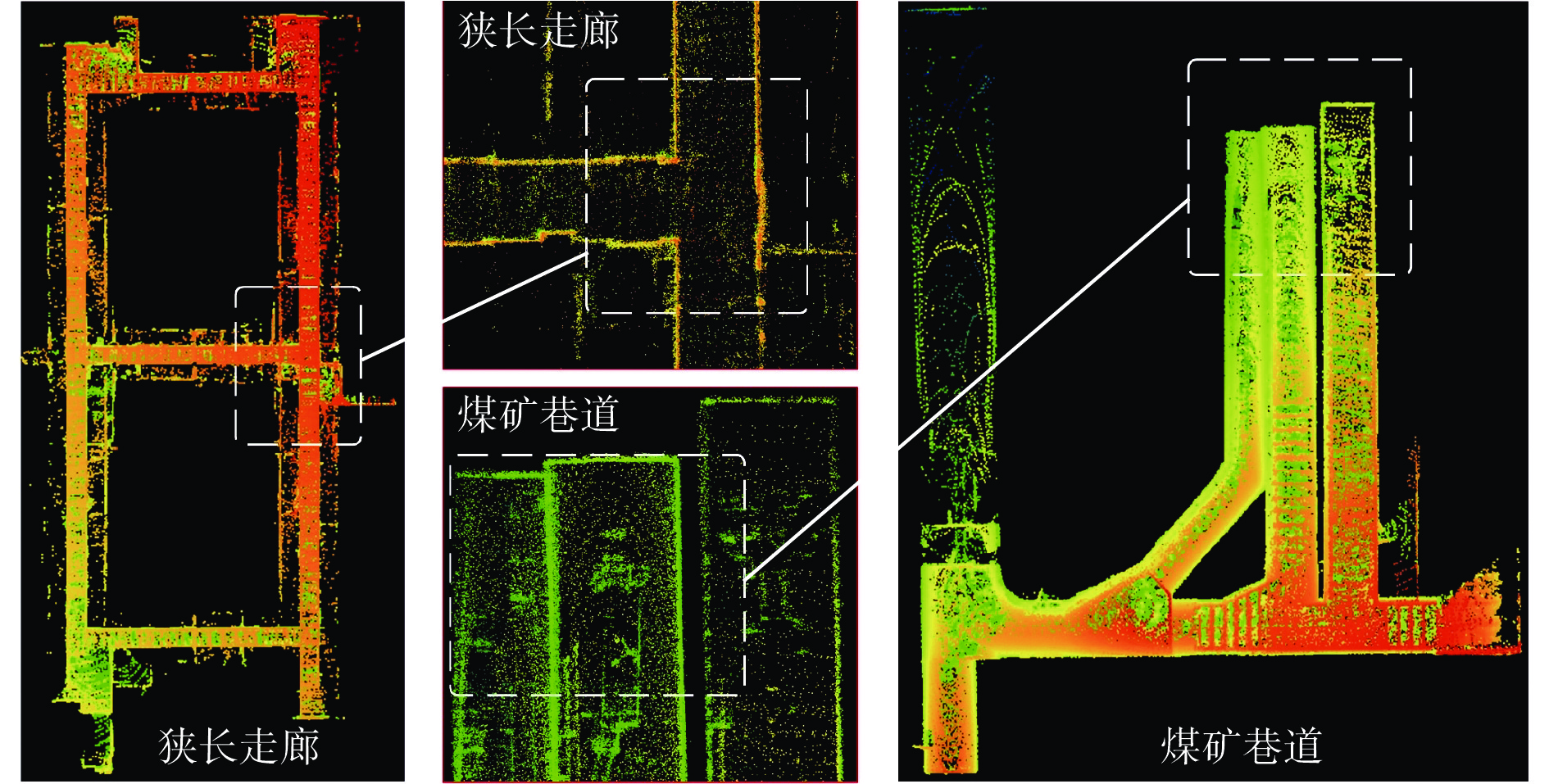
摘要: 基于同时定位与建图(SLAM)技术的移动机器人能够快速、准确、自动化地采集空间数据,进行空间智能感知和环境地图构建,是实现煤矿智能化和无人化的关键。针对目前煤矿井下多传感器融合SLAM方法存在机器人前端位姿估计退化失效和后端融合精度不足的问题,提出了一种煤矿井下移动机器人激光雷达(LiDAR)−视觉−惯性(IMU)自适应融合SLAM方法。对LiDAR点云数据进行聚类分割,提取线面特征,利用IMU预积分状态进行畸变校正,采用基于自适应Gamma校正和对比度受限的自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)的图像增强算法处理低照度图像,再提取视觉点线特征。用IMU预积分状态为LiDAR特征匹配与视觉特征跟踪提供位姿初始值。根据LiDAR相邻帧的线面特征匹配得到移动机器人位姿,之后进行视觉点线特征跟踪,分别计算LiDAR、视觉、IMU位姿变化值,通过设定动态阈值来检测前端里程计的稳定性,自适应选取最优位姿。对不同传感器构建残差项,包括点云匹配残差、IMU预积分残差、视觉点线残差、边缘化残差。为了兼顾精度与实时性,基于滑动窗口实现激光点云特征、视觉特征、IMU测量的多源数据联合非线性优化,实现煤矿井下连续可用、精确可靠的SLAM。对图像增强前后效果进行试验验证,结果表明,基于自适应Gamma校正和CLAHE的图像增强算法能显著提升背光区和光照区的亮度和对比度,增加图像中的特征信息,大幅提升特征点提取数量和匹配质量,匹配成功率达90.7%。为验证所提方法的性能,在狭长走廊和煤矿巷道场景下进行试验验证,结果表明,所提方法在狭长走廊场景的定位均方根误差为0.15 m,构建的点云地图一致性较高;在煤矿巷道场景中的定位均方根误差为0.19 m,构建的点云地图可真实地反映煤矿井下环境。Abstract: Mobile robots based on simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology can quickly, accurately, and automatically collect spatial data for spatial intelligent perception and environmental map construction. It is the key to achieving intelligent and unmanned coal mines. However, the current multi sensor fusion SLAM method in coal mines suffers from degradation and failure in robot front-end pose estimation, as well as insufficient precision in back-end fusion. This study proposes a LiDAR-visual-IMU adaptive fusion SLAM method for underground mobile robots in coal mines. The method clusters and segments LiDAR point cloud data, extracts line and surface features, and uses IMU pre integration state for distortion correction. The method uses image enhancement algorithm based on adaptive Gamma correction and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) to process low light images, and then extracts visual point and line features. The method provides initial pose values for LiDAR feature matching and visual feature tracking using IMU pre integration state. The pose of the mobile robot is obtained by matching the line and surface features of adjacent frames of LiDAR. Then, visual point and line feature tracking is performed to calculate the LiDAR, visual, and IMU pose changes. The stability of the front-end odometer is detected by setting dynamic thresholds, and the optimal pose is adaptively selected. The method constructs residuals for different sensors, including point cloud matching residuals, IMU pre integration residuals, visual point line residuals, and edge residuals. In order to balance precision and real-time performance, a sliding window based joint nonlinear optimization of multi-source data for laser point cloud features, visual features, and IMU measurements is implemented to achieve continuous and reliable SLAM in coal mines. Experimental verification is conducted on the effects before and after image enhancement. The results show that the image enhancement algorithm based on adaptive Gamma correction and CLAHE can significantly improve the brightness and contrast of the backlight and lighting areas, increase the feature information in the image, and significantly improve the quality of feature point extraction and matching. It achieves a matching success rate of 90.7%. To verify the performance of the proposed method, experimental verification is conducted in narrow corridor and coal mine roadway scenarios. The results show that the root mean square error of the proposed method in narrow corridor scenarios is 0.15 m, and the consistency of the constructed point cloud map is high. The root mean square error of positioning in the coal mine roadway scenario is 0.19 m. The constructed point cloud map can truly reflect the underground environment of the coal mine.
-
0. 引言
许多煤矿事故是由井下人员的不合理行为造成,因此,井下人员行为识别是保障煤矿安全生产的重要措施。当前井下人员行为识别主要通过图像识别方式实现,由于煤矿井下环境复杂、光线昏暗并存在大量拍摄死角,使得基于视频和图像的识别方法受到一定限制[1]。WiFi网络具有部署简单、覆盖范围大等特点,已在井下得到广泛部署。通过判断WiFi信号强度的变化可实现井下人员行为识别[2-4],然而,由于井下环境复杂,易出现信号延迟、反射等现象,使得信号强度经常发生异常变化[5],不能实现细粒度检测。
随着特殊驱动发布,研究者可以从一些普通设备中获得信道状态信息(Channel Status Information,CSI),相比于信号强度,CSI能够提供更多、更细粒度的特征值[6-8]。初始的研究主要是直接利用CSI提供的幅度和相位作为特征值实现行为识别[9-10],随着研究的深入,一些基于深度学习的方法也被应用到无线感知中。文献[11]提出了一种三层长短期记忆(Long Short-Term Memory,LSTM)网络,实现了对不同行为的分类。文献[12]提出采用三层卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)提取特征,平均行为识别精度为86.3%。
现有研究利用原始信息构造特征值,通过建立不同的神经网络实现人员行为识别,但缺少对感知机理的研究与分析,且特征提取手段单一。针对该问题,本文分析了人员行为感知机理,提出利用CSI时序信息和统计信息构建多维度人员行为特征信息,在此基础上,提出了一种由多尺度CNN与基于门控循环单元(Gate Recurrent Unit,GRU)的编解码器网络组成的融合网络,用于实现井下人员行为识别。
1. 基于CSI的行为感知模型
CSI是物理层的细粒度信息,描述了无线信号在每个信道上的散射、反射和衰减等信息[13]。信号在正交频分复用系统中通过多个子载波进行调制,子载波经过多条路径到达接收端后,信道频率响应(Channel Frequency Response,CFR)为[14]
$$ H({f_k}) = {{\rm{exp}}({ - {\rm{j}}\Delta \theta }})\sum\limits_{l = 1}^L {{ \alpha _l}} {{\rm{exp}}({ - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} {f_k}{\tau _l})}} $$ (1) 式中:fk为第k个子载波的频率;
$ \Delta \theta $ 为不同频率子载波之间的相位差;L为路径总数;$ {\alpha _l} $ 为第l条路径的信号衰减系数;$ {\tau _l} $ 为第l条路径的信号传输时延。将CFR分解为静态分量和动态分量:
$$ H({f_k}) = {{\rm{exp}}({ - {\rm{j}}\Delta \theta }})({H_{\rm{s}}}({f_k}) + {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{\rm{d}}}({f_k})) $$ (2) 式中:
$ {H_{\rm{s}}}({f_k}) $ 为CFR静态分量,可取常量;$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{\rm{d}}}({f_k}) $ 为CFR动态分量,是由人员动作引起的相关动态变化向量的叠加值[15]。结合菲涅尔区阐述不同位置处人员动作导致CSI变化的规律。菲涅耳区原理如图1所示。假设P1,P2分别为接收机和发射机的位置,Qn为以P1,P2为焦点的第n个椭圆上的点,对于波长为
$ \lambda $ 的WiFi信号,有$$ \left| {{P_1}{Q_n}} \right| + \left| {{Q_n}{P_2}} \right| - \left| {{P_1}{P_2}} \right| = n\lambda /2 $$ (3) 当人员动作出现在Q1位置时,动态路径信号与视距信号的行程差为
$ \lambda /2 $ ,相位差为π,同时反射引入的相位偏转为π,则2路信号的相位差为2π。依此类推,当人员在Q2位置动作时,2路信号的相位差为3π。在人员动作切割菲涅耳区的过程中,2路信号不断出现相干叠加和相干相消的现象,CSI将呈现出类正弦波的变化。2. 井下人员行为识别方法
基于融合网络的井下人员行为识别方法如图2所示,主要包括数据预处理、特征构建和判识网络构造3个部分。数据预处理模块通过CSI商模型、子载波去直流和离散小波去噪对采集的CSI数据进行处理,再将动作特征转换为图像,送入融合网络中进行识别。
2.1 数据预处理
2.1.1 CSI商模型
由于设备制作工艺和环境的影响,数据采集过程中会引入误差。为了减少该误差,采用CSI商模型对采集的数据进行处理。CSI商模型是将接收天线之间的CSI信息相除,即振幅相除,相位相减。天线间的CSI商为
$$ {d_{\rm{q}}}({f_k}) = \frac{{{H_{{\rm{s}}1}}({f_k}) + {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\rm{d}}1}}({f_k})}}{{{H_{{\rm{s}}2}}({f_k}) + {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\rm{d}}2}}({f_k})}} $$ (4) $$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{{\rm{d}}1}}}({f_k}) = {A_1}(f_k){{\rm{exp}}\left( { - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} \dfrac{{{m_1}}}{\lambda }}\right)} $$ (5) $$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{{\rm{d}}2}}}({f_k}) = {A_2}(f_k){{\rm{exp}}\left( { - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} \dfrac{{{m_2}}}{\lambda }} \right)} $$ (6) 式中:
$ {H_{{\rm{s}}1}}({f_k}) $ ,$ {H_{{\rm{s}}2}}({f_k}) $ 分别为天线1和天线2的CFR静态分量;$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\rm{d}}1}}({f_k}) $ ,$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\rm{d}}2}}({f_k}) $ 分别为天线1和天线2的CFR动态分量;A1$({f_k}) $ ,A2$({f_k}) $ 分别为2条传输路径的信号衰减系数;m1,m2分别为天线1、天线2到人员的距离。将式(5)和式(6)代入式(4)可得
$$ {d_{\rm{q}}}(f_k) = \frac{{{H_{{\rm{s}}1}}(f_k) + {A_1}(f_k){{\rm{exp}}\left( { - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} \dfrac{{{m_1}}}{\lambda }} \right)}}}{{{H_{{\rm{s}}2}}(f_k) + {A_2}(f_k){{\rm{exp}} \left( { - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} \dfrac{{\Delta m}}{\lambda }}\right)} {{\rm{exp}} \left( { - {\rm{j}}2{\text{π}} \dfrac{{{m_1}}}{\lambda }}\right)}}} $$ (7) 式中
$ \Delta m $ 为2个天线的间距,$ \Delta m $ =m2−m1。2.1.2 子载波去直流
人员动作时,子载波受到直流信号的影响,导致采集数据产生向上或向下的偏移,从而影响数据准确性,需要进行去直流处理。设h为一组经过CSI商模型处理后的数据,对h进行离散傅里叶变换[16],将变换后信号频率置0即可得到直流分量,用处理后的数据减去直流分量,即可去除子载波中的直流信号。
2.1.3 离散小波去噪
在极低信噪比情况下,可用CSI信息会淹没在设备产生的硬件噪声中,从而导致识别结果出现严重偏差。为了降低设备噪声的影响,使用离散小波变换进行去噪处理[17]。
设u为有效数据,e为噪声数据,则h=u+e,对h进行小波处理,可得
$$ {D} (h) = {{D} _u}(a,b) + {{D} _e}(a,b) $$ (8) 式中:D为小波处理函数;Du,De分别为有效数据的近似系数、噪声数据的细节系数;a,b分别为平移因子和伸缩因子。
在小波处理过程中,通过高通滤波器和低通滤波器对h进行降采样,获得含有设备噪声的细节系数及含有人员动作相关信息的近似系数,再对细节系数进行多次小波处理,从而消除设备引入的噪声。
2.2 特征构建
2.2.1 图像特征构建
传统的特征提取方法将处理后的CSI信息直接送入CNN中进行特征提取。然而,这些提取的特征在经过多层池化计算后,表达能力会逐渐减弱,不利于准确描述人员行为[18]。因此,本文利用格拉姆和/差角场 (Gramian Angular Summation/Difference Fields,GASF/GADF)将处理后的数据转换成图像,从而保留数据的空间和时间特性[19]。
对数据X={x1,x2,…,xN}(N为序列中数据个数)进行归一化,将归一化数据编码为角余弦,使用极坐标表示新的序列:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} \phi_i = {\rm{arccos}}\;{{\tilde x}_i} \qquad i =1,2,\cdots, N \\ r_i = \frac{{{t_i}}}{t_0} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (9) 式中:
$ \phi _i$ 为数据序列转变成极坐标后对应的角度;$ {\tilde x_i} $ 为$x_i $ 归一化后的值,$- 1 \leqslant {{\tilde x}_i} \leqslant 1 $ ;ri为xi的归一化采样时间戳;ti为xi的采样时间戳;t0为序列总的采样时间。分别利用余弦和正弦函数计算数据之间的和与差,将计算结果放入矩阵中,从而构建出能够表征数据序列相关性的特征矩阵:
$$ {{{\boldsymbol{S}}}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\cos ({\phi _1} + {\phi _1})}&{\cos ({\phi _1} + {\phi _2})}& \cdots &{{\text{ }}\cos ({\phi _1} + {\phi _N})} \\ {\cos ({\phi _2} + {\phi _1})}&{{\text{ }}\cos ({\phi _2} + {\phi _2})}& \cdots &{{\text{ }}\cos ({\phi _2} + {\phi _N})} \\ { \vdots {\text{ }}}& \vdots & & \vdots \\ {\cos ({\phi _N} + {\phi _1}){\text{ }}}&{\cos ({\phi _N} + {\phi _2}){\text{ }}}& \cdots &{\cos ({\phi _N} + {\phi _N})} \end{array}{\text{ }}} \right] $$ (10) $$ {\boldsymbol{E}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\sin ({\phi _1} - {\phi _1})}&{\sin ({\phi _1} - {\phi _2})}& \cdots &{{\text{ }}\sin ({\phi _1} - {\phi _N})} \\ {\sin ({\phi _2} - {\phi _1})}&{{\text{ }}\sin ({\phi _2} - {\phi _2})}& \cdots &{{\text{ }}\sin ({\phi _2} - {\phi _N})} \\ { \vdots {\text{ }}}& \vdots & & \vdots \\ {\sin ({\phi _N} - {\phi _1}){\text{ }}}&{\sin ({\phi _N} - {\phi _2}){\text{ }}}& \cdots &{\sin ({\phi _N} - {\phi _N})} \end{array}} \right] $$ (11) 2.2.2 统计特征提取
由于人员动作的复杂性和多样性,需要构建更多有用的特征来提高分类精度。本文提取的特征信息包括10个时域特征、5个频域特征和1个能量特征。时域特征为最大值、最小值、均值、方差、标准差、峰峰值、均方根、偏度、四分位距、波形因数,频域特征为峰值因子、最小频率、最大频率、谱概率、频谱熵,能量特征为信号能量。
2.3 判识网络构造
根据人员动作的特点,提出一种由基于GRU的编解码网络和多尺度CNN组成的融合网络,如图3所示。利用GRU保留前后数据之间的关联性,同时利用注意力机制的权重分配策略有效提取关键特征,以提高行为识别的准确率。输入数据主要来自2个部分:一部分是利用GASF/GADF建立的图像特征,该部分特征用多尺度CNN进行处理;另一部分是从CSI信息中提取的统计特征,该部分特征用基于GRU的编解码网络进行处理。对2个部分的特征进行拼接,再通过多层感知机实现动作识别。
表 1 基于GRU的编解码网络参数Table 1. Parameters of encoding and decoding network based on GRU序号 网络层 输出维度 1 GRU 256×512 2 GRU 256×256 3 GRU 128×256 4 GRU 128×128 5 Transposed Convolution 128×128 6 Self−Attention 128×128 7 Transposed Convolution 128×256 8 Self−Attention 128×256 9 Transposed Convolution 128×512 10 Self−Attention 128×512 11 1D−Convolution 64×256 12 Flattern 2048×1 表 2 多尺度CNN参数Table 2. Parameters of multi-scale CNN序号 网络层 核大小 核数目 输出维度 1 ECA 512×1600 1−1 Con1−1 5 256 256×800 1−2 Con1−2 7 256 256×800 1−3 Con1−3 1 256 256×800 2−1 Con2−1 7 512 512×400 2−2 Con2−2 3 512 512×400 2−3 Con2−3 5 512 512×400 3−1 Con3−1 3 256 256×400 3−2 Con3−2 5 256 256×400 3−3 Con3−3 7 256 256×400 4−1 Pooling4−1 128×512 4−2 Pooling4−2 128×512 4−3 Pooling4−3 128×512 5−1 ECA 128×512 5−2 ECA 128×512 5−3 ECA 128×512 6 Flatten 2048×1 3. 实验分析
3.1 实验平台
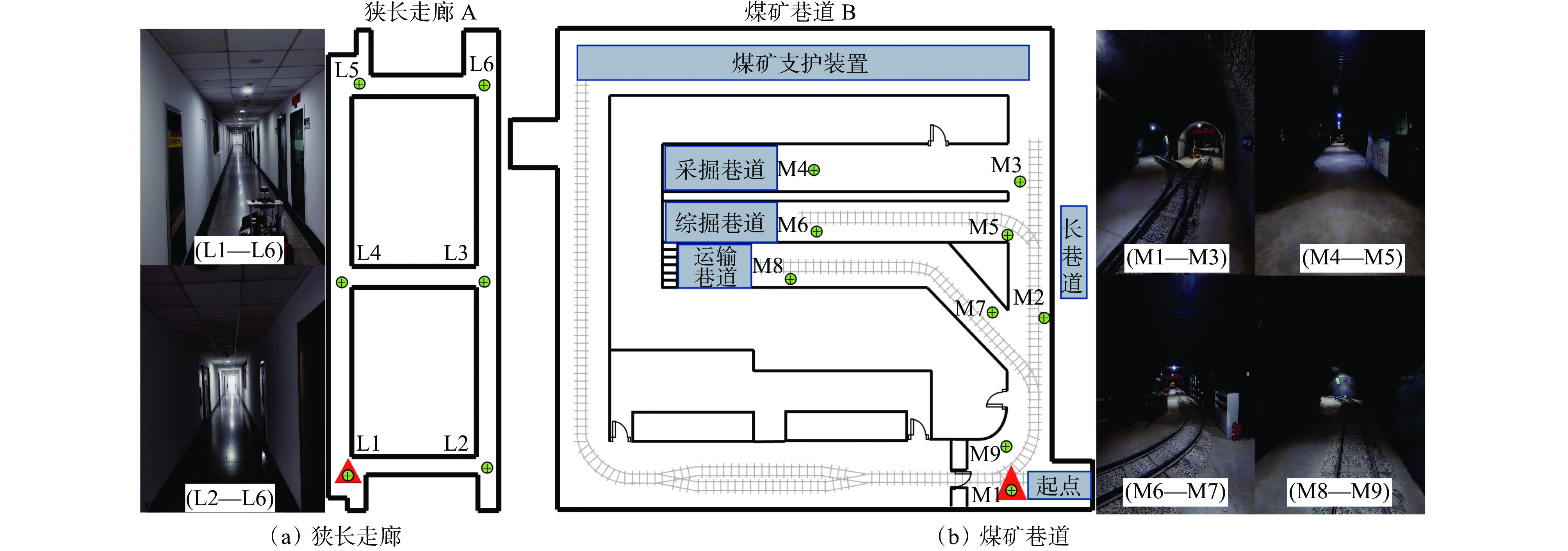
为了验证井下人员行为识别方法的普适性,在中国矿业大学文昌校区的实验巷道内进行了实验。实验巷道长度为45 m,宽度约为5 m,如图4所示。
在实验过程中,使用带有三天线的D−LINK85无线路由器作为CSI信息发射端,使用装有Intel 5300网卡的计算机作为CSI信息接收端,并在主机中安装了CSI−tool工具。为了方便查看结果,开发了人员行为识别结果显示程序,如图5所示,通过该程序能够直观显示判识网络的运行结果。
3.2 实验结果
实验中共邀请8位性别和体型各异的志愿者完成包括行走、摘帽子等在内的8种动作,见表3。这8种动作代表井下工作人员存在潜在的危险行为。
表 3 实验动作Table 3. Experimental actions动作 潜在危险行为 行走 进入危险区域 摘帽子 摘安全帽 扔东西 乱扔工具 坐 在危险区域休息 抽烟 违规抽烟 挥手 斗殴 跑动 违规下车 睡觉 在危险区域睡觉 对8种动作进行识别后得到的混淆矩阵如图6所示。矩阵的每一行代表真实动作,每一列代表模型预测的动作。8种动作的平均识别准确率为97.37%,其中,对睡觉和坐的识别准确率最高,因为这2个动作相对简单,所以更容易识别。而抽烟等上肢动作持续时间和幅度差距较小,存在一定的判识难度。在所有动作中,最容易发生误判的动作是行走和跑动,因为这2个动作只是在速度上有差异,人员肢体动作十分相近。
3.3 对比分析
使用准确率、精确率、召回率和F1分数作为评价指标,将融合网络分别与CNN和GRU进行比较,结果如图7所示。可看出融合网络的性能最佳,其次是GRU。这主要是由于动作存在一定时间相关性,融合网络在利用时间相关性的同时,还通过不同链路信息构建图像,从而充分利用了链路之间的信息。而CNN将链接信息直接整合到矩阵中,对链路信息的利用不完整。
将本文方法与HAR系统[20]、WiWave系统[21]和Wi−Sense系统[22]进行比较。其中HAR系统采用KNN作为行为识别模型,WiWave系统在卷积架构中引入了离散小波变换,Wi−Sense系统根据处理后的时变数据谱图形成多普勒指纹,并将其输入神经网络中进行判识。实验结果如图8所示。在HAR系统中,由于KNN不能表示动作之间的复杂关系,所以识别精度低于WiWave系统和本文方法。WiWave系统可以将小波变换良好的时频局部特征与神经网络的自学习能力相结合,但是没有考虑不同动作在连续时间内的不同特征,导致识别精度低于本文方法。Wi−Sense系统缺少对整体数据特征的挖掘,因此准确率低于本文方法。
3.4 影响因素分析
3.4.1 优化器和学习率对识别精度的影响
分别选择Adam,SGD,Ada Delta和RMS Prop作为网络优化器,测试在不同学习率下的识别准确率,结果见表4。可看出采用Adam作为优化器,学习率为0.001时,8种动作的平均识别准确率最高,达97.37%,而当学习率大于0.001时,模型的准确率开始下降。因此,在模型训练过程中,选择Adam作为优化器,并将学习率设置为0.001。
表 4 不同优化器和学习率下的识别准确率Table 4. Recognition accuracy under different optimizers and learning rates学习率 准确率/% Ada Delta SGD RMS Prop Adam 0.0001 95.54 94.75 96.33 97.01 0.001 93.43 94.37 94.64 97.37 0.01 96.45 94.88 93.41 92.15 0.05 92.97 92.64 90.72 92.89 0.1 88.25 89.76 91.45 91.99 3.4.2 动作速度对识别精度的影响
由于不同人员做相同动作的时间和幅度不同,可能导致在一定持续时间内采集的数据存在差异,从而影响识别精度。测试了行走与摘帽子2种动作在快速、正常速度和慢速完成时的平均识别准确率,结果如图9所示。可看出本文提出的方法能够在不同速率下取得较高的识别准确率。对正常速度动作的平均识别准确率为95.6%,高于快速动作情况下的93.6%和慢速动作情况下的92.7%。这主要是由于速度较快时能够获取的特征较少,而速度较慢时则会引入无用信息,从而对识别精度产生影响。
3.4.3 距离对识别精度的影响
分别设置收发设备之间的距离为0.5,1,1.5,2,2.5,3,3.5 m,测试不同距离对识别精度的影响,结果如图10所示。可看出距离为2 m和2.5 m时,识别准确率较高。当距离为0.5 m时,由于距离较近,一些对信号传输路径干扰较小的动作会使原来的多通信链路退化为单通信链路,从而使获得的特征信息减少,导致识别准确率下降。而当距离增加时,会引入额外的传输路径,引入更多噪声,从而影响识别精度。
4. 结论
1) 提出一种基于融合网络的井下人员行为识别方法。通过CSI商模型、子载波去直流和离散小波去噪对采集的CSI数据进行预处理,采用GASF/GADF将CSI数据转换成图像数据,最后通过融合网络实现井下人员行为识别。
2) 实验结果表明,该方法对行走、摘帽子、扔东西、坐、抽烟、挥手、跑动、睡觉8种动作的平均识别准确率为97.37%,对睡觉和坐的识别准确率最高,最容易发生误判的动作是行走和跑动。
3) 对比分析结果表明,融合网络的性能优于CNN和GRU,人员行为识别准确率高于HAR系统、WiWave系统和Wi−Sense系统。
4) 影响因素分析结果表明:采用Adam作为优化器,学习率为0.001时,8种动作的平均识别准确率最高;正常速度下行走和摘帽子2种动作的平均识别精度为95.6%,高于快速动作情况下的93.6%和慢速动作情况下的92.7%;收发设备之间的距离为2 m和2.5 m时,识别准确率较高。
-
表 1 多源传感器设备型号与信息
Table 1 Sensors model and information
设备 设备型号 设备信息 LiDAR VLP−16 频率:10 Hz ;最大测量距离:150 m IMU Ellipse2−N 频率:200 Hz ;横滚/俯仰误差为±0.1°;航向误差为0.5° 相机 Zed−2i 频率:30 Hz; 图像分辨率(H×V):1 280×720 控制台 Autolabor−PC CPU:AMD Ryzen3 3 200G、DDR4 8 G 机器人 Autolabor−Pro1 驱动模式:四驱;位移速度:0.5~1.5 m/s;旋转角速度:0.56 rad/s 表 2 特征提取与跟踪对比
Table 2 Features extraction and tracking comparison
算法 特征点数量/个 匹配数量/个 匹配成功率% M7 M9 M7 M9 M7 M9 原图 273 308 89 122 32.6 39.6 Retinex算法 368 390 242 269 65.8 69.0 自适应Gamma校正算法 330 367 250 286 75.8 77.9 CLAHE算法 329 356 276 303 83.9 85.1 文献[30]算法 347 374 297 331 85.6 88.5 本文算法 365 392 331 365 90.7 93.1 表 3 定位轨迹的标准差和均方根误差
Table 3 Root mean squared error and standard deviation of positioning trajectory
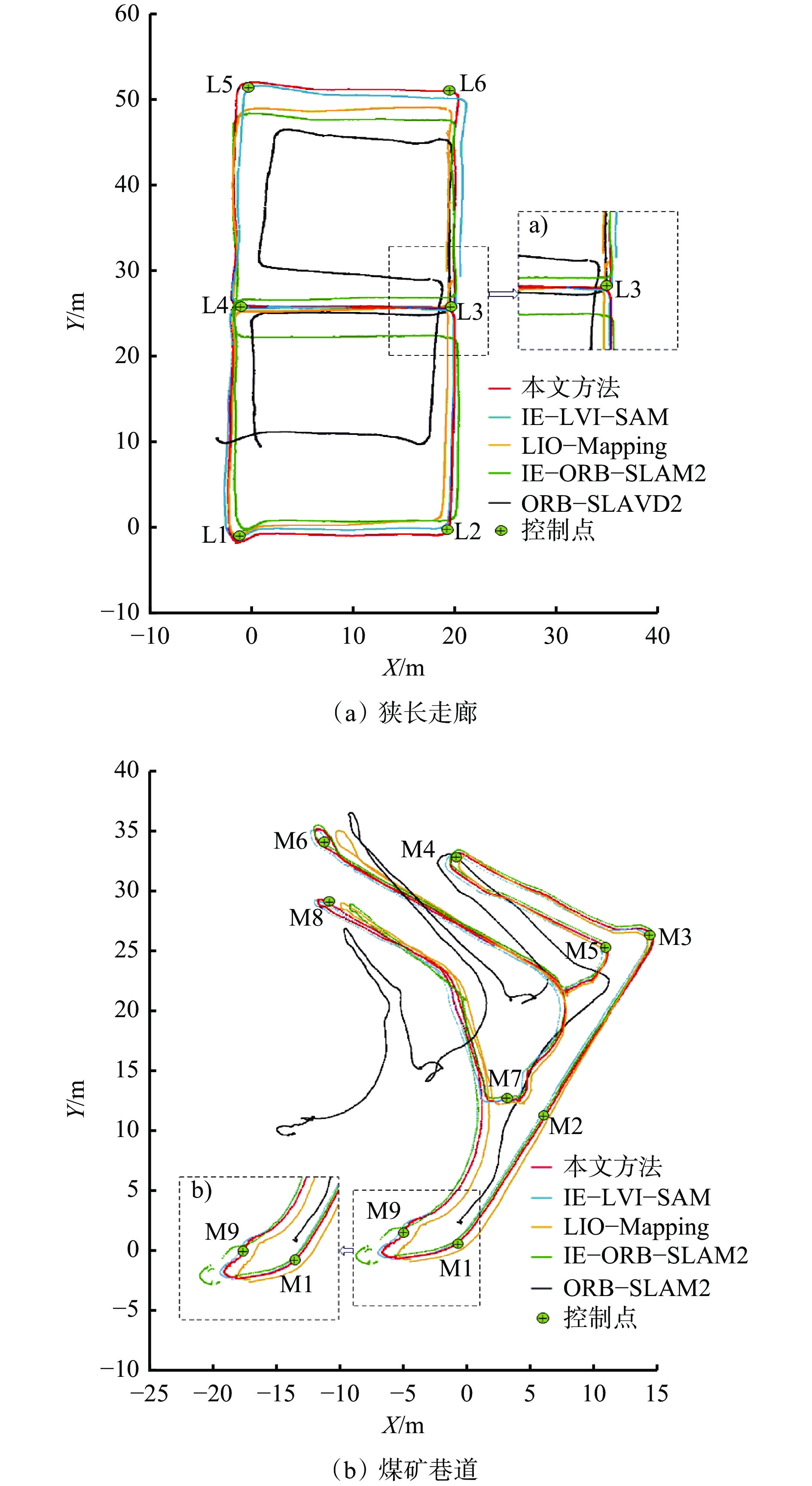
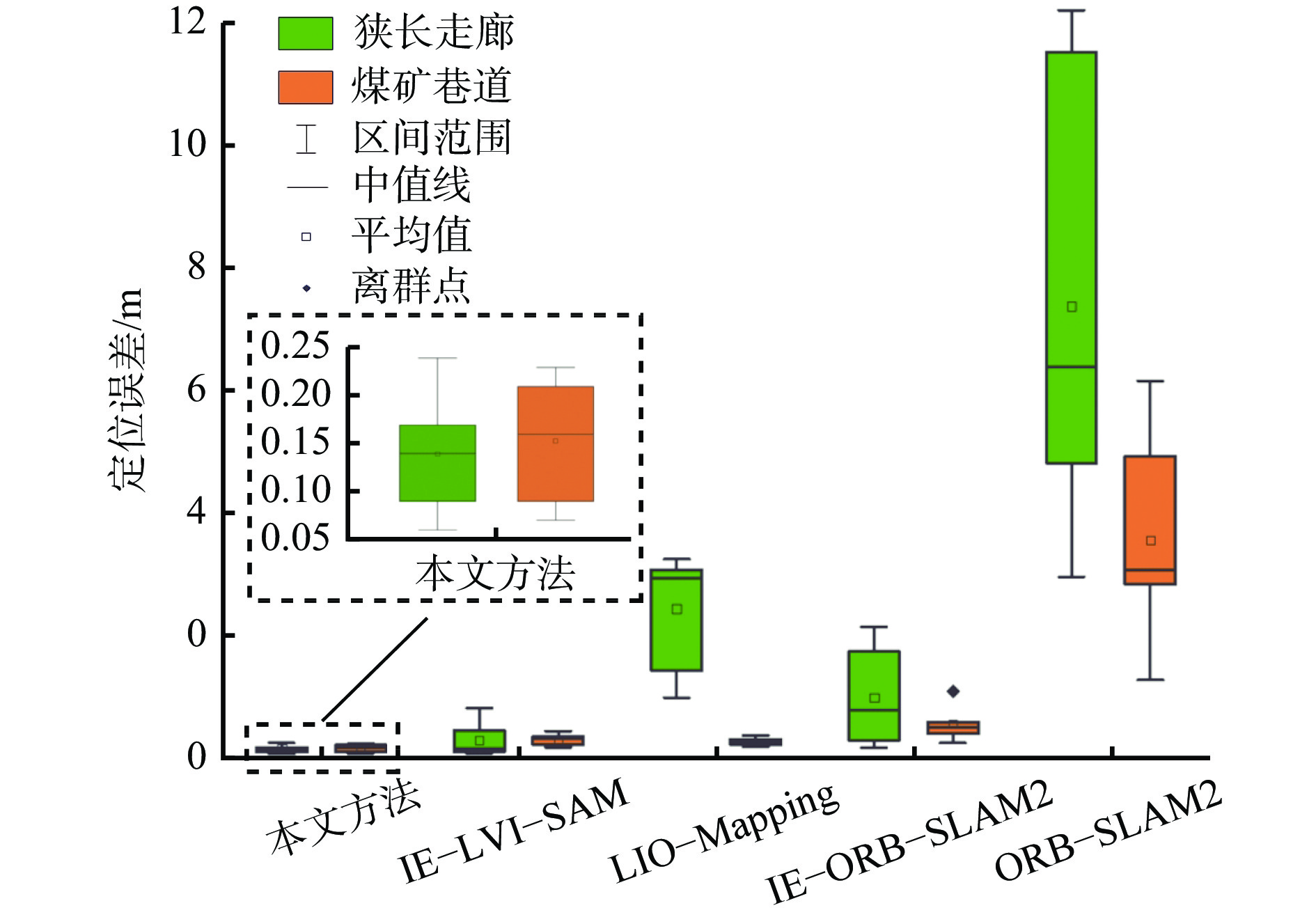
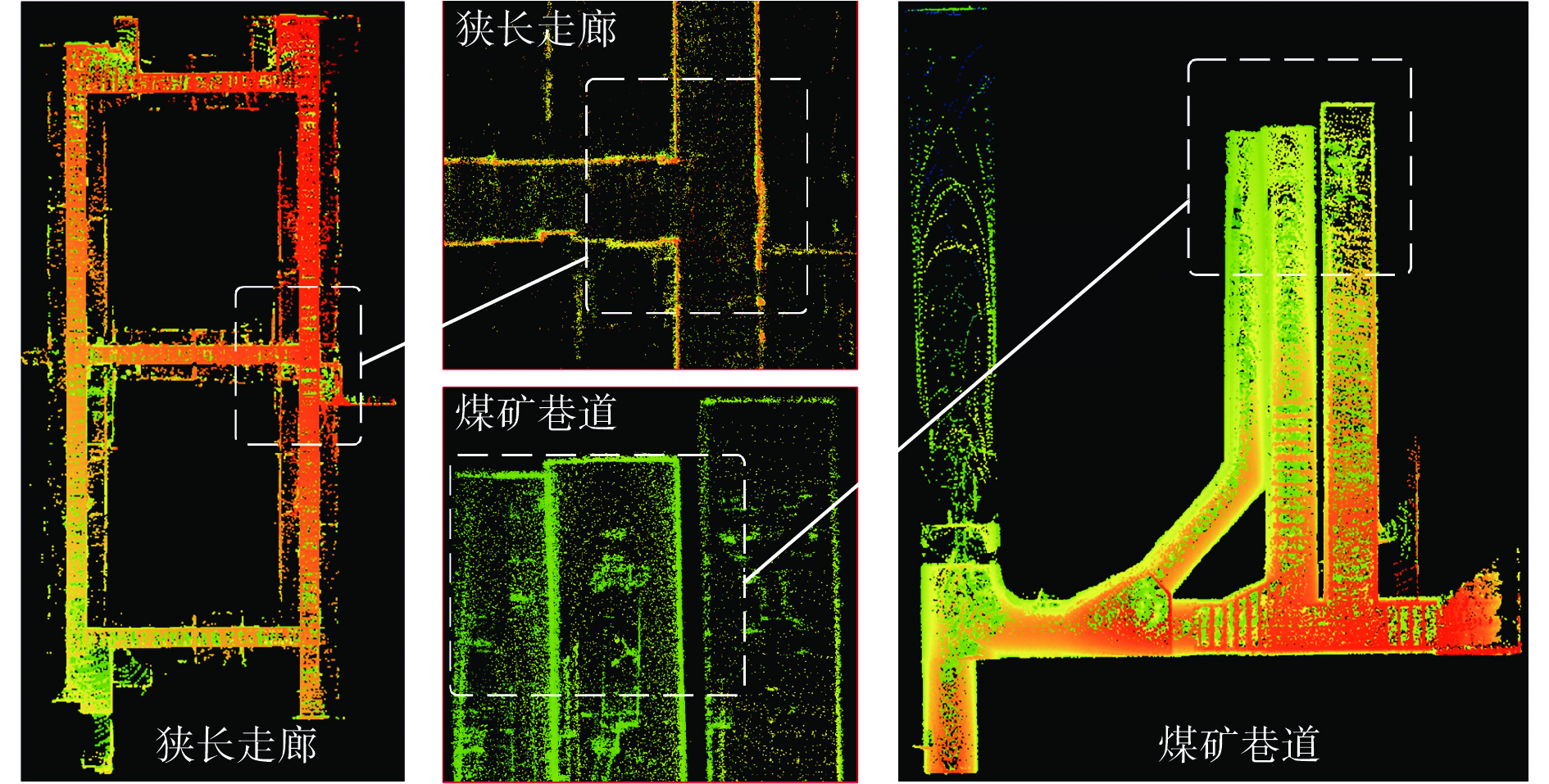
m 误差 狭长走廊 煤矿巷道 本文方法 IE−LVI−SAM LIO−Mapping IE−ORB−SLAM2 ORB−SLAM2 本文方法 IE−LVI−SAM LIO−Mapping IE−ORB−SLAM2 ORB−SLAM2 STD 0.06 0.27 0.78 0.89 3.39 0.08 0.10 0.24 0.57 4.05 RMSE 0.15 0.39 1.25 2.58 8.12 0.19 0.28 0.75 0.60 6.82 -
[1] 肖琳芬. 王国法院士:煤矿智能化技术体系建设进展与煤炭产业数字化转型[J]. 高科技与产业化,2024,30(2):12-15. XIAO Linfen. Academician Wang Guofa:progress in the construction of intelligent technology system in coal mines and the digital transformation of coal industry[J]. High-Technology & Commercialization,2024,30(2):12-15.
[2] 任满翊. 无人化智能煤矿建设探索与实践[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(增刊1):27-29. REN Manyi. Exploration and practice of unmanned intelligent coal mine construction[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(S1):27-29.
[3] KHATTAK S,NGUYEN H,MASCARICH F,et al. Complementary multi-modal sensor fusion for resilient robot pose estimation in subterranean environments[C]. International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems,Athens,2020:1024-1029.
[4] 龚云,颉昕宇. 基于同态滤波方法的煤矿井下图像增强技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(3):241-250. GONG Yun,JIE Xinyu. Research on coal mine underground image recognition technology based on homomorphic filtering method[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2023,51(3):241-250.
[5] YANG Xin,LIN Xiaohu,YANG Wanqiang,et al. A robust LiDAR SLAM method for underground coal mine robot with degenerated scene compensation[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,15(1). DOI: 10.3390/RS15010186.
[6] WU Weitong,LI Jianping,CHEN Chi,et al. AFLI-Calib:robust LiDAR-IMU extrinsic self-calibration based on adaptive frame length LiDAR odometry[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2023,199:157-181. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.04.004
[7] COLE D M,NEWMAN P M. Using laser range data for 3D SLAM in outdoor environments[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation,Orlando,2006:1556-1563.
[8] LI Menggang,ZHU Hua,YOU Shaoze,et al. Efficient laser-based 3D SLAM in real time for coal mine rescue robots[C]. 8th Annual International Conference on Technology in Automation,Control,and Intelligent Systems,Tianjin,2018:971-976.
[9] KNEIP L,WEISS S,SIEGWART R. Deterministic initialization of metric state estimation filters for loosely-coupled monocular vision-inertial systems[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,San Francisco,2011:2235-2241.
[10] BLOESCH M,BURRI M,OMARI S,et al. Iterated extended Kalman filter based visual-inertial odometry using direct photometric feedback[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research,2017,36(10):1053-1072. DOI: 10.1177/0278364917728574
[11] GOMEZ-OJEDA R,MORENO F A,ZUNIGA-NOëL D,et al. PL-SLAM:a stereo SLAM system through the combination of points and line segments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2019,35(3):734-746. DOI: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2899783
[12] YANG Gaochao,WANG Qing,LIU Pengfei,et al. An improved monocular PL-SlAM method with point-line feature fusion under low-texture environment[C]. 4th International Conference on Control and Computer Vision,Macau,2021:119-125.
[13] ZHAO Shibo,FANG Zheng,LI Haolai,et al. A robust laser-inertial odometry and mapping method for large-scale highway environments[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Macau,2019:1285-1292.
[14] SHAN Tixiao,ENGLOT B,MEYERS D,et al. Lio-sam:tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Las Vegas,2020:5135-5142.
[15] ZHANG Ji,SINGH S. Visual-lidar odometry and mapping:low-drift,robust,and fast[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation,Seattle,2015:2174-2181.
[16] LIU Yanqing,YANG Dongdong,LI Jiamao,et al. Stereo visual-inertial SLAM with points and lines[J]. IEEE Access,2018,6:69381-69392. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2880689
[17] TIAN Chengjun,LIU Haobo,LIU Zhe,et al. Research on multi-sensor fusion SLAM algorithm based on improved gmapping[J]. IEEE Access,2023,11(9):13690-13703.
[18] SHAN Tixiao,ENGLOT B,RATTI C,et al. Lvi-sam:tightly-coupled lidar-visual-inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation,Xi'an,2021:5692-5698.
[19] 隋心,王思语,罗力,等. 基于点云特征的改进RANSAC地面分割算法[J]. 导航定位学报,2024,12(1):106-114l. SUI Xin,WANG Siyu,LUO Li,et al. Improved RANSAC ground segmentation algorithm based on point cloud features[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning,2024,12(1):106-114.
[20] HUANG S C,CHENG F C,CHIU Y S. Efficient contrast enhancement using adaptive gamma correction with weighting distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2013,22(3):1032-1041. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2226047
[21] WANG Jun,WANG Rui,WU Anwen. Improved gamma correction for visual slam in low-light scenes[C]. IEEE 3rd Advanced Information Management,Communicates,Electronic and Automation Control Conference,Chongqing,2019:1159-1163.
[22] HUANG Lidong,ZHAO Wei,WANG Jun,et al. Combination of contrast limited adaptive histogram equalisation and discrete wavelet transform for image enhancement[J]. IET Image Processing,2015,9(10):908-915. DOI: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2015.0150
[23] MESSIKOMMER N,FANG C,GEHRIG M,et al. Data-driven feature tracking for event cameras[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Vancouver,2023:5642-5651.
[24] GIOI R G,JAKUBOWICZ J,MOREL J M,et al. LSD:a fast line segment detector with a false detection control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2010,32(4):722-732. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.300
[25] ZHANG Lilian,KOCH R. An efficient and robust line segment matching approach based on LBD descriptor and pairwise geometric consistency[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation,2013,24(7):794-805. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2013.05.006
[26] LIU Zhe,SHI Dianxi,LI Ruihao,et al. PLC-VIO:visual-inertial odometry based on point-line constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering,2022,19(3):1880-1897. DOI: 10.1109/TASE.2021.3077026
[27] TRIGGS B,MCLAUCHLAN P F,HARTLEY R I,et al. Bundle adjustment-a modern synthesis[C]. Vision Algorithms:Theory and Practic,1999. DOI: 10.1007/3-540-44480-7_21.
[28] LI Ang,ZOU Danping,YU Wenxian. Robust initialization of multi-camera slam with limited view overlaps and inaccurate extrinsic calibration[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Pargue,2021:3361-3367.
[29] FURGALE P,REHDER J,SIEGWART R. Unified temporal and spatial calibration for multi-sensor systems[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Tokyo,2013:1280-1286.
[30] MAJEED S H,ISA N A M. Adaptive entropy index histogram equalization for poor contrast images[J]. IEEE Access,2020,9:6402-6437.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 杨艺,杨艳磊,王田,王科平. 基于多重信息自注意力的综采工作面目标行为识别. 煤炭学报. 2025(02): 1425-1442 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 苏晨阳,武文红,牛恒茂,石宝,郝旭,王嘉敏,高勒,汪维泰. 深度学习的工人多种不安全行为识别方法综述. 计算机工程与应用. 2024(05): 30-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 权淑娟. 基于时空关系的井下安全生产AI图像识别系统的应用. 煤矿机电. 2023(02): 17-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)













 下载:
下载: