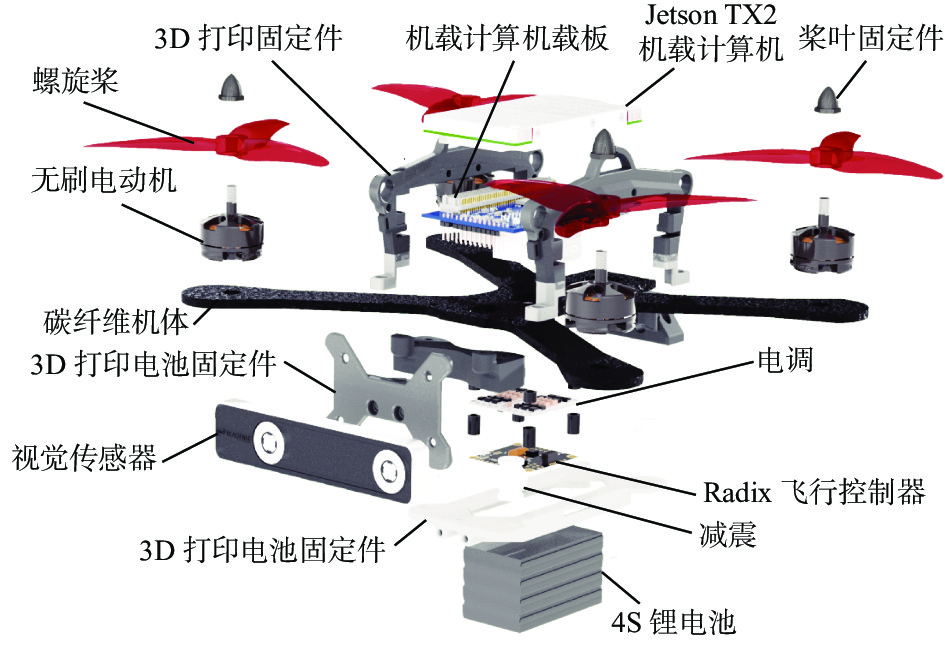
Research progress and challenges faced by unmanned aerial vehicles in complex underground spaces
-
摘要: 分析了地下复杂空间无人机的技术发展与应用现状,指出地下复杂空间无人机面临单体性能不足、环境态势感知与自主导航能力有限、编队协同能力有限等问题,针对上述问题,展望了地下无人机关键技术发展趋势:① 小型化轻量化一体化无人机设计技术。通过改进无人机的机械结构,提高激光雷达、深度相机等信息感知传感器与控制系统的集成度,优化电源管理系统等,最终实现单体无人机巡航速度、续航时间等性能的提升;② GPS拒止环境下态势感知与自主导航技术。攻克即时定位与地图构建(SLAM)导航与实时路径规划等关键技术难题,围绕特定场景逐步突破算法的局限性,提升无人系统的感知能力、环境适应性和鲁棒性;③ 有限信息下编队协同控制技术。攻克异构/同构无人机集群协同、复杂信道环境下的无线通信等技术难题,通过优化无人机群体智能控制策略、信息交互机制及任务决策协同机制等,增强集群无人系统的鲁棒性,提高无人系统在地下复杂环境中的自适应能力,进而提升无人系统的任务执行效率与成功率。Abstract: The technological development and application status of underground complex space UAVs are analyzed. It is pointed out that underground complex space UAVs face problems such as insufficient individual performance, limited environmental situational awareness and autonomous navigation capabilities, and limited formation collaboration capabilities. In order to solve the above problems, the development trends of key technologies for underground UAVs are prospected. ① Small and lightweight integrated UAV design technology is proposed. By improving the mechanical structure of the UAV, improving the integration of information perception sensors such as LiDAR and depth camera with control systems, and optimizing power management systems, the ultimate goal is to improve the cruise speed, endurance time, and other performance of individual UAV. ② Situation awareness and autonomous navigation technology in GPS rejection environment is proposed. The key technical challenges such as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) navigation and real-time path planning should be overcome. The limitations of algorithms around specific scenarios should be gradually broken through. The perception capability, environmental adaptability, and robustness of unmanned systems should be improved. ③ Formation collaboration control technology under limited information is proposed. The technical problems such as heterogeneous/isomorphic UAV cluster collaboration, and wireless communication in complex channel environments should be overcome. By optimizing UAV swarm intelligence control strategies, information interaction mechanisms, and task decision-making collaboration mechanisms, the robustness of clustered unmanned systems should be enhanced. The adaptability of unmanned systems in complex underground environments should be improved. Furthermore, the task execution efficiency and success rate of unmanned systems should be improved.
-
-
表 1 国内外关键技术研究现状总结
Table 1 Summary of the research status of key technologies at home and abroad
研究团队/机构 研究方向及代表算法 存在的问题 浙江大学FAST实验室 研究方向主要集中在无人机运动规划。
针对微小型无人机,提出了一种无需距离场的基于梯度的轨迹规划算法,EGO−Planner偏向理论研究,示范与应用验证较少,算法工程适用性仍需验证 天津大学无人系统自主导航与控制实验室 研究方向主要集中在多无人机集群控制与路径规划。针对多无人机协同系统,提出了基于地图匹配及全局路图的多无人机协同定位及协同调度算法 实际应用场景仅限于无GPS森林、无矿洞和隧道的示范与应用,算法工程适用性仍需验证 香港科技大学空中
机器人研究组研究组与大疆创新科技有限公司建立联合实验室,倾向于使用优化的思路去解决无人机自主飞行中的工程问题,研究方向主要集中在无人机状态估计、建图、运动规划等。
针对深度视觉定位无人机,提出了一种鲁棒且通用的单目视觉惯性状态估计器,VINS Mono无人机控制算法相关的研究较少,示范与应用验证较少 香港大学MaRS实验室 研究方向主要是空中机器人设计、规划和控制,以及基于激光雷达的SLAM。
针对激光雷达定位无人机,提出了一种计算高效且鲁棒的LiDAR惯性里程计框架,FAST−LIO算法路径规划与控制算法相关的研究较少,示范与应用验证较少 卡内基梅隆大学
机器人研究所主要研究方向为导航拒止环境下自主导航和路径规划算法,提出了多种路径规划算法,如Falco、自主探索的方法、TARE、FAR Planner 等 感知定位和鲁棒控制算法相关的研究较少,示范与应用验证较少,算法工程适用性仍需验证 表 2 仿真环境
Table 2 Simulation environment
序号 环境 特征 1 校园环境
(340 m×340 m)包含一些上下坡及盘绕的地形 2 室内环境
(130 m×100 m)包含长且窄的走廊及许多桌子/椅子等障碍物,其中还有一个护栏,由于其中间可以穿透的特性,会对机器人的感知(perception)模块增加挑战性 3 停车场
(140 m×130 m,5层)包含多层楼且有上下坡,会给机器人3D导航任务增加难度 4 隧道(330 m×250 m) 由错综复杂的隧道构成的一个庞大的网格结构 5 森林(150 m×150 m) 包含无规律分布的树木及几栋房子 -
[1] 郑学召,童鑫,张铎,等. 矿井危险区域多旋翼侦测无人机关键技术探讨[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(12):48-56. ZHENG Xuezhao,TONG Xin,ZHANG Duo,et al. Discussion on key technologies of multi-rotor detection UAVs in mine dangerous area[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(12):48-56.
[2] 张铎,吴佩利,郑学召,等. 矿井侦测无人机研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 工矿自动化,2020,46(7):76-81. ZHANG Duo,WU Peili,ZHENG Xuezhao,et al. Research status and development trend of mine detection unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2020,46(7):76-81.
[3] XU Wei,ZHANG Fu. Fast-lio:a fast,robust LiDAR-inertial odometry package by tightly-coupled iterated Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2021,6(2):3317-3324. DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3064227
[4] ZHANG Kunyi,JIANG Chenxing,LI Jinghang,et al. DIDO:deep inertial quadrotor dynamical odometry[J]. arXiv e-prints,2022,7(4):9083-9090.
[5] SHEN Hongming,ZONG Qun,TIAN Bailing,et al. Voxel-based localization and mapping for multi-robot system in GPS-denied environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2022,69(10):10333-10342. DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3153822
[6] ZHANG Ji,HU Chen,CHADHA R G,et al. Falco:fast likelihood-based collision avoidance with extension to human-guided navigation[J]. Journal of Field Robotics,2020,37:1300-1313. DOI: 10.1002/rob.21952.
[7] ZHU Hongbiao, CAO Chao, XIA Yukun, et al. DSVP: dual-stage viewpoint planner for rapid exploration by dynamic expansion[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, 2021: 7623-7630.
[8] CAO Chao, ZHU Hongbiao, CHOSET H, et al. Tare: a hierarchical framework for efficiently exploring complex 3D environments[C]. Robotics: Science and System (RSS), 2021. DOI: 10.15607/RSS.2021.XVII.018.
[9] YANG Fan, CAO Chao, ZHU Hongbiao, et al. Far planner: fast, attemptable route planner using dynamic visibility update[J]. Computer Science ArXiv, 2021. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2110.09460
[10] ZHOU Boyu,ZHANG Yichen,CHEN Xinyi,et al. Fuel:fast UAV exploration using incremental frontier structure and hierarchical planning[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2021,6(2):779-786. DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3051563
[11] ZHOU Xin,WANG Zhepei,YE Hongkai,et al. EGO-planner:an ESDF-free gradient-based local planner for quadrotors[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2021,6(2):478-485. DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3047728
[12] ZHOU Boyu, GAO Fei, PAN Jie, et al. Robust real-time UAV replanning using guided gradient-based optimization and topological paths[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, 2020: 208-1214.
[13] 张学伟,田栢苓,鲁瀚辰,等. 面向复杂未知多障碍环境的多无人机分布式在线轨迹规划[J]. 中国科学:信息科学,2022,52(9):1627-1641. ZHANG Xuewei,TIAN Bailing,LU Hanchen,et al. Multi-UAV decentralized online trajectory planning in complex unknown obstacle-rich environments[J]. Scientia Sinica(Informationis),2022,52(9):1627-1641.
[14] HOU Jialiang,ZHOU Xin,GAN Zhongxue,et al. Enhanced decentralized autonomous aerial robot teams with group planning[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2022,7(4):9240-9247. DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3191037
[15] 刘栋. 矿井无人机飞行轨迹定位及多机协同搜索方法的研究 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. LIU Dong. Research on UAV flight trajectory localization and multi-UAV collaborative search method for coal mine environment[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018.
[16] TIAN Bailing, LIU Lihong, LU Hanchen, et al. Multivariable finite time attitude control for quadrotor UAV: theory and experimentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018(3). DOI: 10.1109/tie.2017.2739700.
[17] JI Jialin, ZHOU Xin, XU Chao, et al. CMPCC: corridor-based model predictive contouring control for aggressive drone flight[J]. arXiv, 2020. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2007.03271.
[18] DING Ziming, YANG Tiankai, ZHANG Kunyi, et al. VID-fusion: robust visual-inertial-dynamics odometry for accurate externa VID-fusion l force estimation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi'an, 2021: 14469-14475.
[19] SEO H, LEE D, SON C, et al. Robust trajectory planning for a multirotor against disturbance based on Hamilton-Jacobi reachability analysis[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS), Macau, 2019: 3150-3157.
[20] PHILIPP F, KAUFMANN E, ROMERO A, et al. Agilicious: open-source and open-hardware agile quadrotor for vision-based flight[J]. Research Article: Science Robotics, 2022, 7(67). DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.abl6259.
[21] CAO Chao, ZHU Hongbiao, YANG Fan, et al. Autonomous exploration development environment and the planning algorithms[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, 2022: 8921-8928.
[22] Tactical Technology Office (TTO) . DARPA subterranean (SubT) challenge[R]. Arlington: Tactical Technology Office (TTO), 2018.
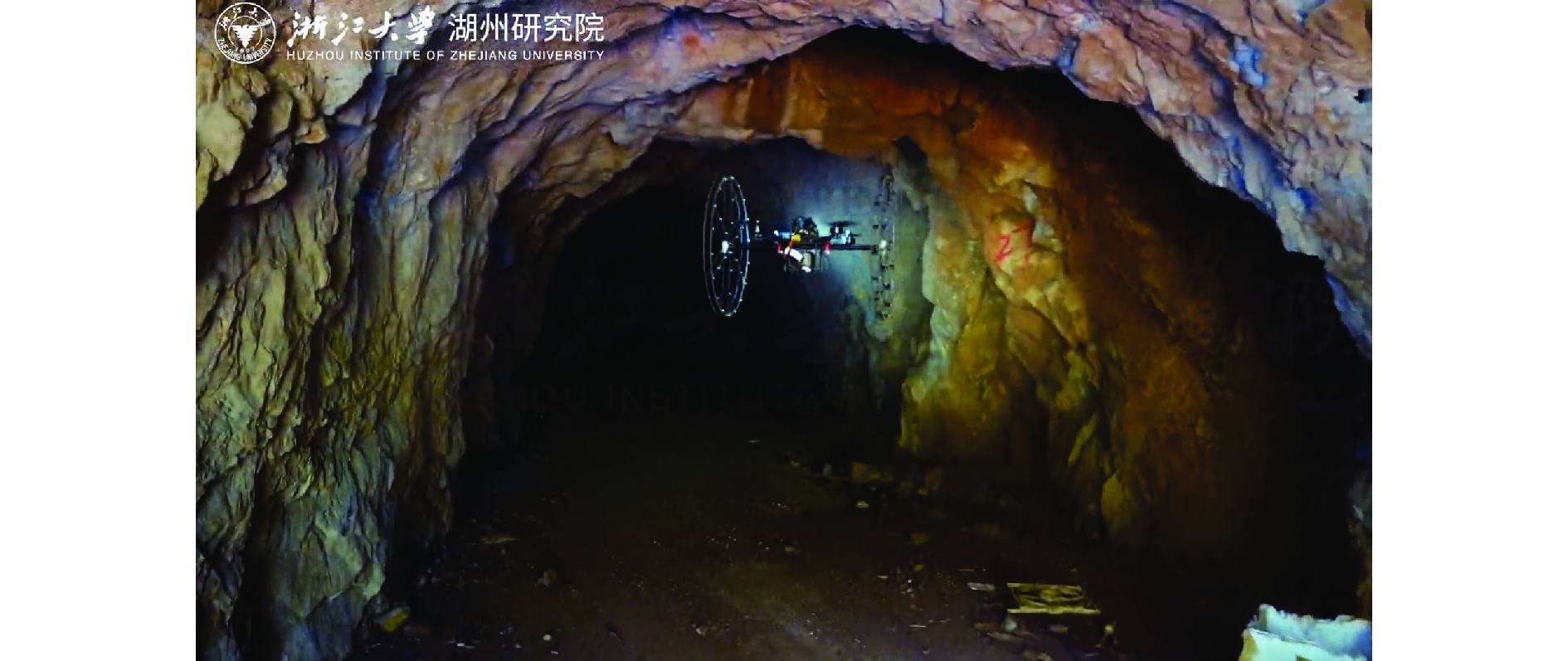
[23] 浙江在线. “机器探长”集结 智探湖州黄龙洞[EB/OL]. (2022-08-15)[2022-10-27]. https://huzhou.zjol.com.cn/yw18229/202208/t20220815_24660994.shtml. Zhejiang online. "Machine inspector" gathered wisdom to explore the Huanglong Cave of Huzhou[EB/OL]. (2022-08-15)[2022-10-27]. https://huzhou.zjol.com.cn/yw18229/202208/t20220815_24660994.shtml.
[24] 王彤,李磊,蒋琪. 美国“快速轻量自主”项目推进无人系统自主能力发展[J]. 无人系统技术,2019,2(1):58-64. WANG Tong,LI Lei,JIANG Qi. DARPA fast lightweight autonomy program promotes unmanned system autonomy development[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology,2019,2(1):58-64.
[25] PASCHALL S, ROSE J. Fast, lightweight autonomy through an unknown cluttered environment: Distribution statement: A—approved for public release;distribution unlimited[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, 2017: 1-8.
[26] GOHL P, BURRI M, OMARI S, et al. Towards autonomous mine inspection[C]. The 2014 3rd International Conference on Applied Robotics for the Power Industry, Foz do Iguacu, 2014. DOI: 10.1109/CARPI.2014.7030057.
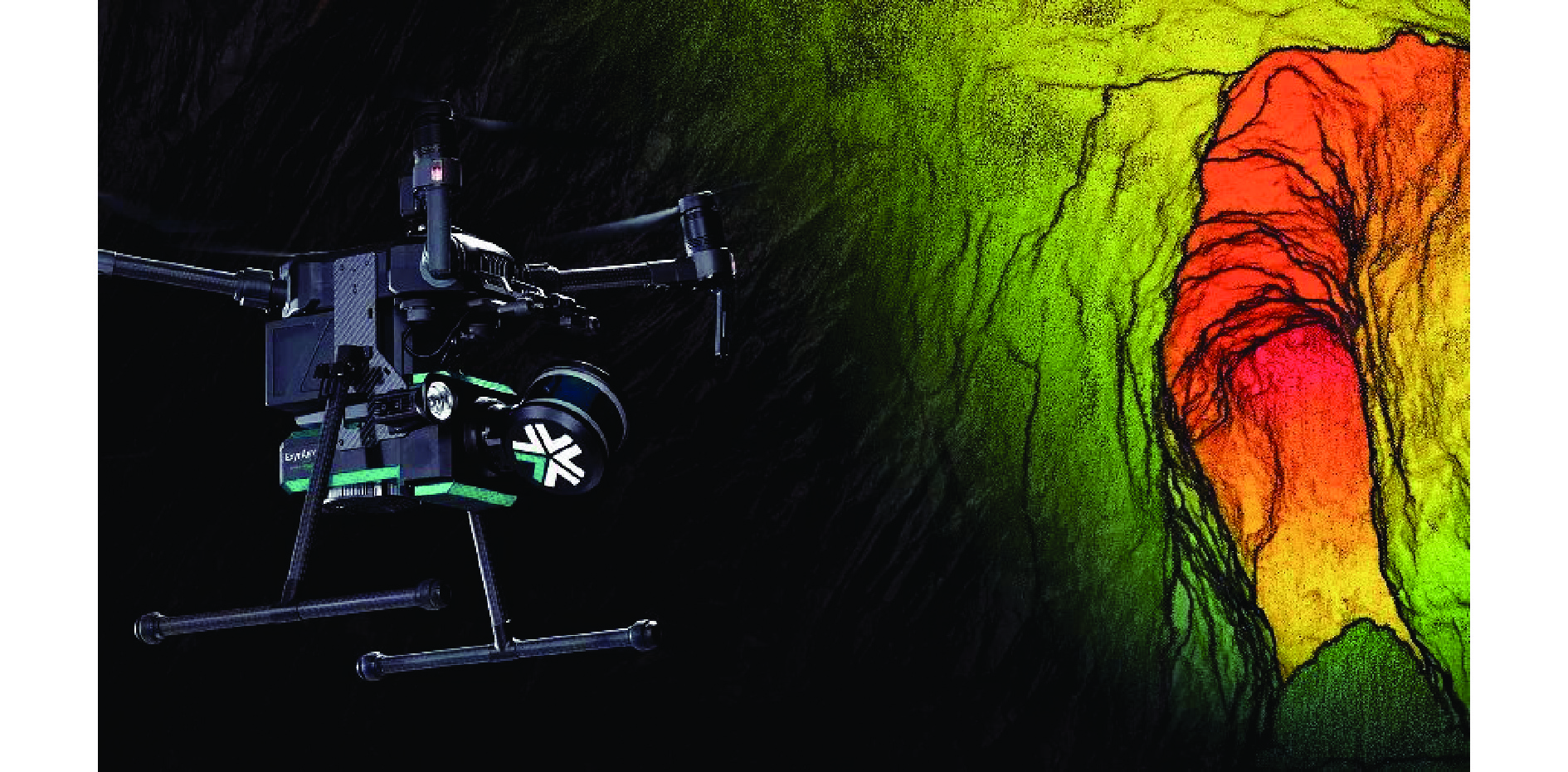
[27] Exyn Technologies. Exyn aero aerial mapping drone [EB/OL].[2022-07-27]. https://www.exyn.com/products/exyn-aero-aerial-mapping-drone.
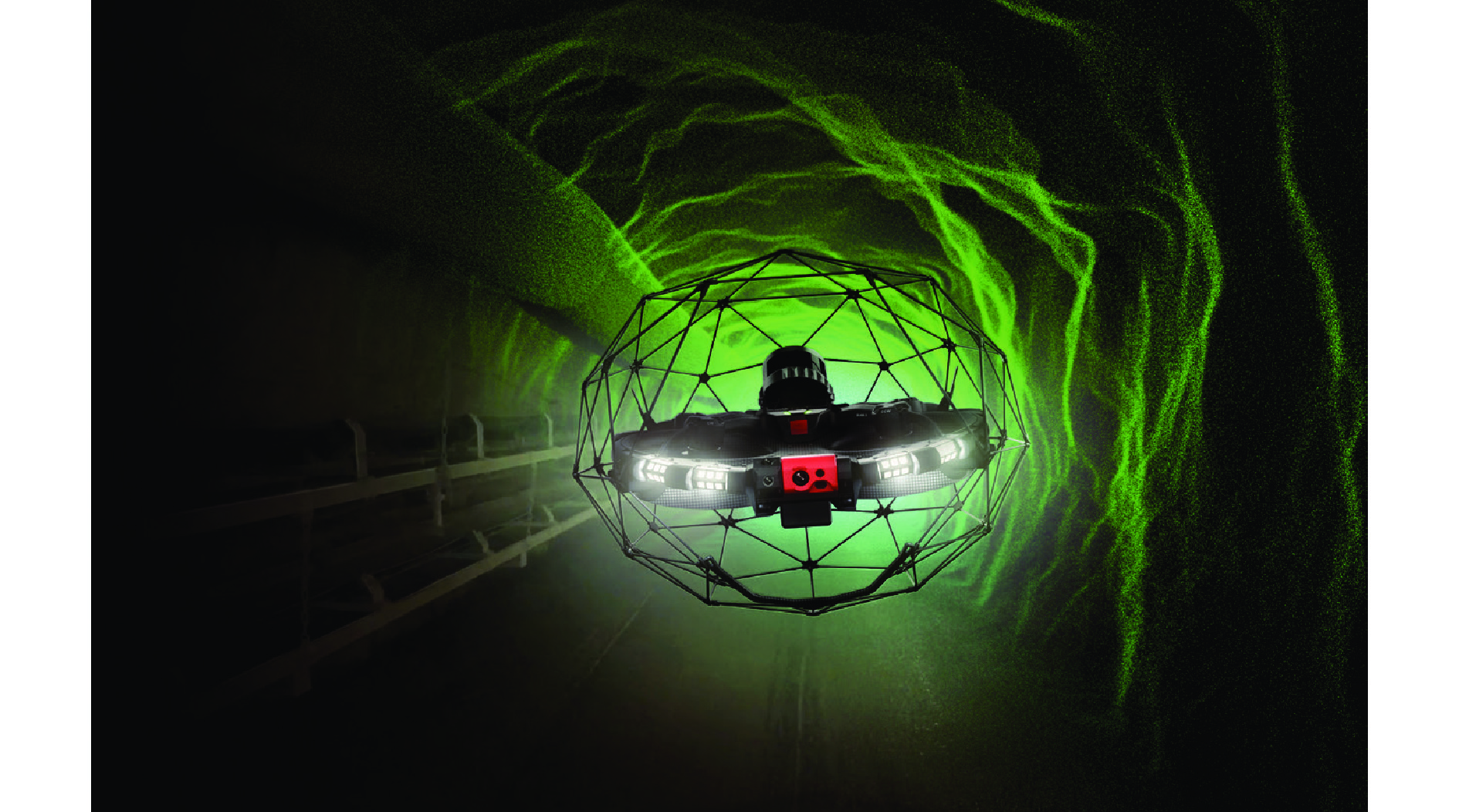
[28] FLYABLITY. Elios 3-Digitizing the inaccessible. [DB/OL]. [2022-07-27]. https://www.flyability.com/elios-3.
[29] 孙继平,钱晓红. 煤矿重特大事故应急救援技术及装备[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(1):112-116,153. SUN Jiping,QIAN Xiaohong. Emergency rescue technology and equipment of mine extraordinary accidents[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(1):112-116,153.
[30] 李新年,李清华,王常虹,等. 美国地下领域无人系统发展现状及启示[J]. 导航定位与授时,2021,8(6):52-59. LI Xinnian,LI Qinghua,WANG Changhong,et al. Development and enlightenment of unmanned underground system in the United States[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing,2021,8(6):52-59.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王翔,汪进超,刘厚成,宋万鹏,李姝祺. 基于声光组合测量的水下构筑物表面缺陷3维可视化方法. 工程科学与技术. 2025(02): 64-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 余勇冬,田逸宁,王斌. 常驻型有缆遥控水下机器人水下定位与通信技术研究进展. 科技创新与应用. 2023(07): 25-28+33 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王一鸣,谢旭. 水下磁感应通信阵列天线磁场仿真与特性研究. 舰船科学技术. 2022(06): 106-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王一鸣,谢旭. 协作式磁感应通信的线圈阵列优化设计. 电波科学学报. 2022(02): 304-313 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高欣,孙远灿. 水下无线通信网络安全关键技术研究. 物联网技术. 2022(06): 45-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈刃,姜军. 城市水环境监测信息多级分布式采集系统. 西安工程大学学报. 2020(03): 81-86+116 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 贾凤玲. 多信道传输下物联网通信数据抗干扰算法. 计算机仿真. 2020(12): 122-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李良玉,杨林. 物联网技术在水环境监测中的研究进展. 环境保护与循环经济. 2020(12): 59-64+74 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



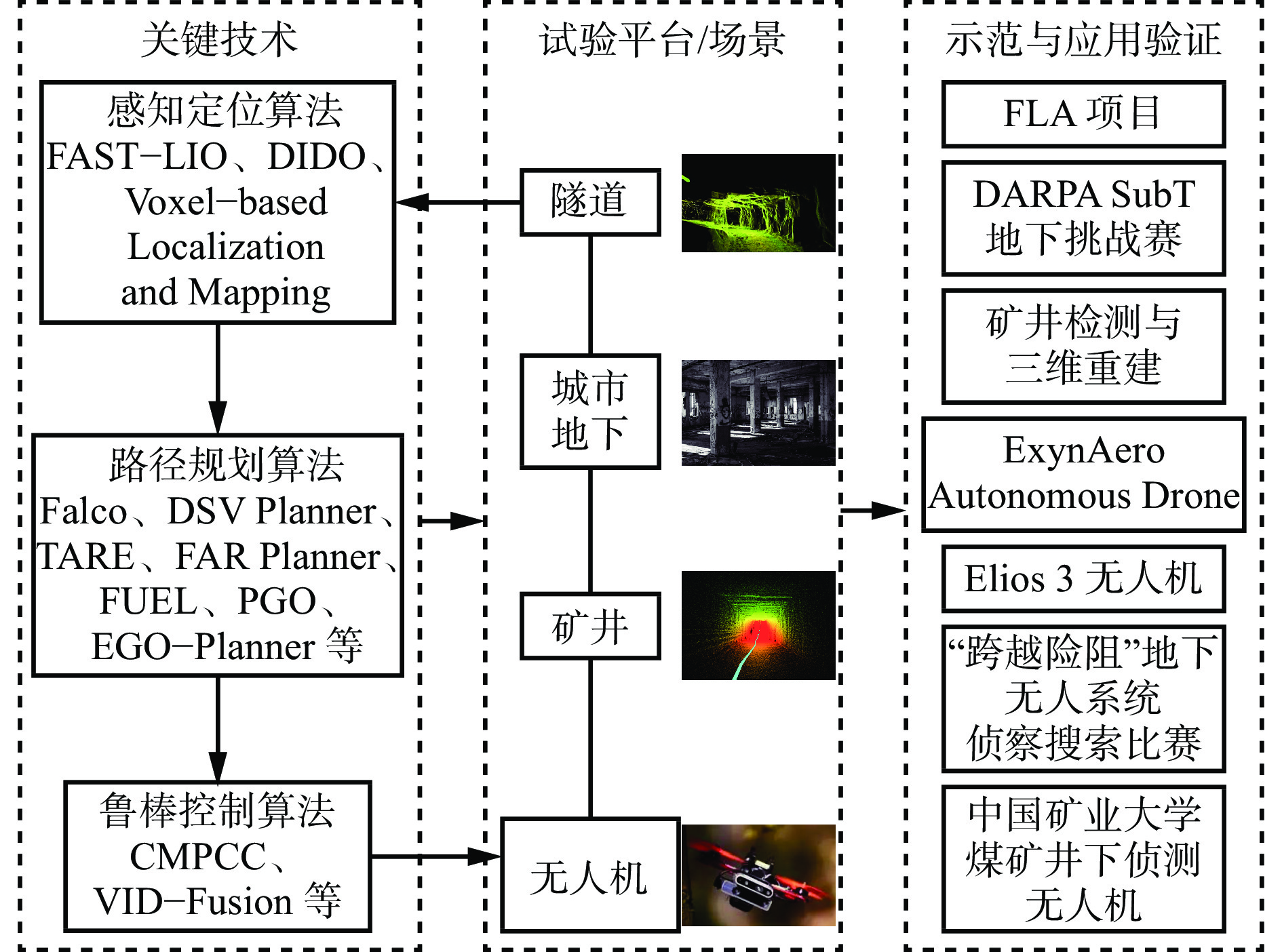
 下载:
下载: