IMU-LiDAR integrated SLAM technology for unmanned driving in mines
-
摘要: 同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)是无人驾驶关键技术,现有SLAM技术在煤矿巷道环境下存在累计误差大、漂移等问题。提出一种巷道环境特征辅助的惯性测量单元(IMU)与激光雷达融合SLAM算法。利用IMU观测数据预测点云运动状态并进行运动补偿,减少由设备运动引起的点云畸变;通过点云配准得到雷达里程计位姿变换信息,构成雷达里程计约束;提取巷道侧壁和地面点云并进行平面拟合,构成环境约束;基于IMU预积分约束、雷达里程计约束和环境约束,采用因子图优化方法完成激光雷达与IMU紧耦合,实现对巷道三维场景的高精度重建和无人驾驶车辆定位。仿真实验表明,巷道环境特征辅助的IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法的绝对轨迹均方根误差为0.116 2 m,相对轨迹均方根误差为0.040 9 m,定位精度较常用的LeGO−LOAM算法和LIO−SAM算法有所提升。真实环境测试结果表明,该算法具有良好的建图效果,未出现漂移和拖尾现象,具有较强的环境适应性和鲁棒性。Abstract: Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a critical technology for unmanned driving. Existing SLAM methods have the drawbacks of significant cumulative errors and drift in coal mine roadway environment. In this study, a roadway environment feature-assisted SLAM algorithm integrating inertial measurement unit (IMU) and LiDAR was proposed. IMU observation data was used to predict the motion state of point cloud and motion compensation was applied to reduce point cloud distortion caused by equipment movement. Pose transformation information from LiDAR odometry was obtained through point cloud registration, forming a LiDAR odometry constraint. Point clouds from roadway sidewalls and floor were extracted and fitted to planes, establishing environmental constraints. Using IMU pre-integration constraints, LiDAR odometry constraints, and environmental constraints, the algorithm applied factor graph optimization to achieve tight coupling between LiDAR and IMU, enabling high-precision 3D reconstruction of roadway scenes and accurate localization of autonomous vehicles. Simulation experiments showed that the absolute trajectory root mean square error (RMSE) of the roadway environment feature-assisted IMU-LiDAR integrated SLAM algorithm was 0.1162 m, and the relative trajectory RMSE was 0.0409 m, improving positioning accuracy compared to commonly used algorithms such as LeGO-LOAM and LIO-SAM. Based on the test results in a real environment, the algorithm provides excellent mapping performance with no drift or trailing, demonstrating strong environmental adaptability and robustness.
-
0. 引言
智能化、无人化运输是提高井工煤矿运输安全性和效率的重要保障[1]。近年来,矿井无人驾驶技术研究主要集中在环境感知、路径规划、自主导航等方面,其中环境感知和自主导航是实现无人驾驶的关键[2]。同时定位与地图构建(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping,SLAM)技术可使移动机器人在未知环境中实时定位,同时构建环境地图[3],是无人驾驶、灾后救援等领域的核心技术[4]。然而,矿井生产环境恶劣,地形复杂、巷道狭窄、光照条件差、信号衰减大等因素增加了SLAM技术在井下应用的难度。
SLAM技术常用传感器包括激光雷达、摄像头(单目、立体、RGB−D、鱼眼)等[5]。视觉传感器提供的信息更丰富,但对环境照明条件非常敏感,在黑暗区域或纹理较弱的场景中可能无法工作。激光雷达作为一种主动式传感器,不受环境照明的影响,具有分辨率高、抗干扰能力强等优点,常被用作SLAM首选传感器[6]。但激光雷达存在运动失真、低频更新、稀疏点云等问题。与激光雷达不同,惯性测量单元(Inertial Measurement Unit,IMU)不受结构特征或环境剧烈变化的影响,可在短时间内提供高精度、高频率的姿态估计,但其累计误差随时间漂移[7]。
IMU与激光雷达融合[8-10]是实现复杂环境中SLAM技术的重要方法。二者的融合方式主要有松耦合和紧耦合。松耦合是将IMU提供的运动估计结果作为先验信息,用于辅助激光雷达的SLAM过程;紧耦合是用IMU和激光雷达数据互相估计与更新。针对矿井巷道特殊环境,文献[11]提出了IMU与激光雷达融合的SLAM方法,通过选取关键帧、采用因子图优化方式对激光雷达和IMU数据进行整体优化,降低了SLAM累计误差,但未充分利用巷道环境信息的辅助作用。文献[12]采用回环检测、扫描匹配、IMU预积分分别构建约束因子图来优化约束因子,完成激光雷达和IMU的紧耦合,但在狭长巷道内可能不存在机器人的回环,此时定位与建图效果会受到影响。文献[13]在前端加入卡尔曼滤波算法,后端使用位姿图优化算法,实现了激光雷达和IMU耦合,并引入巷道的地面约束,但只考虑地面约束对定位精度和鲁棒性的提高有限。
本文提出一种巷道环境特征辅助的IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法,用于矿井无人驾驶的高精度定位。该算法由IMU提供运动状态的实时观测数据,通过激光雷达获取环境中的点云信息,进而提取侧壁和地面信息,结合巷道环境特征来提高SLAM精确性和鲁棒性。
1. IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法框架
巷道环境特征辅助的IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法框架如图1所示。对激光雷达获取的原始点云数据进行去畸变处理,以消除传感器运动而引入的误差;对IMU观测数据进行预积分,为激光雷达点云匹配提供初值。选取关键帧构成局部地图,对局部地图中的点云进行平面特征提取,通过点云匹配算法与已知局部地图进行匹配,以确定相邻关键帧之间的位姿变换关系。通过激光雷达里程计约束、IMU预积分和巷道环境约束共同进行因子图优化,限制惯导零偏等参数的漂移,优化位姿变化,实现对无人驾驶车辆运动和环境的精确估计。
2. IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法关键技术
2.1 IMU预积分约束
为降低畸变对激光雷达数据的影响,采用IMU观测数据对激光雷达数据进行校正[14]。假设第k帧和第f帧激光雷达数据分别为${{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}$和${{\boldsymbol{S}}_f}$,对IMU数据积分,获取${{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}$与${{\boldsymbol{S}}_f}$间的初始匹配值。
假设IMU相邻帧间加速度和角速度恒定,加速度和角速度零偏为常数,则IMU观测模型为
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {{\hat {\boldsymbol{\omega}} }_t} = {{\boldsymbol{\omega}} _t} + {\boldsymbol{b}}_{{t}}^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} + {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} \\ {{\hat {\boldsymbol{a}}}_t} = {\boldsymbol{R}}_t^{{\text{BW}}}({{\boldsymbol{a}}_t} - {\boldsymbol{g}}) + {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\bf{a}} + {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\bf{a}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (1) 式中:$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{\omega}} _t} $,$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{a}}_t} $分别为t时刻IMU的角速度和加速度观测值;ωt,at分别为t时刻IMU的角速度和加速度;$ {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\bf{a}} $分别为t时刻陀螺仪和加速度计的零偏;$ {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\bf{a}} $分别为t时刻陀螺仪和加速度计的观测噪声;$ {\boldsymbol{R}}_t^{{\text{BW}}} $为t时刻世界坐标系到IMU坐标系的旋转矩阵;g为世界坐标系下的重力加速度。
根据$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{\omega}} _t} $,$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{a}}_t} $可得无人驾驶汽车的运动状态:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {{\boldsymbol{v}}_{t + \Delta t}} = {{\boldsymbol{v}}_t} + {{{\boldsymbol{g}}}}\Delta t + {{\boldsymbol{R}}_t}({{\hat {\boldsymbol{a}}}_t} - {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\bf{a}} - {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\bf{a}})\Delta t \\ {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{t + \Delta t}} = {{\boldsymbol{p}}_t} + {{\boldsymbol{v}}_t}\Delta t + \frac{1}{2} {{{\boldsymbol{g}}}}\Delta {t^2} + \frac{1}{2}{{\boldsymbol{R}}_t}({{\hat {\boldsymbol{a}}}_t} - {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\bf{a}} - {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\bf{a}})\Delta {t^2} \\ {{\boldsymbol{R}}_{t + \Delta t}} = {{\boldsymbol{R}}_t}{\mathrm{exp}}\left( {({{\hat {\boldsymbol{\omega}} }_t} - {\boldsymbol{b}}_t^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} - {\boldsymbol{n}}_t^{\boldsymbol{\omega}} )\Delta t} \right) \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (2) 式中:$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}_t} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}_{t + \Delta t}} $分别为$t$,$ t + \Delta t $时刻的速度;$ {{\boldsymbol{p}}_t} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{t + \Delta t}} $分别为$t$,$ t + \Delta t $时刻的位置;$ {{\boldsymbol{R}}_t} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{R}}_{t + \Delta t}} $分别为$t$,$ t + \Delta t $时刻的旋转矩阵。
IMU预积分模型构建2个关键帧之间的一种约束,可用2个关键帧之间的状态变量值和预积分观测值做差,得到残差。通过IMU预积分将IMU数据转换为帧间约束边,集成至因子图优化框架,以避免重复积分,减少计算量。
2.2 激光雷达里程计约束
根据激光雷达参数,确定扫描线上各点的位置和角度。对于每个点,利用IMU观测数据对点云数据进行比例插值,实现点云的运动补偿。雷达里程计对无人驾驶车辆连续2帧的运动进行估计,利用高效扫描匹配算法,结合IMU观测模型初始化位姿变换,进行点云匹配。本文采用LOAM方法提取特征点[8]。通过将当前帧的特征点与局部地图中的特征点进行匹配,预估当前帧的姿态变化。在线特征点中找2个匹配点构成一条直线,在面特征点中找3个匹配点构成一个平面,分别通过最小化点到线和点到面的距离建立约束,求解出最优的位姿变换[15]。具体地,对于第k帧点云,其点到线的距离$ {{{{d}}}}_{k}^{\mathrm{l}} $、点到面的距离$ {{{{d}}}}_{k}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} $分别为
$$ {{d}}_{k}^{\mathrm{l}} = \frac{{\left\| {\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k}^{\mathrm{l}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{\mathrm{l}}} \right) \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k}^{\mathrm{l}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{\mathrm{l}}} \right)} \right\|}}{{\left\| {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{\mathrm{l}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{\mathrm{l}}} \right\|}} $$ (3) $$ {{d}}_{k}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} = \frac{{\left\| {\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}}} \right) \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}}} \right) \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,m}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}}} \right)} \right\|}}{{\left\| {\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}}} \right) \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}} - {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,m}^{{{\mathrm{p}}}}} \right)} \right\|}} $$ (4) 式中:$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k}^{\mathrm{l}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k}^{\rm{p}} $分别为第k帧线特征点和面特征点;$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{\mathrm{l}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{\mathrm{l}} $分别为第k−1帧中第i,j个构成线的匹配点;$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,i}^{\rm{p}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,j}^{\rm{p}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{p}}_{k - 1,m}^{\rm{p}} $ 分别为第k−1帧中第i,j,m个构成平面的匹配点位置。
使用L−M法[15]最小化距离误差,求解最优位姿变换${{\boldsymbol{T}}_{t{\boldsymbol{ + }}{\text{1}}}}$,迭代计算的初始值由帧间IMU预积分提供,以有效减少迭代次数。计算当前位姿${{\boldsymbol{T}}_{\boldsymbol{t}}}$和预测位姿${{\boldsymbol{T}}_{t{\boldsymbol{ + }}{\text{1}}}}$之间的相对位姿变换:
$$ {\boldsymbol{\Delta }}{{\boldsymbol{T}}_{t,t{\boldsymbol{ + }}{\text{1}}}}{\boldsymbol{ = }}{\boldsymbol{T}}_t^{{{ - 1}}}{{\boldsymbol{T}}_{t{\boldsymbol{ + }}{\text{1}}}} $$ (5) 2.3 巷道环境约束
为简化计算,仅将位姿变化超过阈值或时间超过阈值的激光雷达扫描帧作为关键帧加入因子图优化[16]。关键帧与无人驾驶车辆状态节点关联,非关键帧被丢弃,构建局部地图。为降低单帧扫描数据量少、纹理结构不充分的影响,在每个关键帧处构建以传感器为中心的滑动窗口地图,对滑动窗口地图中的地面和侧壁点云数据进行平面拟合。
2.3.1 巷道平面信息提取
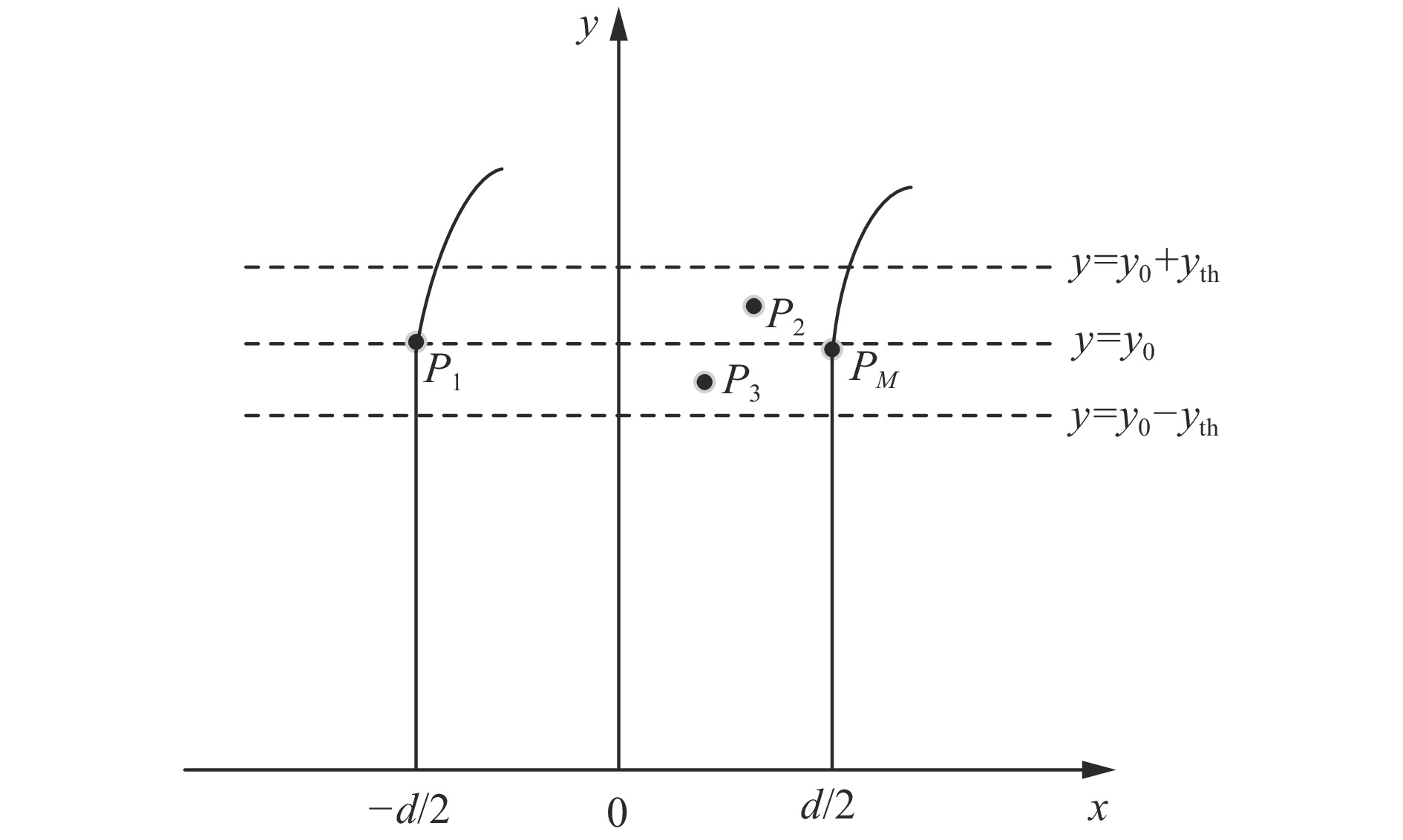
为提升拟合精度,降低计算量,同时应对巷道拐弯处的复杂情况,提出局部侧壁空间平面拟合方法。定义坐标系:x轴垂直于巷道入口中心线方向,y轴垂直于x轴并指向入口方向。局部地图中侧壁点云提取方法如图2所示。先限定局部侧壁宽度范围内的平面点云。假设当前局部地图中激光雷达的y轴坐标为y0,阈值为$ {y_{{\mathrm{th}}}} $,保留y轴坐标在$ {y_0} \pm {y_{{\mathrm{th}}}} $区间内的M个平面点云,设为P1,P2,$ \cdots $,PM。计算相邻2个点的x轴坐标差值Δx,若Δx接近巷道宽度d(阈值为dth),则认为这2个点位于侧壁附近并保留,否则滤除。再设定高度区间z,其阈值为zth。侧壁局部空间点云坐标满足下式。提取侧壁点云并进行平面拟合。
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {y_0} - {y_{{\mathrm{th}}}} \leqslant y \leqslant {y_0} + {y_{{\mathrm{th}}}} \\ d - {d_{{\mathrm{th}}}} \leqslant \Delta x \leqslant d + {d_{{\mathrm{th}}}} \\ 0 \leqslant {\textit{z}} \leqslant {{\textit{z}}_{{\mathrm{th}}}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (6) 若较多平面点云的x轴差值Δx大于巷道宽度d,说明出现岔路或进入非长直巷道空间,此时不加入空间约束。当巷道出现大拐角时,设定的坐标系定义会失效,因此引入动态调整机制:计算平面法向量时,监测法向量之间的夹角变化,若累计夹角变化超过设定阈值,则认为出现拐角,重新定义坐标系,以平面点云的平均法向量方向作为x轴,其垂直方向作为y轴,z轴方向不变。基于新坐标系重新进行侧壁点云提取和平面拟合,确保在复杂情况下仍保持较高的拟合精度。
为避免多平面拟合,进行密度过滤。定义邻域,计算点密度,保留高密度点。采用RANSAC算法[17]进行平面拟合。迭代中随机选点用于拟合平面,标记距离小于阈值的点为内点,直至满足停止条件。用所有内点重新拟合,得到最佳平面。对于多个局部平面,通过计算距离和角度合并为更大的侧壁平面。首先,将拟合的所有平面放入平面集合中,计算其平均平面。假设有N个平面,第r个平面方程为
$$ {A_r}x + {B_r}y + {C_r}{\textit{z}} + {D_r} = 0 $$ (7) 式中:$ ({A_r},{B_r},{C_r}) $为平面法向量;${D_r}$为平面截距。
则初始平均平面为
$$ \left\{\begin{array}{l}\boldsymbol{n}_{\mathrm{a}}^{(0)}=\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum_{r-1}^N\boldsymbol{n}_r \\ D_{\mathrm{a}}^{(0)}=\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum_{r=1}^ND_r\end{array}\right. $$ (8) 式中:${\boldsymbol{n}}_{\text{a}}^{(0)}$,$D_{\text{a}}^{(0)}$分别为初始平均平面的法向量和截距;${\boldsymbol{n}}_{{r}} $为第r个平面法向量,${\boldsymbol{n}}_r $=(Ar,Br,Cr)。
针对每个平面,计算当前平面到平均平面的距离误差和角度误差,对二者进行加权,计算总误差。
$$ d_r^{(s)} = \frac{{|A_{\text{a}}^{(s)}{A_r} + B_{\text{a}}^{(s)}{B_r} + C_{\text{a}}^{(s)}{C_r} + (D_{\text{a}}^{(s)} - {D_r})|}}{{\sqrt {(A_{\text{a}}^{{{(s)}}})^2 + (B_{\text{a}}^{{{(s)}}})^2 + (C_{\text{a}}^{{{(s)}}})^2} }} $$ (9) $$ \cos \; \theta _r^{(s)} = \frac{{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\text{a}}^{(s)} {{\boldsymbol{n}}_r}}}{{||{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\text{a}}^{(s)}||\; ||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_r}||}} $$ (10) $$ E^{(s)}=\sum_{r=1}^{N}\left(w_{{\mathrm{d}}}-d_{r}^{(s)}+w_{\theta}-\theta_{r}^{(s)}\right) $$ (11) 式中:$ d_r^{(s)} $,$\theta _r^{(s)}$分别为第s次迭代后第r个平面到平均平面的距离误差和角度误差;($A_{\mathrm{a}}^{(s)},B_{\mathrm{a}}^{(s)},C_{\mathrm{a}}^{(s)} $)为第s次迭代后平均平面法向量;${E^{(s)}}$为距离误差和角度误差的加权和;${w_{\mathrm{d}}}$,${w_\theta }$为距离误差和角度误差的权重系数。
找到误差最大的平面,将其从平面集合中剔除,得到新的平面集合。重复上述步骤并迭代,若前后2次迭代的总误差变化不大(小于误差阈值$\varepsilon $),即满足下式,则终止迭代。
$$ \mid {E}^{(s+1)}-{E}^{(s)}\mid < \varepsilon $$ (12) 最后一次迭代得到的平均平面为最终输出平面。
巷道侧壁点云提取伪代码如下。
巷道侧壁点云提取算法
输入:点云帧,提取空间的y轴长度阈值yth,z轴提取区间,巷道宽度d,平面合并的误差阈值$ \varepsilon $
输出:该帧点云两侧壁平面法向量
1 初始化;
2 提取y轴在设定区间内的点云;
提取位于局部侧壁附近的点云;
提取高度区间内的侧壁局部空间点云;
区分左右侧壁点云,分别放入集合LeftPoints和RightPoints;
3 输入点云集合;
4 点云密度过滤;
4 使用RANSAC算法进行平面拟合;
5 迭代并合并多个局部平面;
计算当前平均平面;
计算每个平面到平均平面的距离和角度误差及总误差;
剔除误差最大的平面;
检查收敛条件;
6 输出最终合并平面法向量;
利用文献[18]中的地面点云分割和拟合方法得到地面信息,将其与拟合的侧壁作为环境约束集成至因子图优化框架,以提升定位精度和鲁棒性。
2.3.2 巷道环境约束构建
完成平面拟合后,地面和巷道侧壁可表示为$Ax + By + C{\textit{z}} + D = 0$,平面法向量为主方向$ {\boldsymbol{n}} = (A, B,C) $。该法向量可能存在方向对偶性,需要调整角度,若其为负值,则角度加π以转换为正值。巷道的2个侧壁应相互平行,且均与底板垂直。根据向量点乘性质,平行向量点乘结果为其模长的乘积乘以夹角的余弦值。平行向量夹角为0,余弦值为1;垂直向量夹角为90°,余弦值为0。因此,侧壁间的平行约束、左侧壁与地面的垂直约束、右侧壁与地面的垂直约束如下:
$$ {{{e}}_{\mathrm{L}}} = 1 - \frac{{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{L}}^{\mathrm{T}}{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{R}}}}}{{||{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{L}}^{\mathrm{T}}||\; ||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{R}}}||}} $$ (13) $$ {{{e}}_{\mathrm{g}}} = \frac{{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{L}}^{\mathrm{T}}{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{g}}}}}{{||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{L}}}||\; ||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{g}}}||}} $$ (14) $$ {{e}}_{{\mathrm{g}}}^{\prime} = \frac{{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{R}}^{\mathrm{T}}{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{g}}}}}{{||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{R}}}||\; ||{{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{g}}}||}} $$ (15) 式中:$ {{{e}}_{\mathrm{L}}} $,$ {{{e}}_{\mathrm{g}}} $,$ {{e}}_{{\mathrm{g}}}^{\prime} $分别为左侧壁与地面垂直关系、左右侧壁平行关系、右侧壁与地面垂直关系的误差项;$ {{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{L}}} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{R}}} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{n}}_{\mathrm{g}}} $分别为左侧壁、右侧壁、底板的平面法向量。
环境约束的总体误差因子为
$$ {{{e}}} = {{{e}}_{\mathrm{L}}} + {{{e}}_{\mathrm{g}}} + {{e}}_{{\mathrm{g}}}^{\prime} $$ (16) 2.4 因子图优化
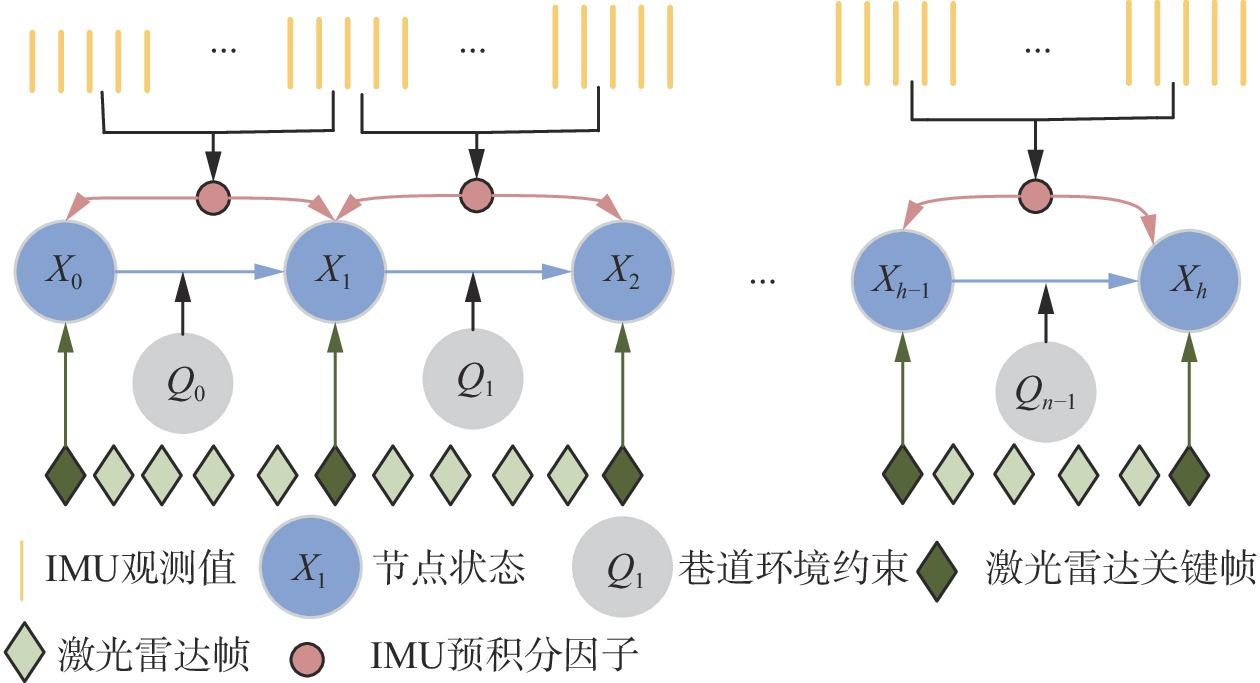
后端使用因子图优化方法,包括激光雷达里程计约束因子、IMU预积分约束因子、巷道环境约束因子,以维护全局地图的一致性。将连续关键帧之间的IMU预积分因子、连续关键帧之间的约束姿态构成的激光雷达里程计因子和巷道环境约束因子分别加入因子图,如图3所示。
优化目标函数为
$$ \hat {\boldsymbol{X}} = \arg {\min }\sum\limits_l {({\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{I}},l}^{\mathrm{T}}{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{I}},l}^{ - 1}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{\mathrm{I}},l}} + {\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{L}},l}^{\mathrm{T}}{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{L}},l}^{ - 1}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{\mathrm{L}},l}} + {\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{P}},l}^{\mathrm{T}}{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{P}},l}^{ - 1}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{{\mathrm{P}},l}})} $$ (17) 式中:$ \hat {\boldsymbol{X}} $为优化后的最优状态估计;$ {{\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{I}},l}} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{L}},l}} $,$ {{\boldsymbol{F}}_{{\mathrm{P}},l}} $分别为第l个IMU预积分因子、激光雷达里程计因子、巷道环境约束因子的残差;${{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{I}},l}}$,${{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{L}},l}}$,${{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\mathrm{P}},l}}$分别为与IMU预积分约束因子、激光雷达里程计约束因子、巷道环境约束因子相关的协方差矩阵。
3. 算法性能测试
利用Gazebo仿真平台对本文算法的性能进行仿真验证,在涵洞和车库2个场景进行实测验证。
3.1 仿真巷道性能测试
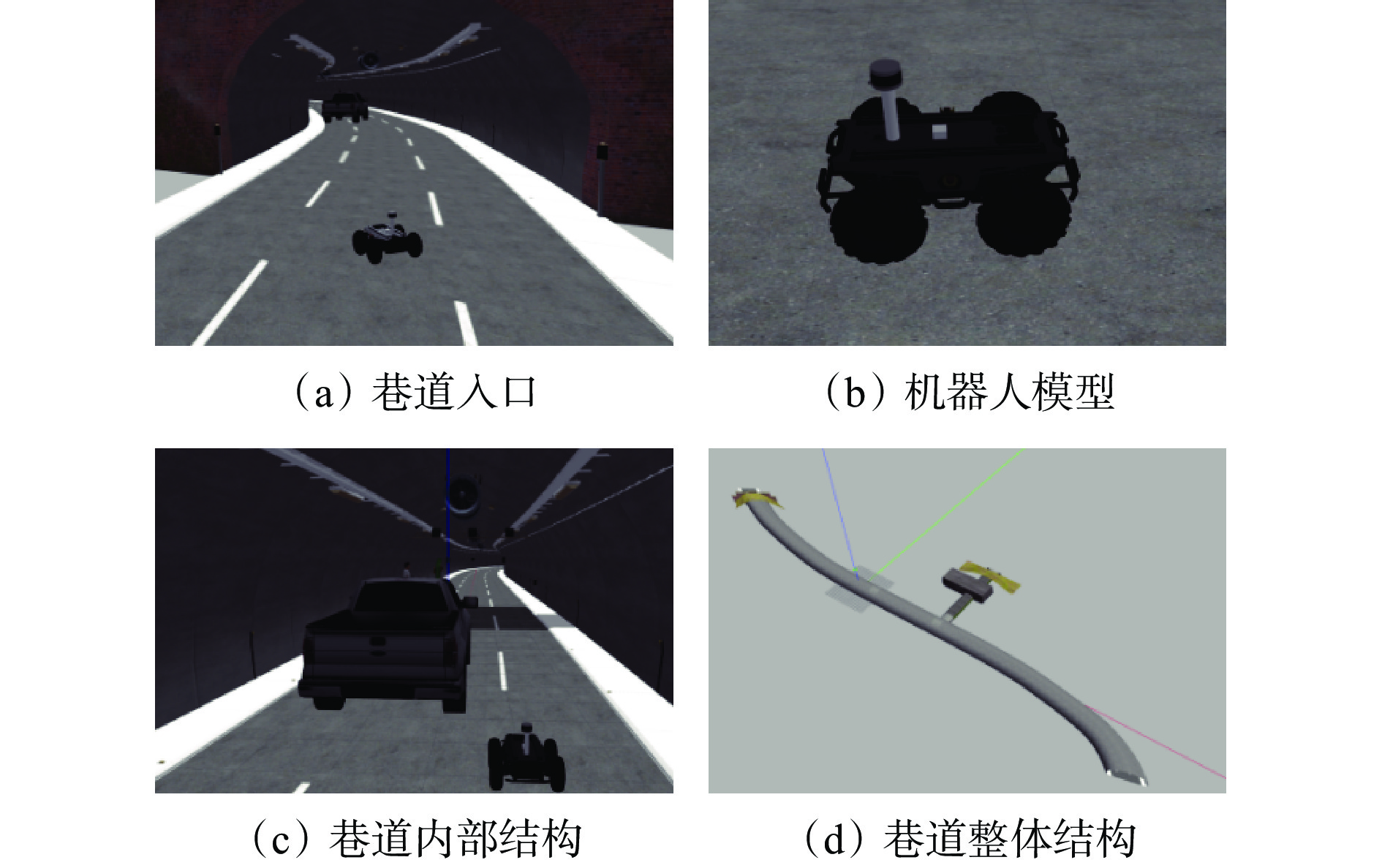
在Gazebo软件中搭建一个长200 m、宽5 m、高3 m的巷道模型,其包括直道、弯道、岔口等复杂情况。在巷道中部署一个ScoutV2轮式机器人模型代替无人驾驶小车,其配备Velodyne VLP−16激光雷达和9轴IMU传感器,用于采集仿真环境数据。部分仿真场景如图4所示。
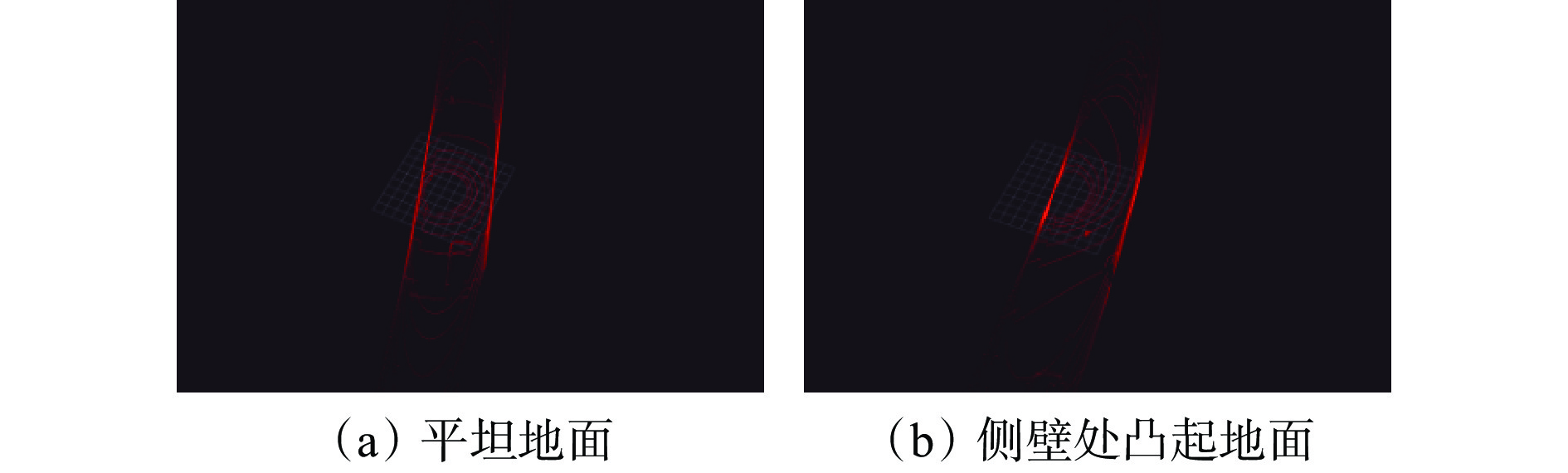
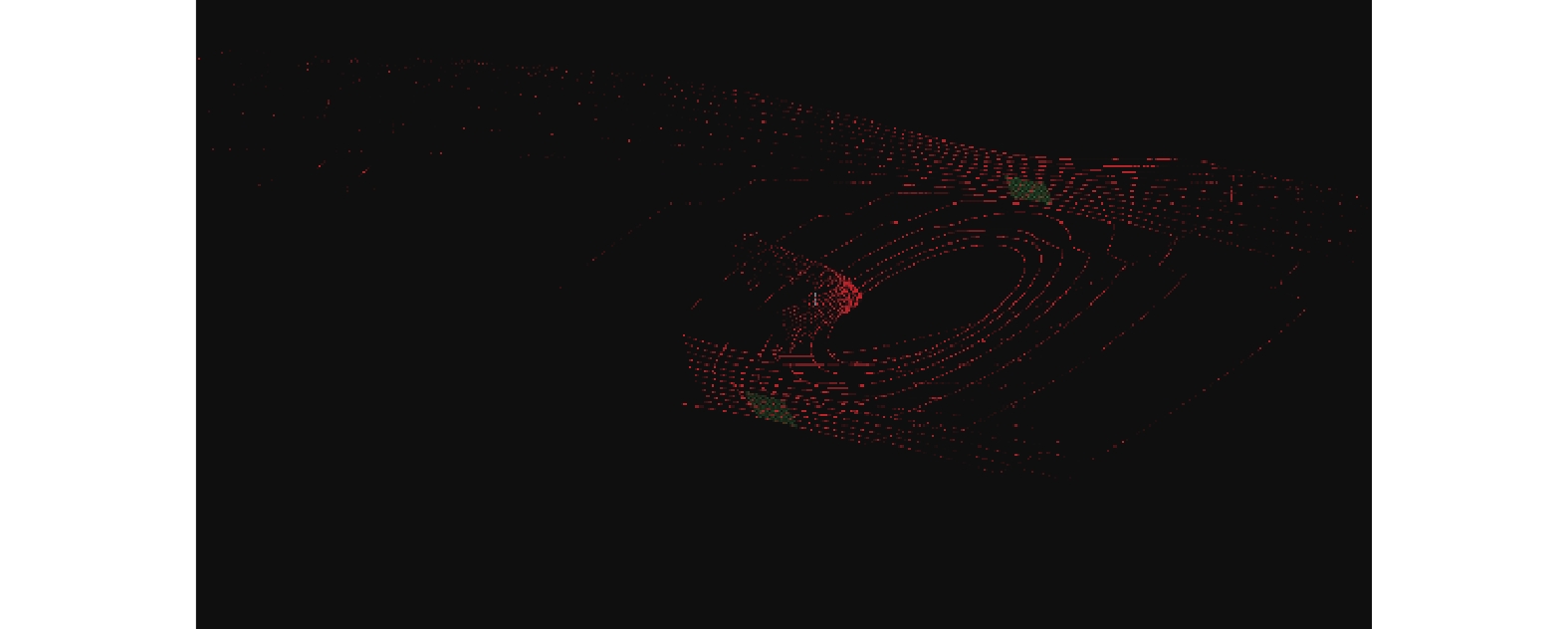
小车在平坦地面和侧壁处凸起地面上行驶时采集的点云如图5所示。
通过巷道侧壁信息提取方法对采集的点云进行处理,结果如图6所示。
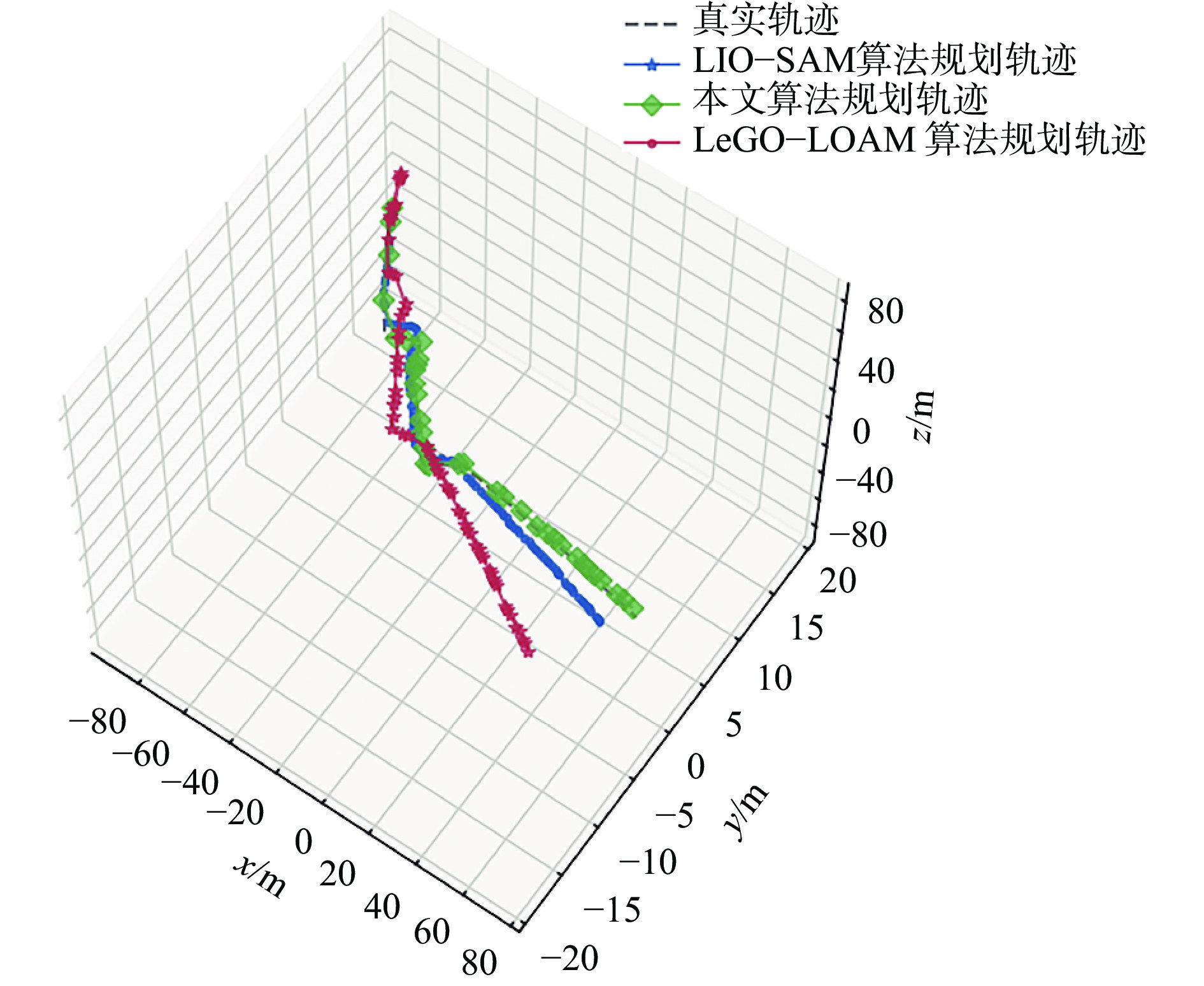
为验证本文算法的准确性和鲁棒性,将其与应用广泛的LeGO−LOAM[19],LIO−SAM算法进行对比。3种算法规划的三维轨迹如图7所示。可看出本文算法规划的轨迹与真实轨迹的偏差较小,而LeGO−LOAM算法和LIO−SAM算法规划的轨迹出现了不同程度的偏差,尤其在运动幅度较大和较长时间后,偏差更明显。
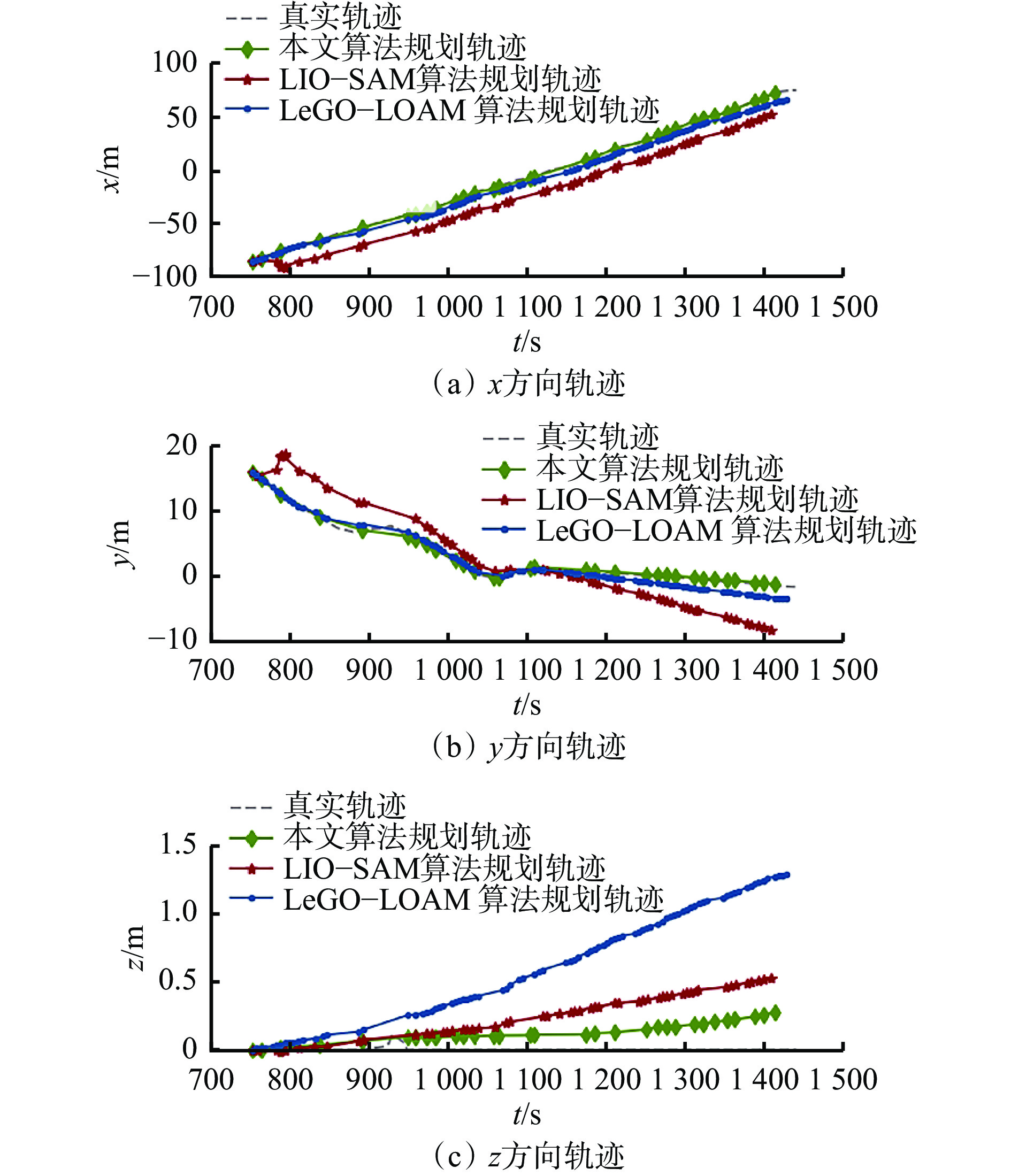
3种算法规划的二维轨迹如图8所示。可看出本文算法在x,y轴上的规划轨迹几乎与真实轨迹重合,且预测的巷道长度与真实值差别不大,但LeGO−LOAM算法和LIO−SAM算法在定位上有较大偏差。在z轴方向,LeGO−LOAM,LIO−SAM算法的定位值漂移较大,特别是1 000 s后(运动较长时间),漂移更加显著。而本文算法的定位结果虽然也不可避免地存在漂移、误差累计情况,但明显小于其他2种算法,验证了本文算法在垂直方向上具有强鲁棒性。
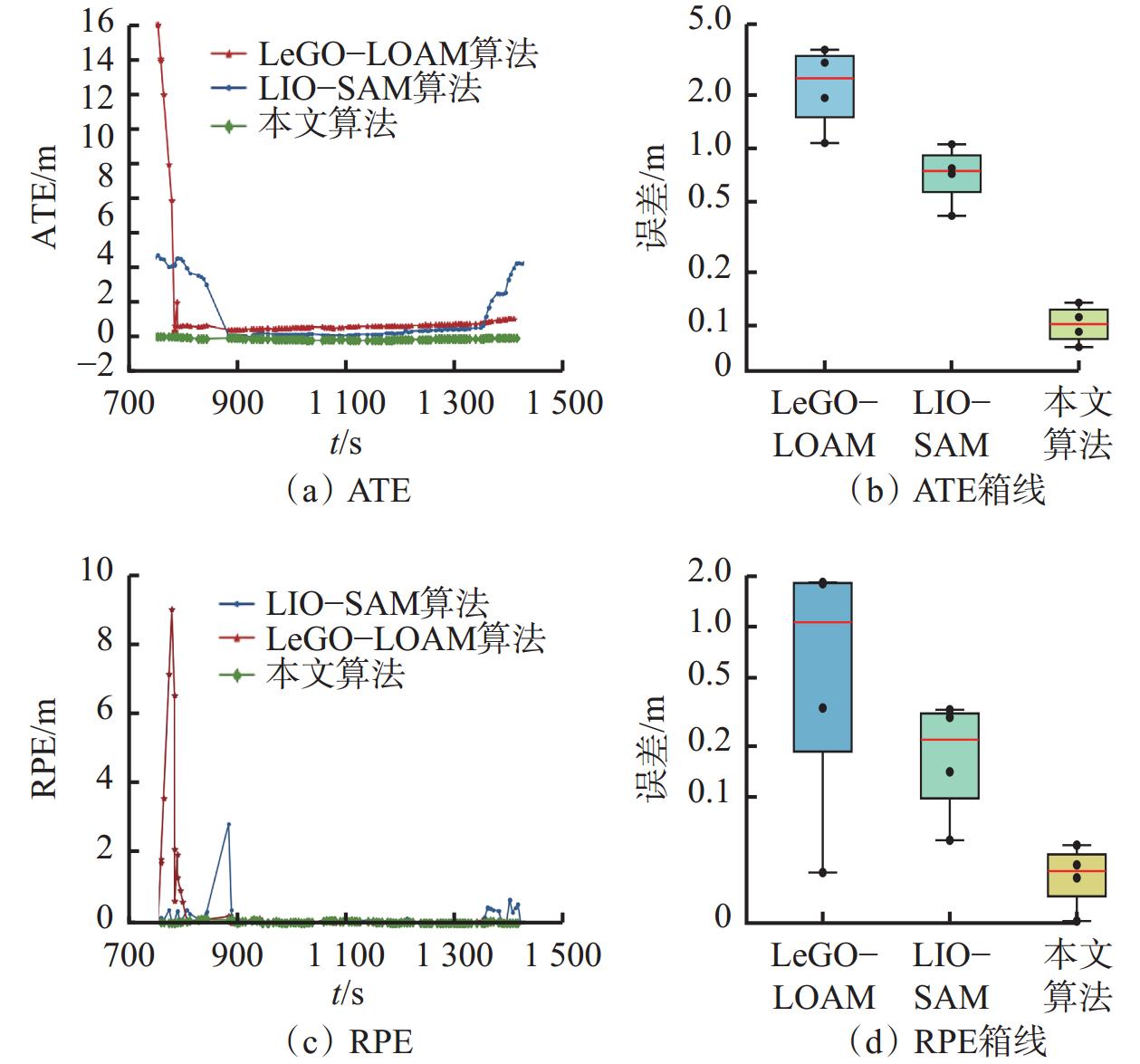
3种算法的绝对轨迹误差(Absolute Trajectory Error,ATE)和相对轨迹误差(Relative Pose Error,RPE)如图9所示,具体值见表1、表2。
从图9、表1、表2可看出,LeGO−LOAM算法定位误差明显,且误差波动更大,表明其在巷道环境中可靠性较低;LIO−SAM算法性能优于LeGO−LOAM算法,但定位误差仍有波动,且累计误差随时间增长而增大;本文算法的ATE和RPE最低且最稳定,定位精度、稳定性和鲁棒性最优。
表 1 3种算法的绝对轨迹误差Table 1. Absolute trajectory error (ATE) of three algorithmsm 指标 LeGO−LOAMS算法 LIO−SAM算法 本文算法 均方根误差 3.2237 1.9166 0.1162 平均值 1.4160 1.2771 0.1053 中值 0.7579 0.5030 0.1052 标准差 2.8961 1.4291 0.0495 表 2 3种算法的相对轨迹误差Table 2. Relative pose error (RPE) of three algorithmsm 指标 LeGO−LOAM算法 LIO−SAM算法 本文算法 均方根误差 1.4924 0.3303 0.0409 平均值 0.3627 0.1236 0.0298 中值 1.0193 0.2061 0.0254 标准差 1.4476 0.3063 0.0283 3.2 真实环境性能测试
在一条长约600 m、宽6 m的复杂巷道(包含上下坡、大拐角等场景)中对本文算法进行测试,定性分析建图效果。测试场景如图10所示。
实验平台采用Autolabor机器人代替无人驾驶车辆,如图11所示。机器人配备hipnuc−CH104M 9轴IMU和Velodyne 16线激光雷达。雷达、IMU的采样频率分别为10,200 Hz。平台搭载的计算机为Intel Core i7,8个内核,16 GiB内存。算法用C++编写,用ROS的melodic版本在Ubuntu 18.04系统上运行[20]。
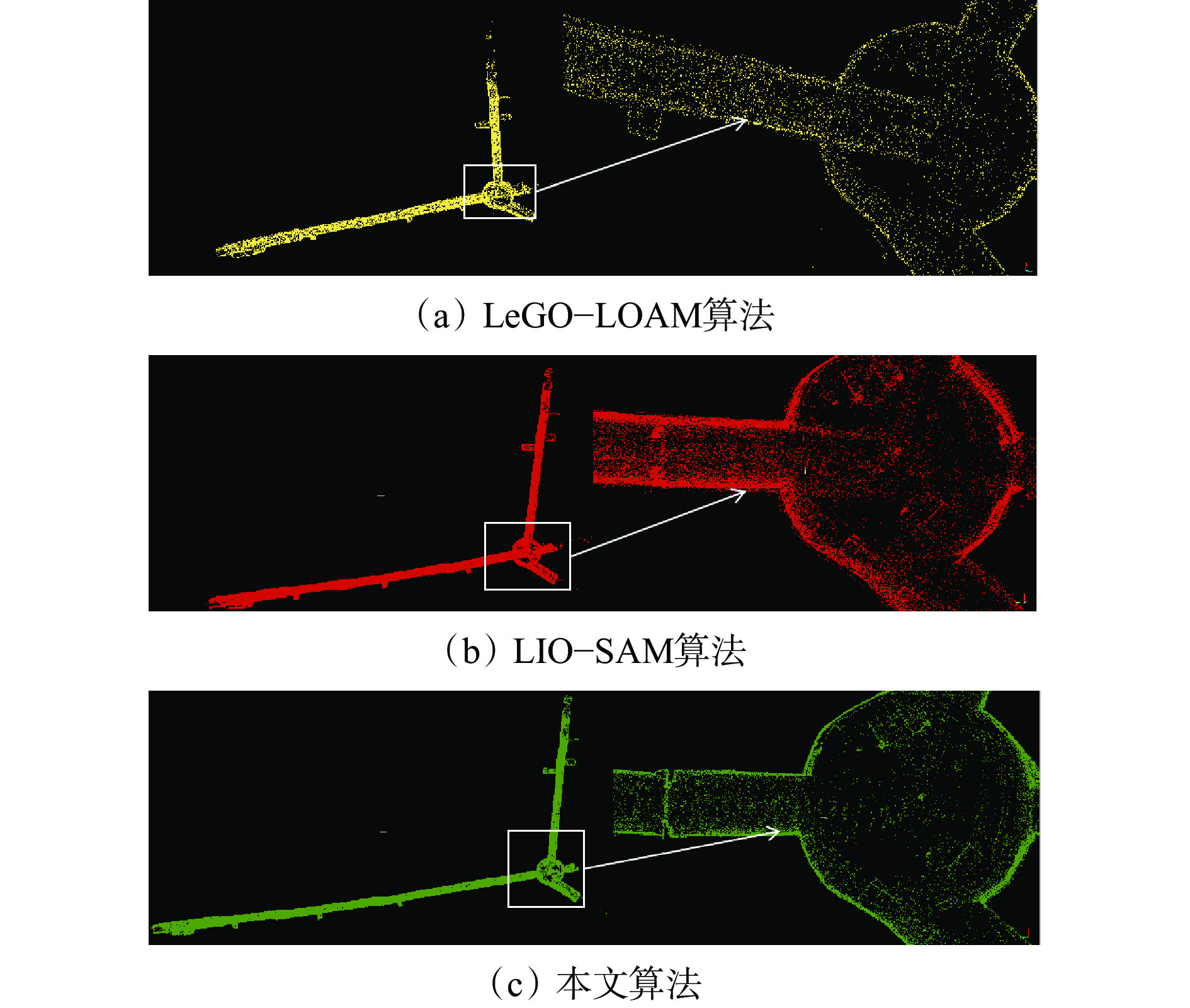
采用LeGO−LOAM算法、LIO−SAM算法和本文算法进行SLAM测试,结果如图12所示。可看出使用LeGO−LOAM算法时,巷道边缘呈模糊状态,并伴随大量杂乱点云,表明该算法在巷道环境中具有局限性。LIO−SAM算法针对长巷道边缘的对齐精度较低。本文算法在巷道边缘建图方面表现优异,即使在大拐角处也能保持良好效果,证明了其在复杂环境中的适应性和有效性。
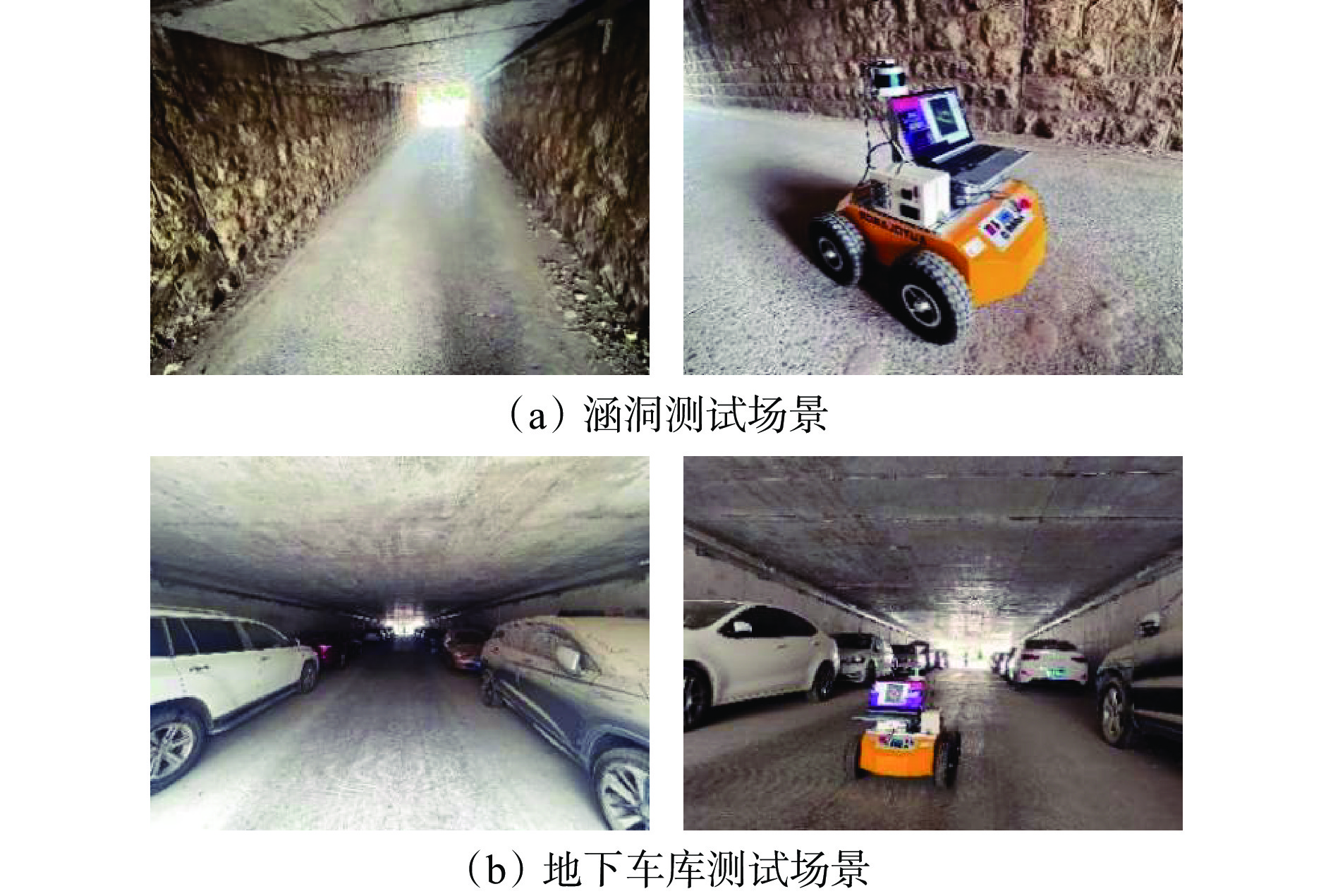
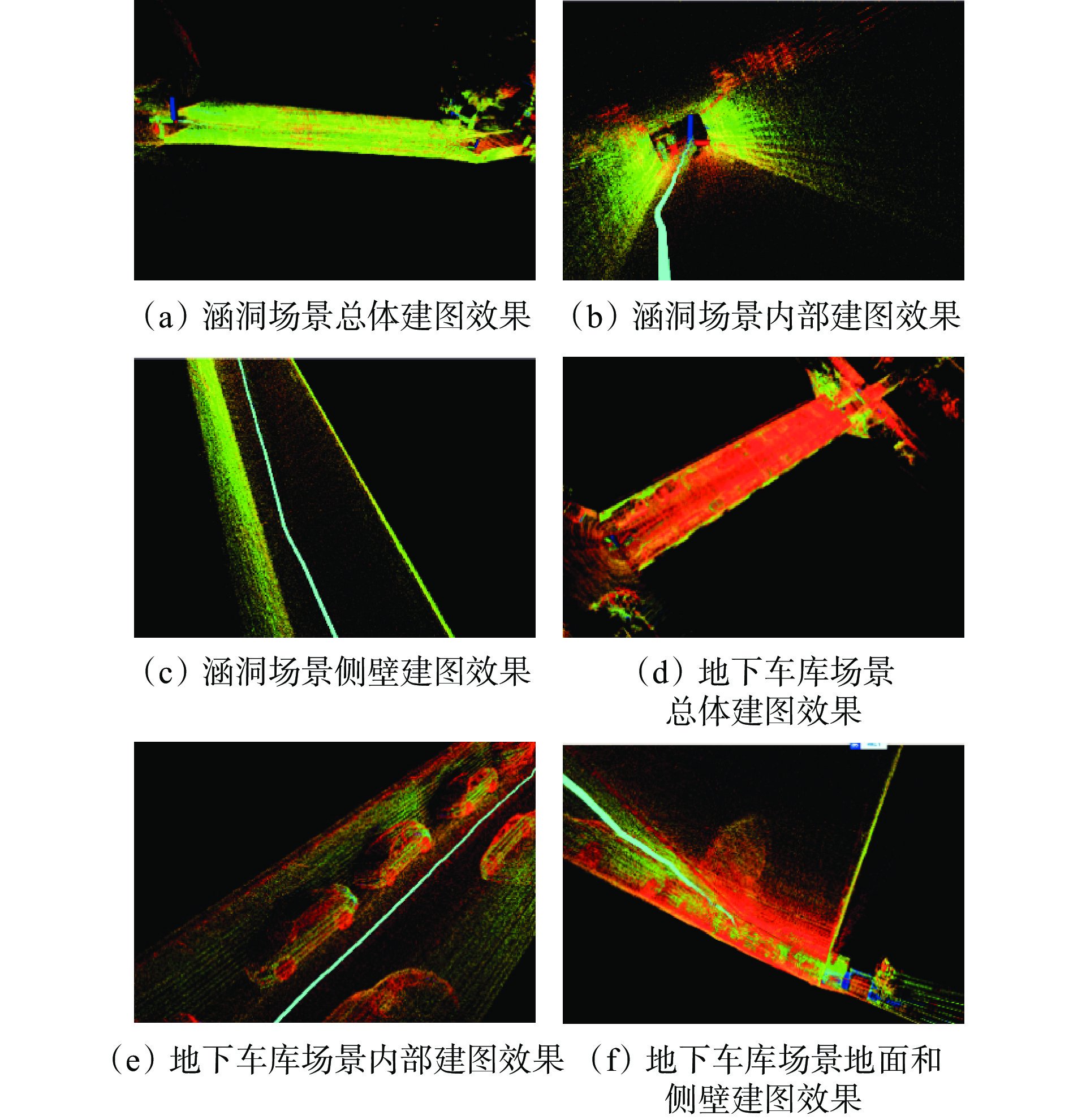
在与矿井巷道具有相似性的2个代表性场景中对本文算法进行实测。① 涵洞场景,如图13(a)所示。该场景具有地面坑洼、侧壁粗糙等特点,用于测试算法在不平整地面和复杂壁面环境中的表现。② 地下车库场景,如图13(b)所示。该场景存在较多的车辆和其他障碍物,用于测试算法在复杂动态环境中的定位与建图能力。
在涵洞和地下车库测试场景中分别进行多次实验,在不同路径和不同障碍物分布情况下,本文算法的SLAM结果如图14所示。可看出本文算法在涵洞和地下车库场景中均表现出良好的适应性和鲁棒性。在涵洞场景中,小车在地面坑洼和侧壁粗糙条件下能准确定位并建图,且侧壁为一条直线,没有出现弯曲、扭曲效果。在地下车库较多障碍物的情况下,本文算法能实现准确定位和建图,效果良好,未出现拖尾、漂移现象。
4. 结论
1) 巷道环境特征辅助的IMU与激光雷达融合SLAM算法通过IMU预积分校正、侧壁和地面平面信息提取、因子图优化等,实现复杂矿井环境的高精度定位与建图。
2) 仿真及真实环境测试结果表明,该算法的定位精度和鲁棒性较常用的LeGO−LOAM、LIO−SAM算法有明显提升,在复杂巷道、涵洞、地下车库场景中均具有较好的建图效果,未出现漂移和拖尾现象,定位精度和鲁棒性较高。
3) 今后将进一步提升算法的计算效率,并对SLAM框架进行优化扩展,以适应更复杂的环境和任务需求。
-
表 1 3种算法的绝对轨迹误差
Table 1 Absolute trajectory error (ATE) of three algorithms
m 指标 LeGO−LOAMS算法 LIO−SAM算法 本文算法 均方根误差 3.2237 1.9166 0.1162 平均值 1.4160 1.2771 0.1053 中值 0.7579 0.5030 0.1052 标准差 2.8961 1.4291 0.0495 表 2 3种算法的相对轨迹误差
Table 2 Relative pose error (RPE) of three algorithms
m 指标 LeGO−LOAM算法 LIO−SAM算法 本文算法 均方根误差 1.4924 0.3303 0.0409 平均值 0.3627 0.1236 0.0298 中值 1.0193 0.2061 0.0254 标准差 1.4476 0.3063 0.0283 -
[1] 胡青松,孟春蕾,李世银,等. 矿井无人驾驶环境感知技术研究现状及展望[J]. 工矿自动化,2023,49(6):128-140. HU Qingsong,MENG Chunlei,LI Shiyin,et al. Research status and prospects of perception technology for unmanned mining vehicle driving environment[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2023,49(6):128-140.
[2] 陈善有,郭洋,田斌,等. 国内外露天矿山无人驾驶研究现状分析与发展前景[J]. 现代矿业,2023,39(12):12-16. CHEN Shanyou,GUO Yang,TIAN Bin,et al. Analysis of current research status and development prospects of unmanned driving in open-pit mines at home and abroad[J]. Modern Mining,2023,39(12):12-16.
[3] 危双丰,庞帆,刘振彬,等. 基于激光雷达的同时定位与地图构建方法综述[J]. 计算机应用研究,2020,37(2):327-332. WEI Shuangfeng,PANG Fan,LIU Zhenbin,et al. Survey of LiDAR-based SLAM algorithm[J]. Application Research of Computers,2020,37(2):327-332.
[4] 张新,徐建华,陈彤,等. 面向重大自然灾害的救援装备研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(25):10552-10565. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.25.002 ZHANG Xin,XU Jianhua,CHEN Tong,et al. Research status and development trend of rescue equipment for major natural disasters[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(25):10552-10565. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.25.002
[5] 蒋济州,徐文福,潘尔振. 仿生扑翼飞行机器人自主导航系统研究进展[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2023,44(11):66-84. JIANG Jizhou,XU Wenfu,PAN Erzhen. Survey on autonomous navigation systems of bionic flapping-wing flying robot[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument,2023,44(11):66-84.
[6] 周治国,曹江微,邸顺帆. 3D激光雷达SLAM算法综述[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2021,42(9):13-27. ZHOU Zhiguo,CAO Jiangwei,DI Shunfan. Overview of 3D lidar SLAM algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument,2021,42(9):13-27.
[7] 聂明炎,杨诚. 一种LiDAR平面配准方法辅助的IMU室内定位算法[J]. 测绘地理信息,2021,46(5):27-30. NIE Mingyan,YANG Cheng. An IMU indoor location algorithm assisted by LiDAR plane registration method[J]. Journal of Geomatics,2021,46(5):27-30.
[8] ZHANG Ji,SINGH S. Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping[J]. Autonomous Robots,2017,41:401-416 . DOI: 10.1007/s10514-016-9548-2
[9] TANG Jian,CHEN Yuwei,NIU Xiaoji,et al. LiDAR scan matching aided inertial navigation system in GNSS-denied environments[J]. Sensors,2015,15(7):16710-16728. DOI: 10.3390/s150716710
[10] FRANK S A B D G. Tight coupling of laser scanner and inertial measurements for a fully autonomous relative navigation solution[J]. Navigation,2007,54(3):189-205. DOI: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.2007.tb00404.x
[11] 马艾强,姚顽强,蔺小虎,等. 面向煤矿巷道环境的LiDAR与IMU融合定位与建图方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(12):49-56. MA Aiqiang,YAO Wanqiang,LIN Xiaohu,et al. Coal mine roadway environment-oriented LiDAR and IMU fusion positioning and mapping method[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(12):49-56.
[12] 李猛钢,胡而已,朱华. 煤矿移动机器人LiDAR/IMU紧耦合SLAM方法[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(12):68-78. LI Menggang,HU Eryi,ZHU Hua. LiDAR/IMU tightly-coupled SLAM method for coal mine mobile robot[J]. Journal of Mine Automation,2022,48(12):68-78.
[13] 杨林,马宏伟,王岩. 基于激光惯性融合的煤矿井下移动机器人SLAM算法[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(9):3523-3534. YANG Lin,MA Hongwei,WANG Yan. LiDAR-inertial SLAM for mobile robot in underground coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(9):3523-3534.
[14] GENTIL C L,VIDAL-CALLEJA T,HUANG S. IN2LAMA:inertial lidar localisation and mapping[C]. International Conference on Robotics and Automation,Montreal,2019:6388-6394.
[15] SHAN Tixiao,ENGLOT B,MEYERS D,et al. LIO-SAM:tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and map[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Las Vegas,2020:5135-5142.
[16] RANGANATHAN A. The levenberg-marquardt algorithm[J]. Tutoral on LM Algorithm,2004,11(1):101-110.
[17] DERPANIS K G. Overview of the RANSAC algorithm[J]. Image Rochester NY,2010,4(1):2-3.
[18] LENG Zhixin,LI Shu,LI Xin,et al. An improved fast ground segmentation algorithm for 3D point cloud[C]. Chinese Control and Decision Conference,Hefei,2020:5016-5020.
[19] SHAN Tixiao,ENGLOT B. LeGO-LOAM:lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Madrid,2018. DOI: 10.1109/IROS.2018.8594299.
[20] 秦学斌,王炳,景宁波,等. 基于矿区巷道巡检机器人的LOAM-SLAM地图重建改进算法的研究[J]. 金属矿山,2022(4):163-168. QIN Xuebin,WANG Bing,JIN Ningbo,et al. Research on improved algorithm of LOAM-SLAM map reconstruction based on mine roadway inspection robot[J]. Metal Mine,2022(4):163-168.




 下载:
下载: