Research progress on intelligent coal caving theory and technology
-
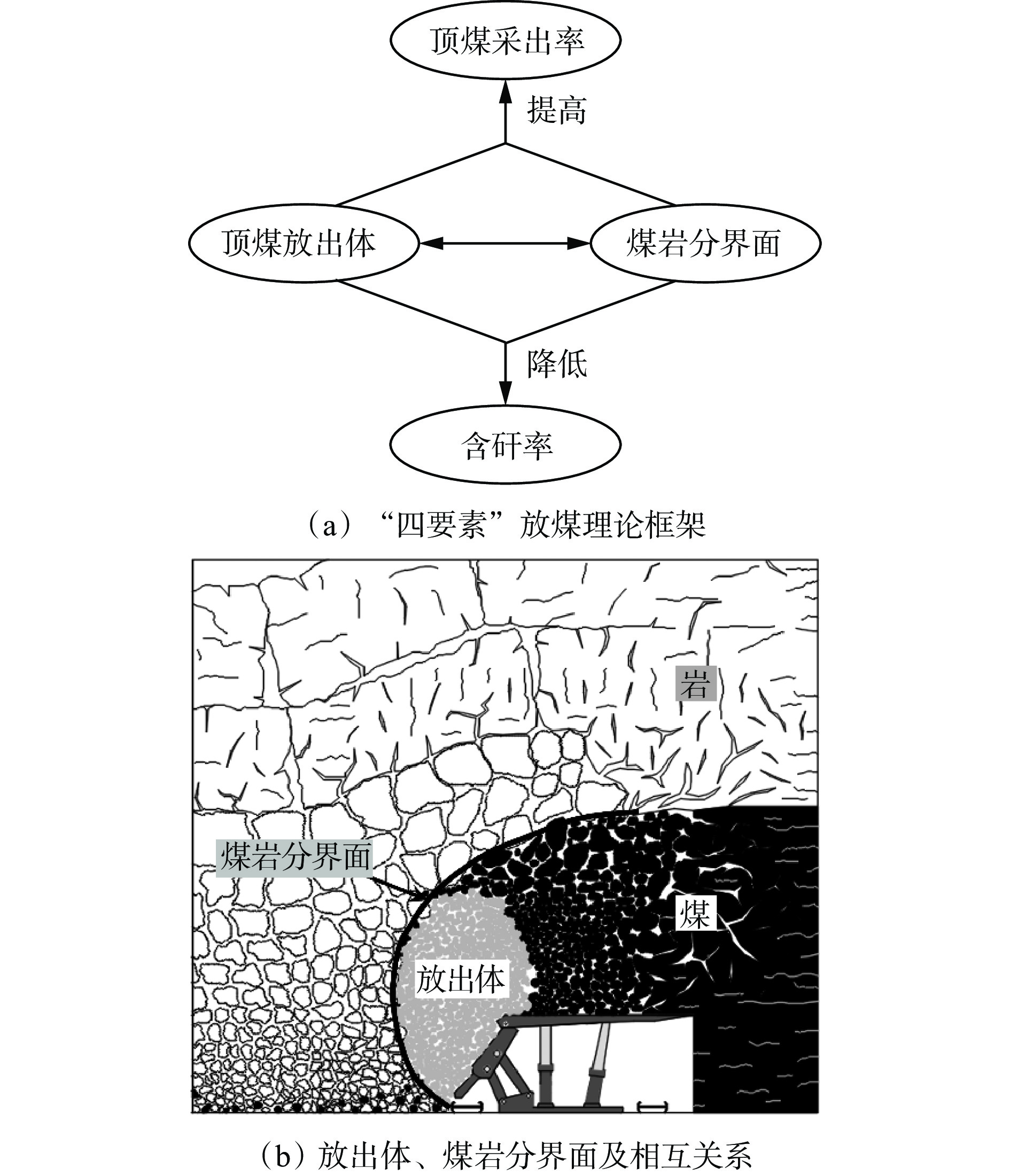
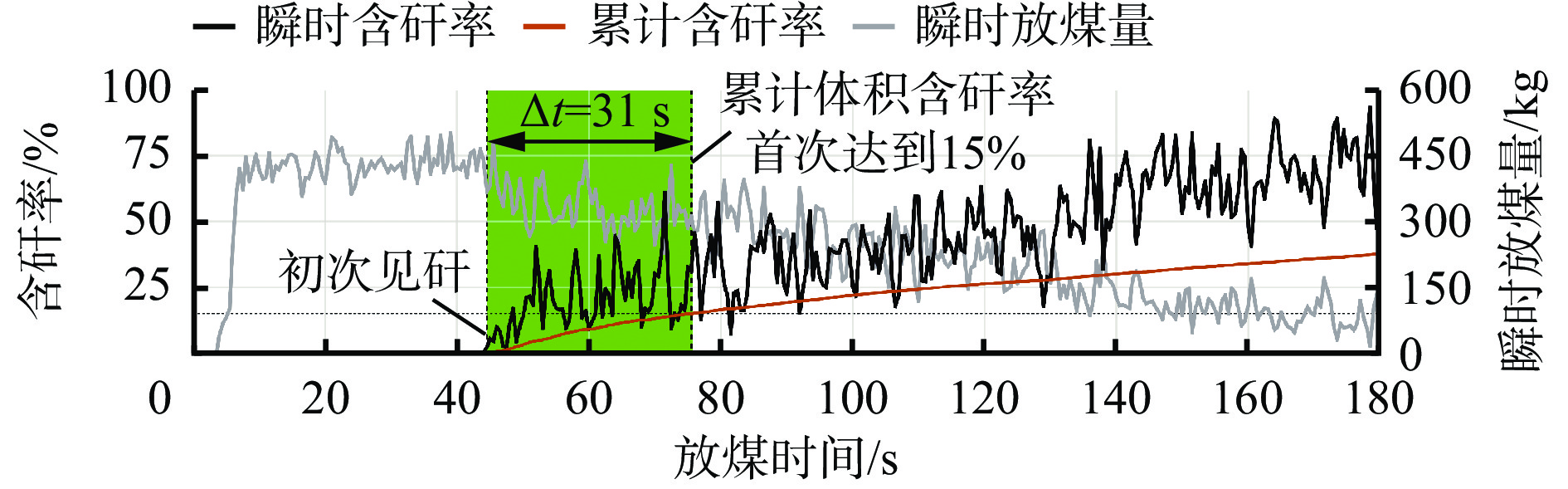
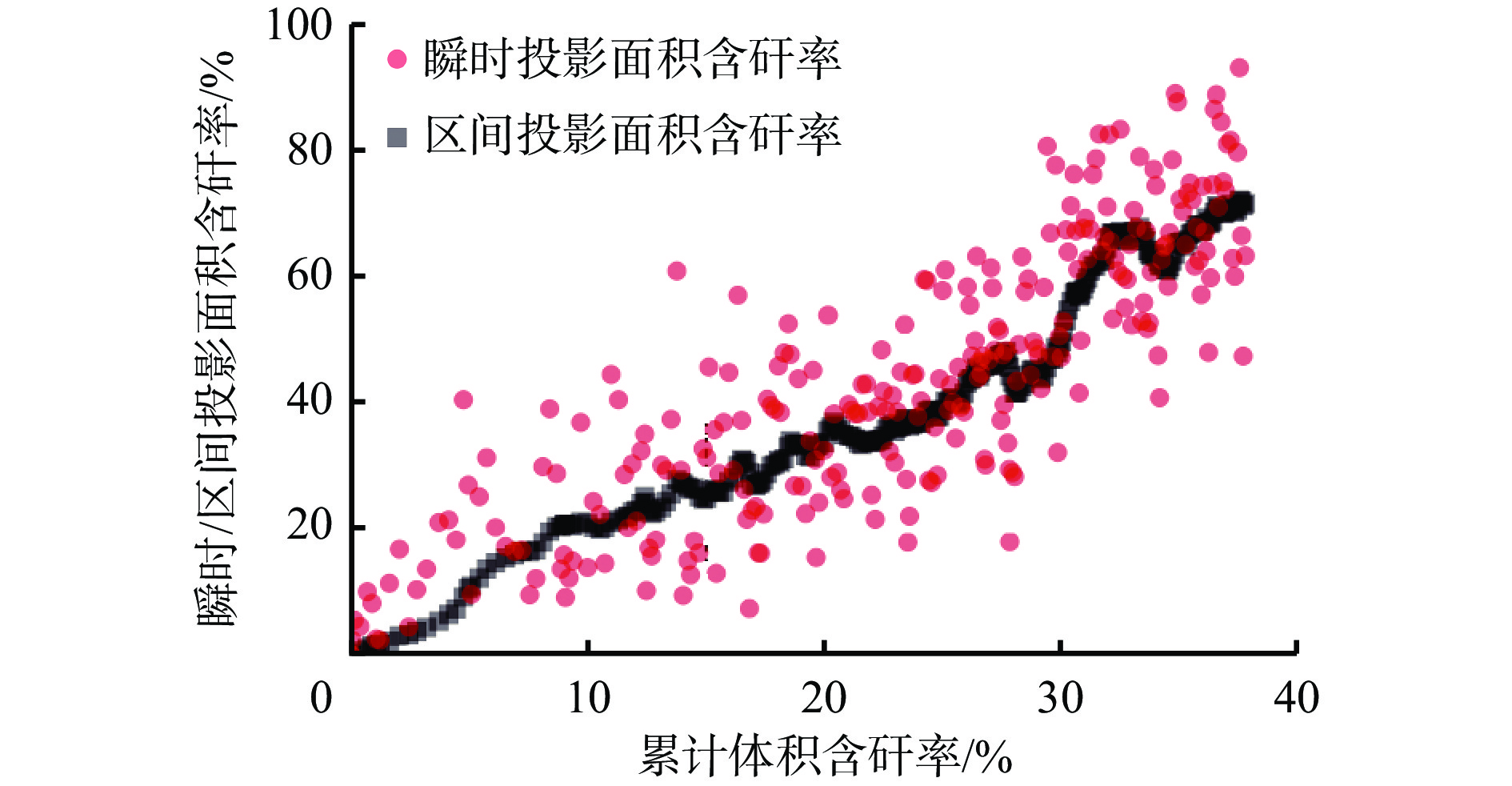
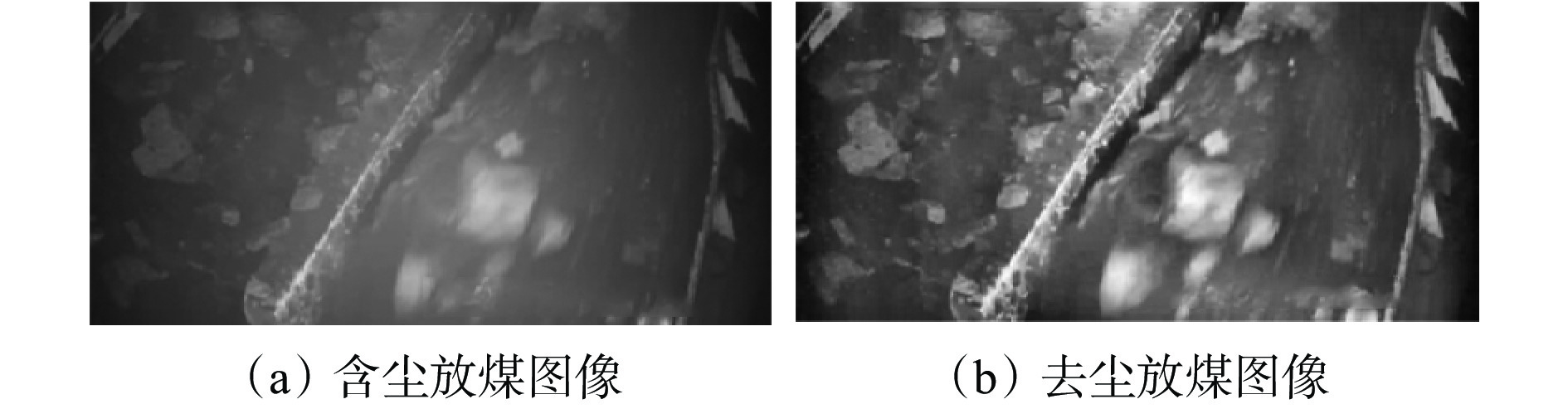
摘要: 综放开采技术是厚及特厚煤层开采的有效方法,已成为我国在世界煤炭开采行业的标志性技术。综述了“四要素”放煤理论、顶煤采出率与含矸率关系、基于块度分布的采出率预测模型、煤流瞬时含矸率−累计含矸率关系等智能放煤理论研究进展。分析了智能放煤技术难点,指出含矸率是影响顶煤采出率和煤质的关键因素,放煤过程中含矸率的快速、准确计算是智能放煤技术突破的重点和关键。将智能放煤技术分为非图像识别智能放煤技术和图像识别智能放煤技术2类,对不同技术的研究进展、优缺点及使用条件进行了详细分析。非图像识别智能放煤技术包括记忆放煤技术、声音振动信号识别技术、γ射线探测技术、探地雷达技术、微波照射+红外探测技术、激光扫描放煤量监测技术等,图像识别智能放煤技术包括井下照度环境精准控制、放煤图像去尘算法、含矸率计算精度保障策略、煤岩红外图像识别等。Abstract: The longwall top-coal caving technology is an effective method for extracting thick and ultra-thick coal seams, and it has become a hallmark technology in China's coal mining industry. This paper reviews the research progress on the "Four elements" coal caving theory, the relationship between the top coal recovery rate and the rock mixed ratio, a recovery rate prediction model based on block distribution, and the relationship between instantaneous rock mixed ratio and cumulative rock mixed ratio. The challenges of intelligent coal caving technology are analyzed, emphasizing that the rock mixed ratio is a key factor affecting the top coal recovery rate and coal quality. Rapid and accurate calculation of the rock mixed ratio during the coal caving process is crucial for breakthroughs in intelligent coal caving technology. This technology is categorized into two types: non-image recognition and image recognition. The research progress, advantages, disadvantages, and usage conditions of different technologies are discussed in detail. Non-image recognition intelligent coal caving technology includes memory coal caving technology, sound and vibration signal detection technology, γ-ray detection technology, ground penetrating radar technology, microwave irradiation combined with infrared detection technology, and laser scanning coal caving monitoring technology. Image-based intelligent coal caving technology encompasses precise control of underground illumination environment, dust removal algorithms for coal caving images, accuracy assurance strategies for rock mixed ratio calculations, and infrared image recognition of coal and rock.
-
0. 引言
我国煤矿智能化开采经历了基于远程可视化的智能化开采1.0阶段,以及基于设备自适应的智能化开采2.0阶段,实现了综采工作面“无人操作、有人巡视”生产方式的应用[1-5]。以国家能源集团神东煤炭集团公司为代表的煤炭企业已经实现了煤矿综采装备从单机控制走向集中控制,并在地质条件较好区域进行了自动化采煤,实现了采煤机记忆截割及远程视频干预控制、液压支架跟机自动化等技术的广泛应用。但是综采工作面自动化开采仍依赖于生产人员在工作面内跟随采煤机作业或在远程集控中心监控设备启停、干预调整[6-7],其原因在于当前自动化开采模式下综采设备与煤层地质条件、地理信息未实现有效关联,设备无法根据煤层赋存变化实现自适应控制。
为解决上述问题,临沂矿业集团有限责任公司、黄陵矿业集团有限责任公司开展了自适应工作面地质条件的智能开采技术研究,并分别在临沂矿业集团菏泽煤电有限公司郭屯煤矿和黄陵矿业集团有限责任公司一号煤矿进行工程实践。郭屯煤矿引入测量机器人系统自动追踪巷道导线点三维大地坐标,实现采煤机等固定或移动标志点大地坐标的动态赋值和修正,达到采煤机与地质模型的自适应耦合,并依托钻探、巷道素描、地层分界测量、三维地震勘探等技术实现基于精确大地坐标的三维地质模型构建与动态修正,自动生成采煤截割线、俯仰采基线,用于指导采煤机自适应割煤[8];但存在工程实践复杂的问题,特别是在复杂地质条件下测量机器人无法自动、精确跟踪采煤机运动,导致综采设备无法获取三维空间位置,影响其与具有大地坐标的三维地质模型的空间位置融合。黄陵一号煤矿利用地质写实、钻孔雷达探测、槽波地震勘探获得的地质数据构建综采工作面静态地质模型,再通过隐式迭代建模、动态更新等大数据技术实现静态地质模型动态更新,达到智能精准开采[9];但在地质模构建过程中,选取相对基准点进行绝对坐标转换将导致各类地质勘探数据误差放大,影响模型实际精度,而且利用数据融合算法实现模型优化需要大量地质数据积累,实际应用存在很大的局限性[10-13]。因此,本文提出了综采工作面透明化开采模式,可根据煤层赋存条件指导采煤机自主割煤,达到综采工作面智能自适应开采目标。
1. 透明化开采模式
综采工作面透明化开采模式以煤层赋存勘探为基础,以工作面三维数字化模型为对象,通过剖切三维数字化模型、提取待开采煤层顶底板轨迹坐标,制定采煤机调高控制策略,最终采煤机依据截割轨迹参数进行调高控制,达到自主割煤目标。
透明化开采模式建立过程分为3个阶段:
(1) 模型构建阶段。通过收集地质勘探资料,获取综采工作面概要地质信息,包括工作面切眼和两巷等揭露的待开采煤层三维坐标信息、工作面煤层等厚线图、矿井钻孔采样图中工作面煤层高度及位置绝对坐标信息等。利用精细化物探技术(如定向钻孔雷达探测、槽波地震勘探等),实现对工作面煤层赋存条件的精细化探测。融合工作面概要地质信息和精细化物探信息,利用GIS(Geographic Information System,地理信息系统)软件建立工作面三维数字化模型,实现对工作面开采条件的预先感知。
(2) 待开采空间定位阶段。利用工作面移动装置搭载三维激光扫描装置、惯性导航装置,实现对综采工作面当前所处空间的三维坐标提取,并将获得的三维坐标导入三维数字化模型中实现模型剖切,从模型剖切面提取工作面当前待割煤循环的煤层顶底板坐标。同时根据工作面液压支架推进步距,可从三维数字化模型中提取后续多个割煤循环的煤层顶底板坐标,为工作面连续割煤控制策略制定提供数据支撑。
(3) 截割控制决策与执行阶段。综合分析待开采煤层顶底板坐标数据,考虑工作面顶底板起伏曲率限定条件、俯仰采阶变过程平滑阶梯多级调整要求等,对未来数个割煤循环采煤机调高控制进行分析、决策,提前制定采煤机截割控制方案并形成采煤机截割高度控制参数集,采煤机开放截割高度控制参数在线编辑功能,依据下发的参数执行自动调高控制。
2. 透明化开采关键技术
2.1 三维数字化模型建立
以矿井地质勘探钻孔和工作面切眼、回撤通道及两巷等实测地质信息为基础,构建工作面初始三维地质模型[14]。为提升模型精度,需要开展定向钻孔施工和地质测绘等精细化物探。沿工作面煤层顶底板分界线实施定向钻孔施工,利用随钻测量仪器获取定向钻孔轨迹,之后经过衍生处理可获得煤层顶底板分界线轨迹,确定分界线的空间位置数据。定时开展地质测绘工作,通过全站仪沿工作面测量已揭露顶底板绝对三维坐标。将通过精细化物探获得的煤层赋存精准数据定期导入初始三维地质模型,实现模型动态优化,从而精准构建三维数字化模型。
2.2 三维激光点云模型建立
依托三维激光扫描技术、惯性导航技术及工作面巡检技术,开展工作面采场空间扫描,构建工作面三维激光点云模型[15-16],从而在三维数字化模型中准确定位当前工作面开采位置目标。
集成三维激光扫描装置、惯性导航装置的工作面巡检机构(图1)以里程编码器数据为基准,每运动一定距离,三维激光扫描装置触发1次环形切片扫描,获得当前一定空间范围内的点云坐标数据。同时惯性导航装置记录该扫描位置的三维激光扫描装置位姿信息,待全工作面扫描结束后,将切片扫描获取的点云坐标数据与位姿信息进行拼接、融合处理,形成工作面三维激光点云模型。工作面三维激光扫描工作原理如图2所示。
三维激光点云模型坐标是相对于三维激光扫描装置位置的相对坐标,需要通过点对点坐标传导方式导入绝对坐标数据来实现坐标转换,原理如图3所示。在工作面与巷道交叉区域布置固定式三维激光扫描装置,巷道内布置3个具有绝对坐标的定位标志球。通过地测方式给予巷道3个定位标志球绝对坐标(x1,y1,z1),(x2,y2,z2),(x3,y3,z3),固定式三维激光扫描装置同时获取巷道定位标志球和工作面定位标志球坐标,通过坐标传导方式获得工作面3个定位标志球绝对坐标(x4,y4,z4),(x5,y5,z5),(x6,y6,z6)。三维激光点云模型中已获取工作面3个定位标志球的相对坐标,将(x4,y4,z4),(x5,y5,z5),(x6,y6,z6)导入三维激光点云模型后,通过坐标传导方式即可将三维激光点云坐标由相对坐标转换为绝对坐标。
2.3 模型剖切与截割规划
由于工作面三维激光点云模型中煤壁与顶板的点云密度存在较明显差异,通过相关算法提取2个平面交接处三维坐标,形成采煤机截割轨迹三维坐标数据集,将提取到的采煤机截割轨迹线三维坐标导入三维数字化模型,即可实现对三维数字化模型的剖切。从模型剖切面数据中提取下一割煤循环煤层顶底板分界线的精准三维坐标数据集,通过分析精准三维坐标集,推算工作面倾向角度变化条件,结合采煤机滚筒高度数学模型,解算出下一割煤循环采煤机前后滚筒对应控制采样点的调整参数,从而有效指导采煤机下一割煤循环滚筒调高控制。
为应对工作面连续推进过程中俯仰采变化需要,在剖切三维数字化模型过程中,应根据工作面液压支架推进步距,同时提取后续若干个割煤循环的煤层顶底板坐标数据集,通过综合分析煤层连续变化趋势,在工作面平直度、当前割顶底板情况、采煤机运行状态等大数据基础上,通过优化算法,制定未来10刀的割煤策略,实现采煤机截割控制提前决策,确保出现俯仰采变化时实现平滑阶梯多级调整。
2.4 采煤机调高控制
采煤机控制系统开放针对截割高度控制数据的第三方可编辑数据接口,以导入调高控制数据。系统根据采煤机调高控制边界条件对导入数据进行校验,对不符合边界条件的参数进行优化,最终形成可执行调控参数。采煤机按照最终调控参数执行自主调高控制。
3. 工程应用
以国家能源集团神东煤炭集团公司榆家梁煤矿43102综采工作面为研究对象,开展了综采工作面透明化开采模式及关键技术应用。
全面收集43102综采工作面相关地质资料,构建初始三维地质模型。在工作面巷道布置ZDY−6000LD型定向钻机实施定向钻孔工程,沿煤层顶底板分界线完成钻孔勘测,实现对工作面赋存情况的精准探测。获取的数据导入初始三维地质模型后,获得精准的工作面三维数字化模型,如图4所示。同时在工作面回采过程中每日安排工作面地质测绘工作,通过测绘数据实现三维数字化模型误差纠偏,进一步提升模型精度,确保工作面前方10 m煤层赋存信息的“精准透明化、动态自优化”。
对于单个割煤循环,构建采场实时三维激光点云模型,如图5所示。
提取三维激光点云模型中煤壁、顶板交接处三维坐标数据集形成剖切线,利用剖切线对三维数字化模型进行剖切,获得下一割煤循环的顶底板轮廓曲线,最终通过截割规划确定下一割煤循环的采煤机截割高度控制参数。为验证三维数字化模型顶底板轮廓曲线的准确度,对下一割煤循环结束后工作面顶底板进行地质测绘,将地质测绘顶底板轮廓曲线与三维数字化模型顶底板轮廓曲线进行对比,如图6所示,结果表明三维数字化模型误差小于±0.2 m。
4. 结论
(1) 融合综采工作面概要地质信息和精细化物探信息,建立综采工作面三维数字化模型;依托三维激光扫描技术、惯性导航技术、工作面巡检技术,构建综采工作面三维激光点云模型,并通过点对点坐标传导方式实现点云坐标由相对坐标转换为绝对坐标。三维数字化模型和三维激光点云模型实现了综采工作面煤层赋存条件和采场空间的数字化,为综采工作面透明化开采提供了重要数据支撑。
(2) 通过提取三维激光点云模型中采煤机截割轨迹三维坐标数据集,实现三维数字化模型剖切,从而获得工作面待开采煤层顶底板坐标数据集,通过综合分析煤层赋存变化情况制定截割规划,指导采煤机后续割煤循环过程中滚筒自主调高控制。
(3) 透明化开采模式及技术在榆家梁煤矿43102综采工作面进行了工程应用,初步实现了采煤机依据工作面煤层赋存条件进行自主割煤。
【编者按】综放开采是我国开采厚煤层的主要方法,智能化综放开采是未来综放开采技术发展的重要方向。近年来我国在智能化综放开采相关技术领域取得了一定成果,但放煤智能化技术仍相对落后,是制约智能化综放开采发展的主要技术瓶颈。为促进智能放煤理论及技术发展、智能放煤装备研发及智能综放工作面建设,提升综放开采智能化水平,推进厚煤层绿色智能开采,《工矿自动化》编辑部特邀中国矿业大学(北京)王家臣教授担任客座主编,山东科技大学张强教授、中煤科工集团庞义辉研究员、中国矿业大学(北京)张锦旺副教授担任客座副主编,于2024年第9期组织出版“放顶煤开采智能化进展”专题。在专题刊出之际,衷心感谢各位专家学者的大力支持! -
表 1 智能放煤方法分类及其研究情况
Table 1 Classification and research status of intelligent coal caving methods
技术
类别技术 主要研究组织(按笔画排序) 非图像
识别
技术记忆放煤技术 大同煤矿集团有限责任公司[17]
山东能源集团有限公司[7]
天地科技股份有限公司[18-19]
中国矿业大学[20]
中国矿业大学(北京)[21]
中矿先进(北京)采矿技术研究院有限公司[21]
中煤华晋集团有限公司[22]
中煤科工开采研究有限公司[19, 23]
北京天地玛珂电液控制系统有限公司[22]
国家能源集团[21]
英国利兹大学[21]
陕西未来能源化工有限公司[23]
煤炭科学研究总院开采研究院[19, 23]声音振动信号识别技术 山东大学[24-26]
山东科技大学[27-30]
山东工商学院[31]
山东交通学院[25-26]
中国矿业大学[10, 32-36]
中国矿业大学(北京)[14]
天地科技股份有限公司[37]
太原理工大学[38]
北京天地玛珂电液控制系统有限公司[39]
北京信息科技大学[40]
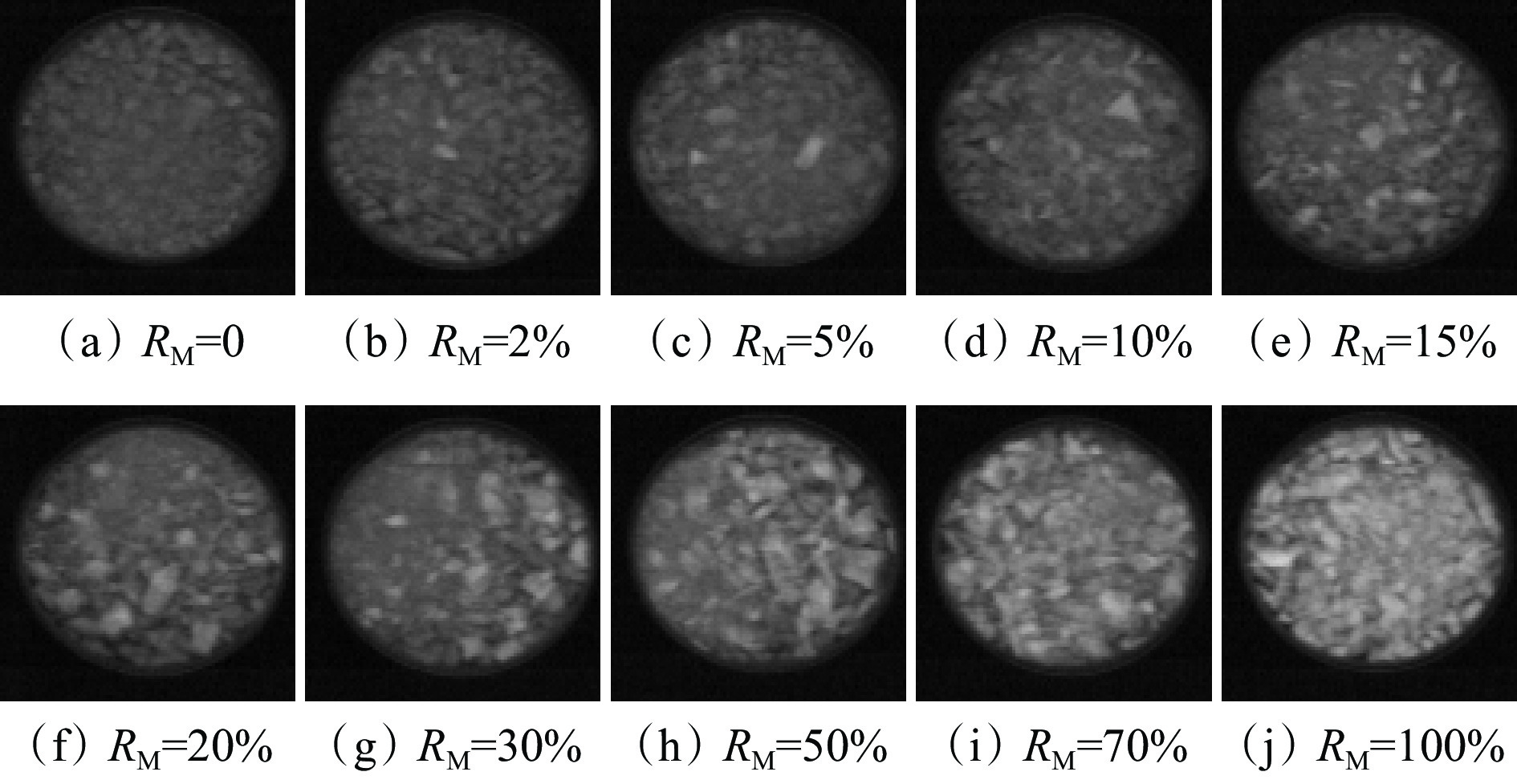
辽宁工程技术大学[41]
潞安矿业(集团)有限责任公司[31]γ射线探测
技术中国矿业大学[13, 35, 42-44]
安徽理工大学[44]探地雷达技术 山东工商学院[45]
太原理工大学[38]
中煤华晋集团有限公司[46]
北京天地玛珂电液控制系统有限公司[45-46]
南阳理工学院[45]微波照射+红外探测技术 河南理工大学[8] 激光扫描放煤量监测技术 中国矿业大学[47-50]
应急管理部信息研究院[47-50]图像
识别
技术可见光图像识别技术 中国矿业大学(北京)[14-15, 21, 51]
中矿先进(北京)采矿技术研究院有限公司[21]
辽宁工程技术大学[41]
西安科技大学[52]
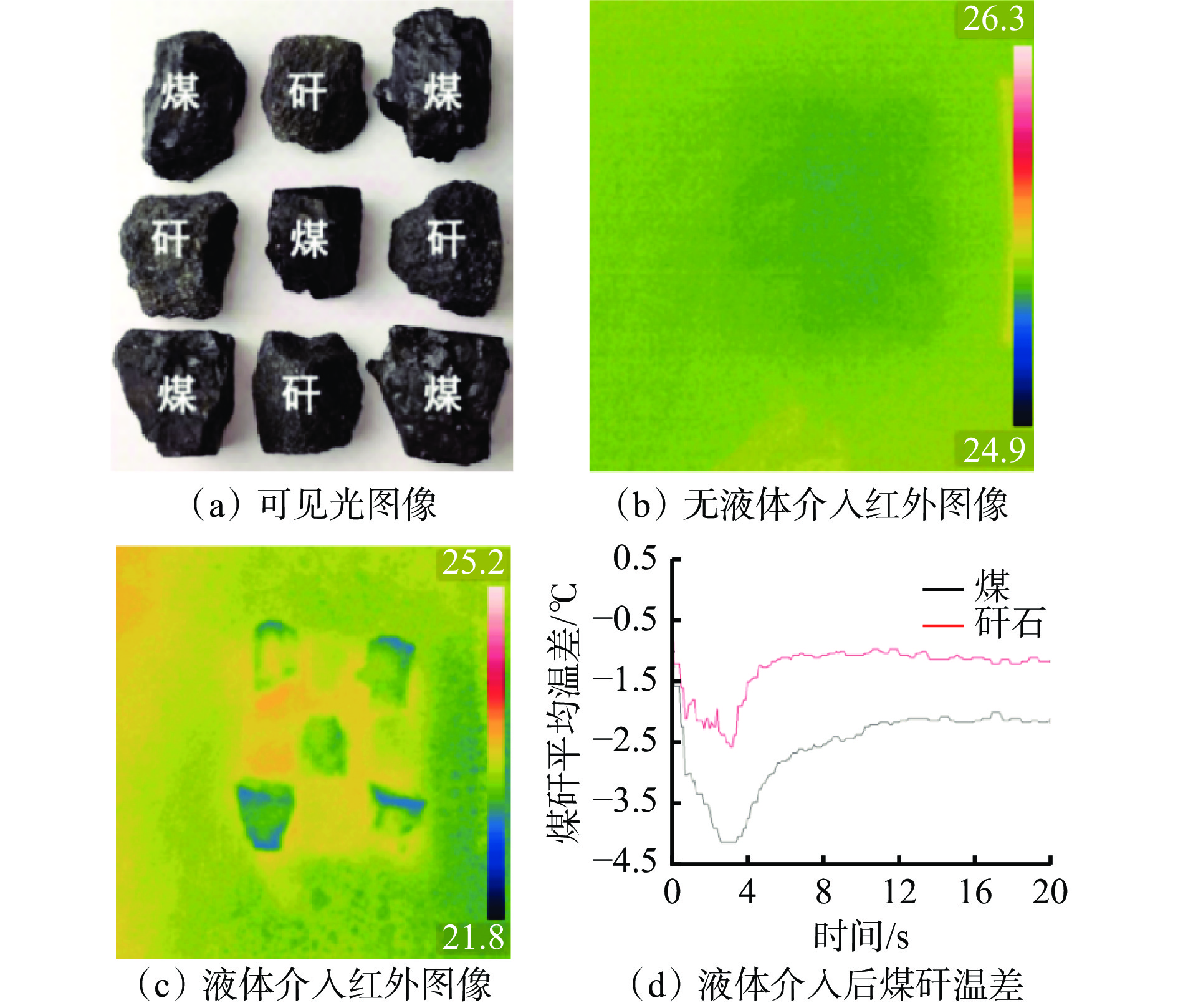
国家能源集团 [21, 53]红外图像识别技术 中国矿业大学[54-55]
中国矿业大学(北京)[56]
辽宁工程技术大学[41]
河南理工大学[8] -
[1] 王家臣,张锦旺,王兆会. 放顶煤开采基础理论与应用[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2018. WANG Jiachen,ZHANG Jinwang,WANG Zhaohui. Basic theories and applications in top-coal caving mining[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2018.
[2] 王家臣. 放煤规律与智能放煤[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2022. WANG Jiachen. Top coal drawing mechanism and intelligent drawing[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2022.
[3] KUMAR R,SINGH A K,MISHRA A K,et al. Underground mining of thick coal seams[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2015,25(6):885-896. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.09.003
[4] ÇELIK A,ÖZÇELIK Y. Investigation of the efficiency of longwall top coal caving method applied by forming a face in horizontal thickness of the seam in steeply inclined thick coal seams by using a physical model[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2021,148. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104917.
[5] KLISHIN V I,KLISHIN S V. Coal extraction from thick flat and steep beds[J]. Journal of Mining Science,2010,46(2):149-159. DOI: 10.1007/s10913-010-0020-y
[6] 王国法,庞义辉,任怀伟. 煤矿智能化开采模式与技术路径[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2020,2(1):5-19. WANG Guofa,PANG Yihui,REN Huaiwei. Intelligent coal mining pattern and technological path[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering,2020,2(1):5-19.
[7] 李伟. 综放开采智能化控制系统研发与应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(10):128-135. LI Wei. Research and application of intelligent control system for full-mechanized caving mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(10):128-135.
[8] 刘闯. 综放工作面多放煤口协同放煤方法及煤岩识别机理研究[D]. 焦作:河南理工大学,2018. LIU Chuang. Study on coal caving method and coal rock identification mechanism of multi-coal caving holes in fully mechanized top-coal caving face[D]. Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University,2018.
[9] 向阳. 近红外光谱煤岩识别环境适应性研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. XIANG Yang. Study on environmental adaptability of coal and rock identification by near infrared spectroscopy[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[10] 宋庆军. 综放工作面放煤自动化技术的研究与应用[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2015. SONG Qingjun. Research and application of coal caving automation technology in fully mechanized top coal caving face[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2015.
[11] 万丽荣,陈博,杨扬,等. 单颗粒煤岩冲击放顶煤液压支架尾梁动态响应分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(9):2905-2913. WAN Lirong,CHEN Bo,YANG Yang,et al. Dynamic response of single coal-rock impacting tail beam of top coal caving hydraulic support[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(9):2905-2913.
[12] 于斌,徐刚,黄志增,等. 特厚煤层智能化综放开采理论与关键技术架构[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):42-53. YU Bin,XU Gang,HUANG Zhizeng,et al. Theory and its key technology framework of intelligentized fully-mechanized caving mining in extremely thick coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):42-53.
[13] ZHANG Ningbo,LIU Changyou. Radiation characteristics of natural gamma-ray from coal and gangue for recognition in top coal caving[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-18625-y.
[14] 王家臣,黄国君,杨胜利,等. 煤矸识别与自动化放煤控制系统:CN200910152006. X[P]. 2009-07-02. WANG Jiachen,HUANG Guojun,YANG Shengli,et al. Coal gangue identification and automated coal caving control system:CN200910152006. X[P]. 2009-07-02.
[15] 王家臣,潘卫东,张国英,等. 图像识别智能放煤技术原理与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):87-101. WANG Jiachen,PAN Weidong,ZHANG Guoying,et al. Principles and applications of image-based recognition of withdrawn coal and intelligent control of draw opening in longwall top coal caving face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):87-101.
[16] WANG Jiachen,WEI Weijie,ZHANG Jinwang,et al. Laboratory and field validation of a LTCC recovery prediction model using relative size of the top coal blocks[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(2):1389-1401. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-020-01970-0
[17] 鲍永生. 特厚煤层综放工作面智能控制关键技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(7):55-61. BAO Yongsheng. Study on key technology of intelligent control in fully-mechanized top coal caving face in extra thick seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(7):55-61.
[18] 马英. 基于记忆放煤时序控制的智能放煤模式研究[J]. 煤矿机电,2015,36(2):1-5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0874.2015.02.001 MA Ying. Research on intelligent coal caving system based on memory coal caving sequential control[J]. Colliery Mechanical & Electrical Technology,2015,36(2):1-5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0874.2015.02.001
[19] 韩会军,王国法,许永祥,等. 6~10 m厚煤层超大采高液压支架及其工作面系统自适应智能耦合控制[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(5):276-288. HAN Huijun,WANG Guofa,XU Yongxiang,et al. Adaptive intelligent coupling control of hydraulic support and working face system for 6-10 m super high mining in thick coal seams[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(5):276-288.
[20] 胡瑞永. 燕子山矿综放工作面煤岩运移规律与智能放煤关键技术研究及应用[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2023. HU Ruiyong. Research and application of coal and rock migration law and key technology of intelligent caving in fully mechanized top-coal caving face of Yanzishan Mine[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2023.
[21] 程伟轩,陈敬川,张立辉,等. 智能放顶煤技术在特厚煤层上覆含水层保护中的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2024,52(增刊1):249-258. CHENG Weixuan,CHEN Jingchuan,ZHANG Lihui,et al. Application of intelligent top coal caving technology in the protection of overlying aquifers on extra thick coal seams[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2024,52(S1):249-258.
[22] 韩秀琪,杨秀宇,孙峰,等. 智能综放工作面自动运行与人工干预分析系统[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(12):31-37. HAN Xiuqi,YANG Xiuyu,SUN Feng,et al. Automatic operation and manual intervention analysis system for intelligent fully mechanized caving face[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(12):31-37.
[23] 许永祥,李申龙,王国法,等. 特厚坚硬煤层超大采高综放首采工作面智能化技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(7):186-194. XU Yongxiang,LI Shenlong,WANG Guofa,et al. Intelligent technology of first-mining face of longwall top-coal caving with super large cutting height in extra-thick and hard coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(7):186-194.
[24] ZHANG Guoxin,WANG Zengcai,ZHAO Lei. Recognition of rock-coal interface in top coal caving through tail beam vibrations by using stacked sparse autoencoders[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering,2016,18(7):4261-4275. DOI: 10.21595/jve.2016.17386
[25] 丛晓妍,王增才,王保平,等. 基于EMD与峭度滤波的煤岩界面识别[J]. 振动.测试与诊断,2015,35(5):950-954. CONG Xiaoyan,WANG Zengcai,WANG Baoping,et al. Application of filtering method based on EMD and kurtosis in coal-rock interface recognition[J]. Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis,2015,35(5):950-954.
[26] 王保平. 放顶煤过程中煤矸界面自动识别研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2012. WANG Baoping. Study on automatic identification of coal gangue interface in top coal caving process[D]. Jinan:Shandong University,2012.
[27] 杨扬. 基于动态冲击滑移接触特性的煤矸识别与试验研究[D]. 青岛:山东科技大学,2020. YANG Yang. Identification and experimental study of coal gangue based on dynamic impact-slip contact characteristics[D]. Qingdao:Shandong University of Science and Technology,2020.
[28] LI He,ZHANG Yao,YANG Yang,et al. Performance analysis of coal gangue recognition based on hierarchical filtering and coupled wrapper feature selection method[J]. IEEE Access,2023,11:85822-85835. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3303394
[29] YANG Yang,ZENG Qingliang. Multipoint acceleration information acquisition of the impact experiments between coal gangue and the metal plate and coal gangue recognition based on SVM and serial splicing data[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2021,46(3):2749-2768. DOI: 10.1007/s13369-020-05227-6
[30] YANG Yang,ZENG Qingliang,YIN Guangjun,et al. Vibration test of single coal gangue particle directly impacting the metal plate and the study of coal gangue recognition based on vibration signal and stacking integration[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:106784-106805. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932118
[31] 张艳丽,张守祥,矫林岳,等. 独立分量分析法在综采煤岩界面识别中的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2007,35(8):22-24,28. ZHANG Yanli,ZHANG Shouxiang,JIAO Linyue,et al. Application on ICA in coal and rock interface identification of the fully mechanized mining[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2007,35(8):22-24,28.
[32] 陈钱有. 综放工作面煤矸冲击特性与识别方法研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. CHEN Qianyou. Study on impact characteristics and identification method of coal gangue in fully mechanized top-coal caving face[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022.
[33] 陈旭. 基于听觉感知原理的综放工作面垮落煤矸识别方法研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. CHEN Xu. Research on recognition method of caving coal gangue in fully mechanized caving face based on the principle of auditory perception[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022.
[34] 孟林. 基于振动谱图像的放顶煤工作面煤矸识别方法研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2023. MENG Lin. Study on identification method of coal gangue in top-coal caving face based on vibration spectrum image[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2023.
[35] 赵明鑫. 综放煤矸放落的环境特征及自动识别的影响因素研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. ZHAO Mingxin. Research on environmental characteristics and influencing factors of automatic identification of coal gangue unloading in comprehensive coal mining[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[36] CHEN Xu,WANG Shibo,LIU Houguang,et al. Coal gangue recognition using multichannel auditory spectrogram of hydraulic support sound in convolutional neural network[J]. Measurement Science and Technology,2022,33(1). DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac3709.
[37] 马英. 基于尾梁振动信号采集的煤矸识别智能放煤方法研究[J]. 煤矿开采,2016,21(4):40-42,25. MA Ying. Intelligent coal caving with gangue identification based on tail beam vibration signal collection[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2016,21(4):40-42,25.
[38] HUO Yuming,ZHAO Dangwei,ZHU Defu,et al. Application of an automated top coal caving control system:the case of Wangjialing Coal Mine[J]. Sustainability,2024,16(10). DOI: 10.3390/su16104261.
[39] 魏冠伟,魏效征. 放顶煤液压支架振动数据采集装置设计[C]. 第23届全国煤矿自动化与信息化学术会议暨第5届中国煤矿信息化与自动化高层论坛,北京,2013:219-225. WEI Guanwei,WEI Xiaozheng. Design of vibration data acquisition device for hydraulic support of top coal caving[C]. The 23rd National Conference on Coal Mine Automation and Informatization and the 5th China Coal Mine Informatization and Automation High Level Forum,Beijing,2013:219-225.
[40] 李一鸣. 基于小波包多尺度模糊熵和加权KL散度的煤岩智能识别[J]. 工矿自动化,2023,49(4):92-98. LI Yiming. Intelligent recognition of coal and rock based on wavelet packet multi-scale fuzzy entropy and weighted KL divergence[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2023,49(4):92-98.
[41] 韩立国. 综合放顶煤开采煤矸识别关键技术研究[D]. 阜新:辽宁工程技术大学,2023. HAN Liguo. Study on key technology of gangue identification in fully mechanized top-coal caving mining[D]. Fuxin:Liaoning Technical University,2023.
[42] 郭凤岐. 复杂结构特厚煤层综放煤−矸−岩放落流动时序规律及识别研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021. GUO Fengqi. Research on the time sequence and identification of coal-gangue-rock caving flow in complex structure thick coal seam fully mechanized mining[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2021.
[43] 张宁波. 综放开采煤矸自然射线辐射规律及识别研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2015. ZHANG Ningbo. Study on natural ray radiation law and identification of fully mechanized top-coal caving mining gangue[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2015.
[44] 刘长友,张宁波,郭凤岐,等. 特厚煤层综放煤−矸−岩放落流动的时序规律及识别方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):137-151. LIU Changyou,ZHANG Ningbo,GUO Fengqi,et al. Sequential rules and identification method of coal-gangue-rock caving flow in fully mechanized top-coal-caving workface of extra thick coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(1):137-151.
[45] 张守祥,张学亮,刘帅,等. 智能化放顶煤开采的精确放煤控制技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(6):2008-2020. ZHANG Shouxiang,ZHANG Xueliang,LIU Shuai,et al. Intelligent precise control technology of fully mechanized top coal caving face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(6):2008-2020.
[46] 张学亮,刘清,郎瑞峰,等. 厚煤层智能放煤工艺及精准控制关键技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2020,52(9):1-6. ZHANG Xueliang,LIU Qing,LANG Ruifeng,et al. Intelligent coal drawing process and the key technologies of precise control for thick coal seam top-coal caving[J]. Coal Engineering,2020,52(9):1-6.
[47] 胡而已. 基于激光扫描的综放工作面放煤量智能监测技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(2):244-251. HU Eryi. Intelligent monitoring technology of coal caving in fully-mechanized caving face based on laser scanning[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(2):244-251.
[48] 胡而已,叶兰,孙益壮,等. 综放工作面放煤量激光扫描自适应监测技术研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2022,48(11):57-66. HU Eryi,YE Lan,SUN Yizhuang,et al. Study on laser scanning adaptive monitoring technology for coal caving volume in fully mechanized top-coal caving face[J]. China Coal,2022,48(11):57-66.
[49] 吕东翰. 综放工作面放煤量激光扫描在线智能监测技术研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021. LYU Donghan. Research on laser scanning online intelligent monitoring technology for coal caving quantity in fully mechanized mining face[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2021.
[50] 孙益壮. 基于激光扫描的综放工作面放煤量自适应监测技术[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. SUN Yizhuang. Adaptive monitoring technology for coal caving volume in fully mechanized top coal caving face based on laser scanning[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022.
[51] 李良晖. 图像识别智能放煤基础研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2023. LI Lianghui. Research on intelligent coal caving fundamentals based on image recognition[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing,2023.
[52] 单鹏飞,孙浩强,来兴平,等. 基于改进Faster R−CNN的综放煤矸混合放出状态识别方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(3):1382-1394. SHAN Pengfei,SUN Haoqiang,LAI Xingping,et al. Identification method on mixed and release state of coal-gangue masses of fully mechanized caving based on improved Faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(3):1382-1394.
[53] 贺海涛,王佳豪,张海峰,等. 基于U−Net的放煤状态控制关键技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(增刊2):237-243. HE Haitao,WANG Jiahao,ZHANG Haifeng,et al. Research on key technologies of coal discharge state control based on U-Net[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(S2):237-243.
[54] 卢召栋. 近红外光谱煤岩识别算法及风速影响研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. LU Zhaodong. Research on near infrared spectroscopy coal rock recognition algorithm and wind speed influence[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022.
[55] ESHAQ R M A,HU Eryi,LI Menggang,et al. Separation between coal and gangue based on infrared radiation and visual extraction of the YCbCr color space[J]. IEEE Access,2020,8:55204-55220. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981534
[56] 张锦旺,王家臣,何庚. 煤矸红外图像识别基础研究[M]. 北京:应急管理出版社,2024. ZHANG Jinwang,WANG Jiachen,HE Geng. Basic research on infrared image recognition of coal gangue[M]. Beijing:Emergency Management Press,2024.
[57] 王增才. 综采放顶煤开采过程煤矸识别研究[J]. 煤矿机械,2002,23(8):13-14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0794.2002.08.007 WANG Zengcai. Study on distributing coal and rock in the process of fully-mechanized coal winning sublevel caving coal technology[J]. Coal Mine Machinery,2002,23(8):13-14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0794.2002.08.007
[58] 许献磊,彭苏萍,马正,等. 基于空气耦合雷达的矿井煤岩界面随采动态探测原理及关键技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(8):2961-2977. XU Xianlei,PENG Suping,MA Zheng,et al. Principle and key technology of dynamic detection of coal-rock interface in coal mine based on air-coupled radar[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(8):2961-2977.
[59] 李术才,刘斌,孙怀凤,等. 隧道施工超前地质预报研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(6):1090-1113. LI Shucai,LIU Bin,SUN Huaifeng,et al. State of art and trends of advanced geological prediction in tunnel construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(6):1090-1113.
[60] 苗曙光. 基于GPR与ESR的煤岩性状识别方法研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2019. MIAO Shuguang. Research on coal rock character recognition method based on GPR and ESR[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2019.
[61] 许献磊,王一丹,朱鹏桥,等. 基于高频雷达波的煤岩层位识别与追踪方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):50-58. XU Xianlei,WANG Yidan,ZHU Pengqiao,et al. Research on coal and rock horizon identification and tracking method based on high frequency radar waves[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2022,50(7):50-58.
[62] 李良晖. 基于差异照度图像的综放开采煤矸混合度识别研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2019. LI Lianghui. Research on the identification of coal gangue mixture in fully mechanized top coal mining based on differential illumination images[D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing,2023.
[63] 潘卫东,李新源,员明涛,等. 基于顶煤运移跟踪仪的自动化放煤技术原理及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(增刊1):23-30. PAN Weidong,LI Xinyuan,YUN Mingtao,et al. Principle and application of automated coal caving technology based on top coal transport tracker[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(S1):23-30.
[64] 米彦军,潘卫东,杨克虎,等. 黄玉川煤矿无人干预自动化放煤研究[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(增刊2):29-31,42. MI Yanjun,PAN Weidong,YANG Kehu,et al. Research of automatic top-coal caving without human intervention in Huangyuchuan Coal Mine[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2021,47(S2):29-31.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王剑,张善兵,樊君. 基于地质保障+5G的智能透明开采技术研究. 能源科技. 2025(01): 10-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 问永忠. 综放工作面基于透明地质的智能协同开采技术. 陕西煤炭. 2024(05): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李重重,姚钰鹏. 基于工况触发的采煤机滚筒截割高度模板生成方法. 工矿自动化. 2024(04): 144-152 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 于建军,王建成,刘百祥. 基于地质物探数据的工作面透明地质模型构建研究与应用. 山东煤炭科技. 2024(04): 157-161+167+173 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王海军,郑三龙,王相业,董敏涛,吴艳,马良,杨伟,朱玉英. 地质构造隐蔽致灾因素透明化勘查技术——以新疆屯宝煤矿为例. 煤炭科学技术. 2024(09): 173-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 牛冠宇,王艳龙,陈明刚. 三维地质模型在智能回采中的应用. 黑龙江科学. 2023(06): 124-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李森,李重重,刘清. 基于透明地质的综采工作面规划截割协同控制系统. 煤炭科学技术. 2023(04): 175-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 梁耍,王世博,葛世荣,柏永泰,谢洋. 综采工作面煤层三维模型动态修正方法研究. 工矿自动化. 2022(07): 58-65+72 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 荣耀,曹琼,安晓宇,温亮,赵云飞. 综采工作面三维激光扫描建模关键技术研究. 工矿自动化. 2022(10): 82-87 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 刘伟. 数字化矿山系统及智能化在矿井中的应用. 产业创新研究. 2022(20): 88-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: