Study on the overburden failure features and microseismic measurements in non-pillar gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting
-
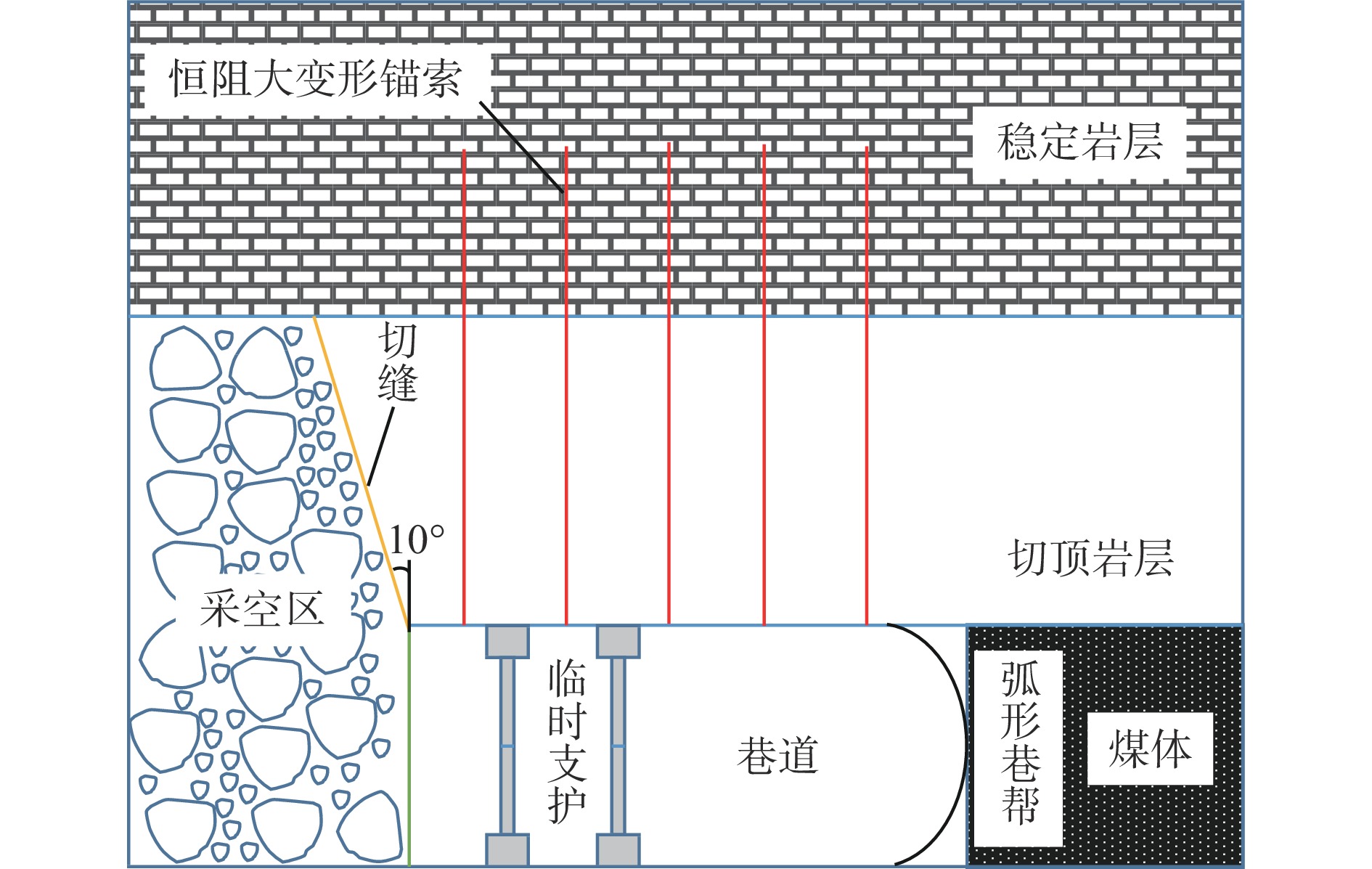
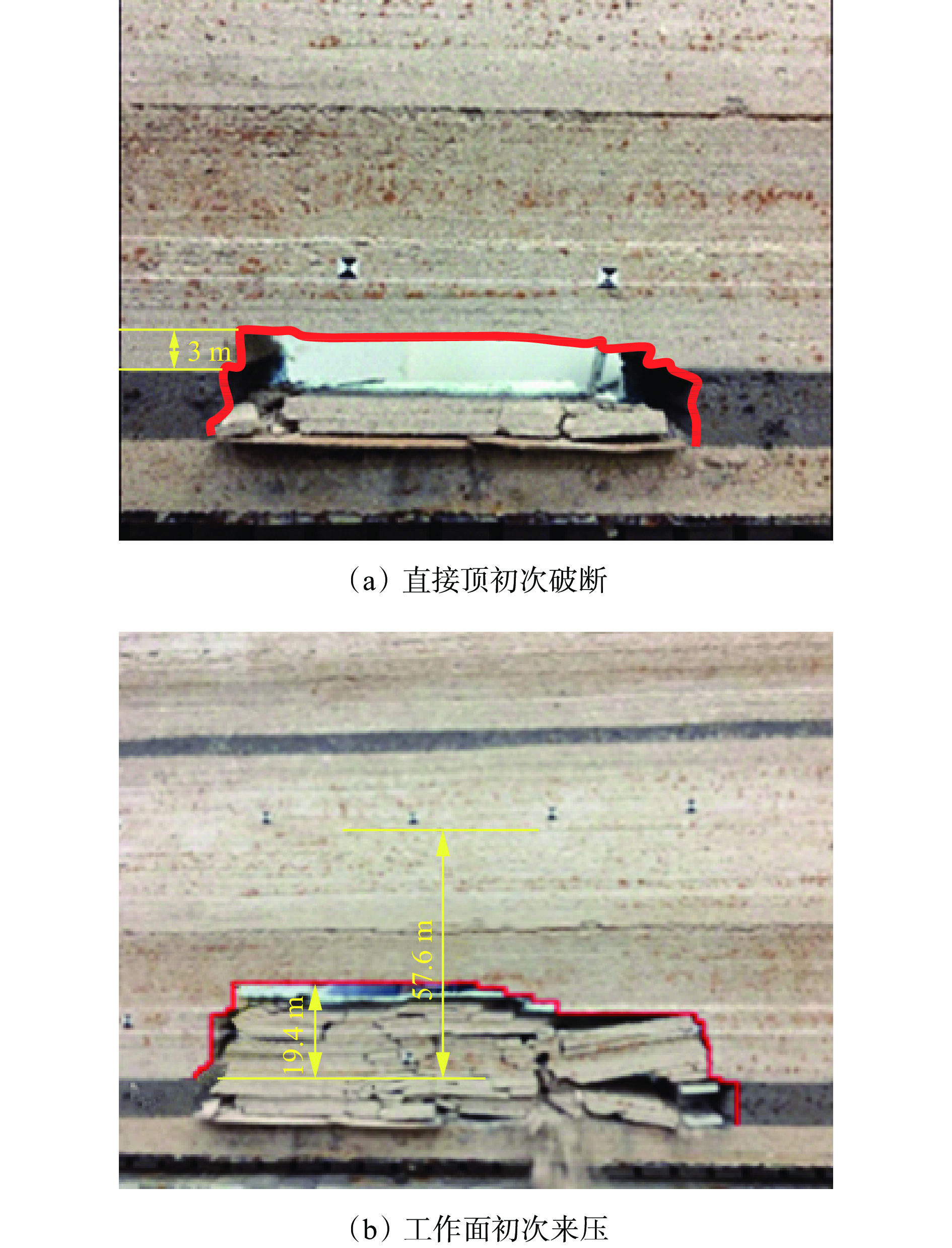
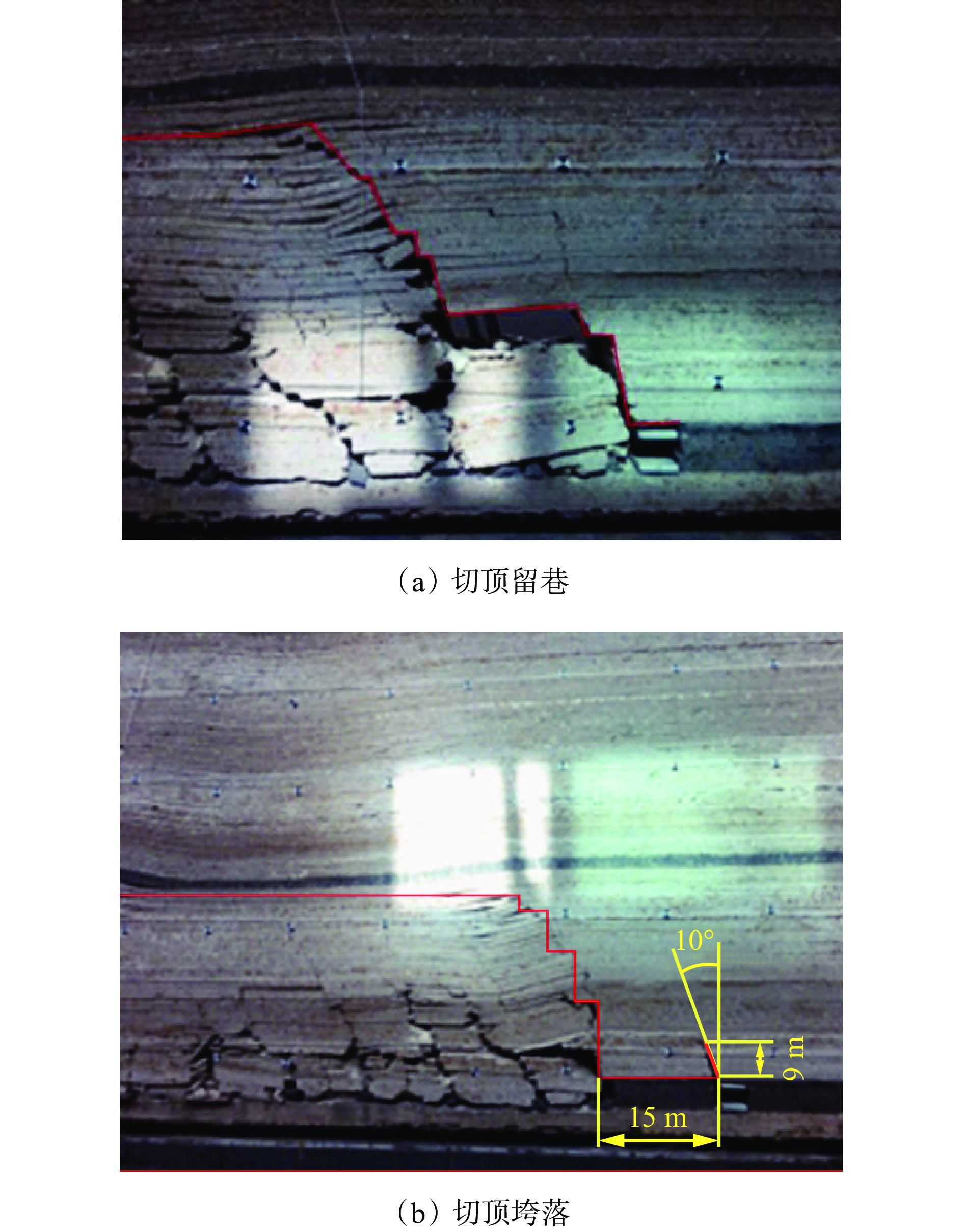
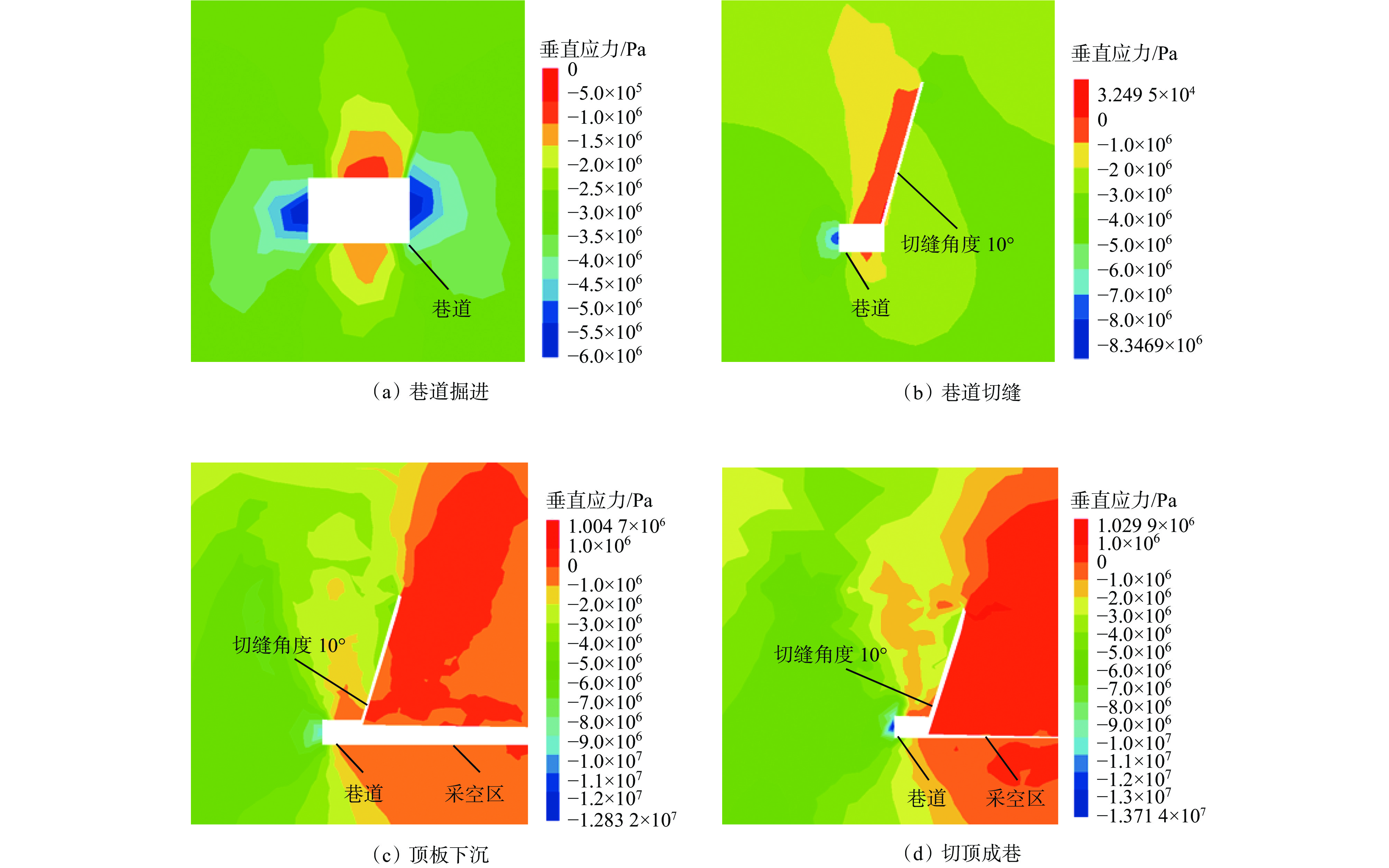
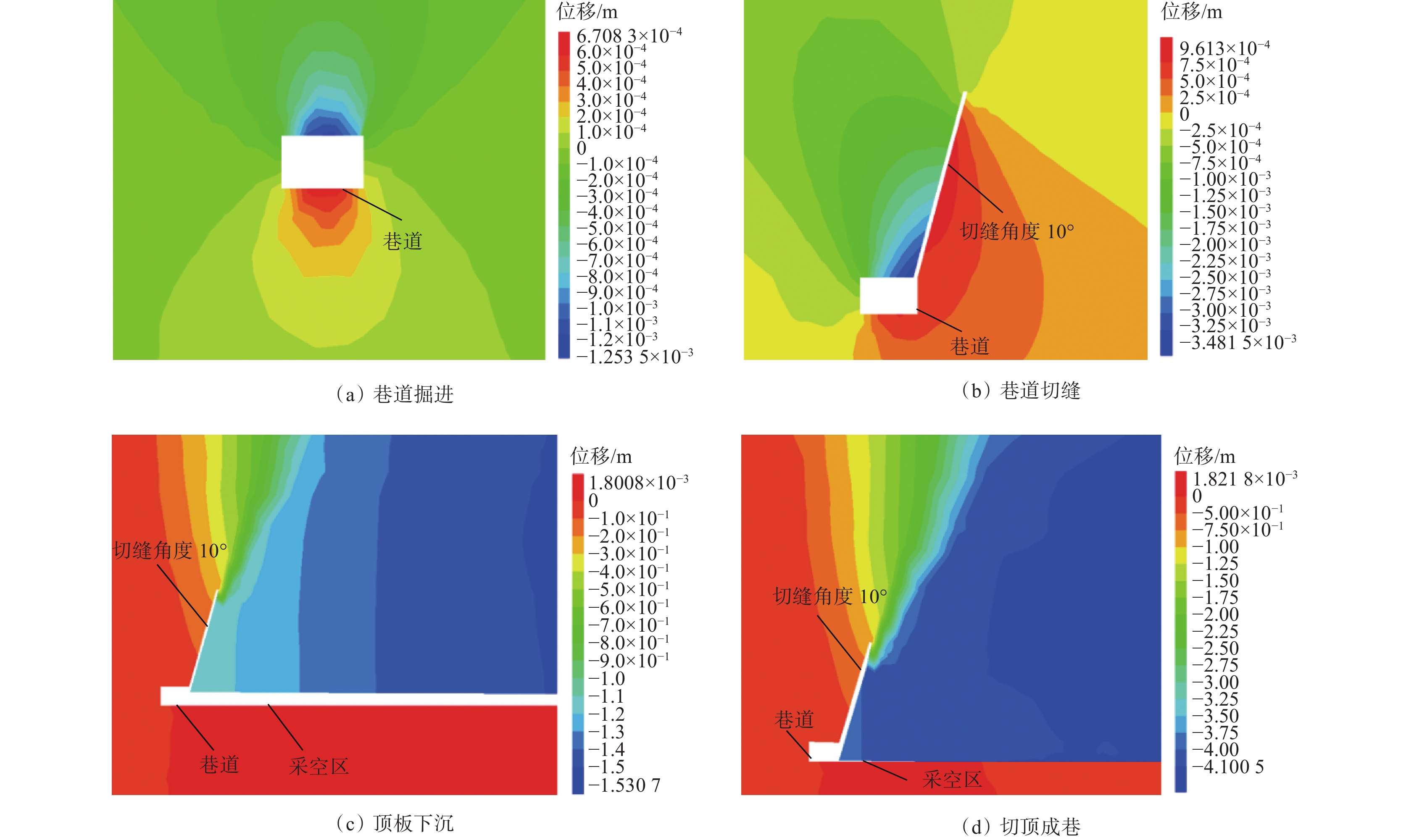
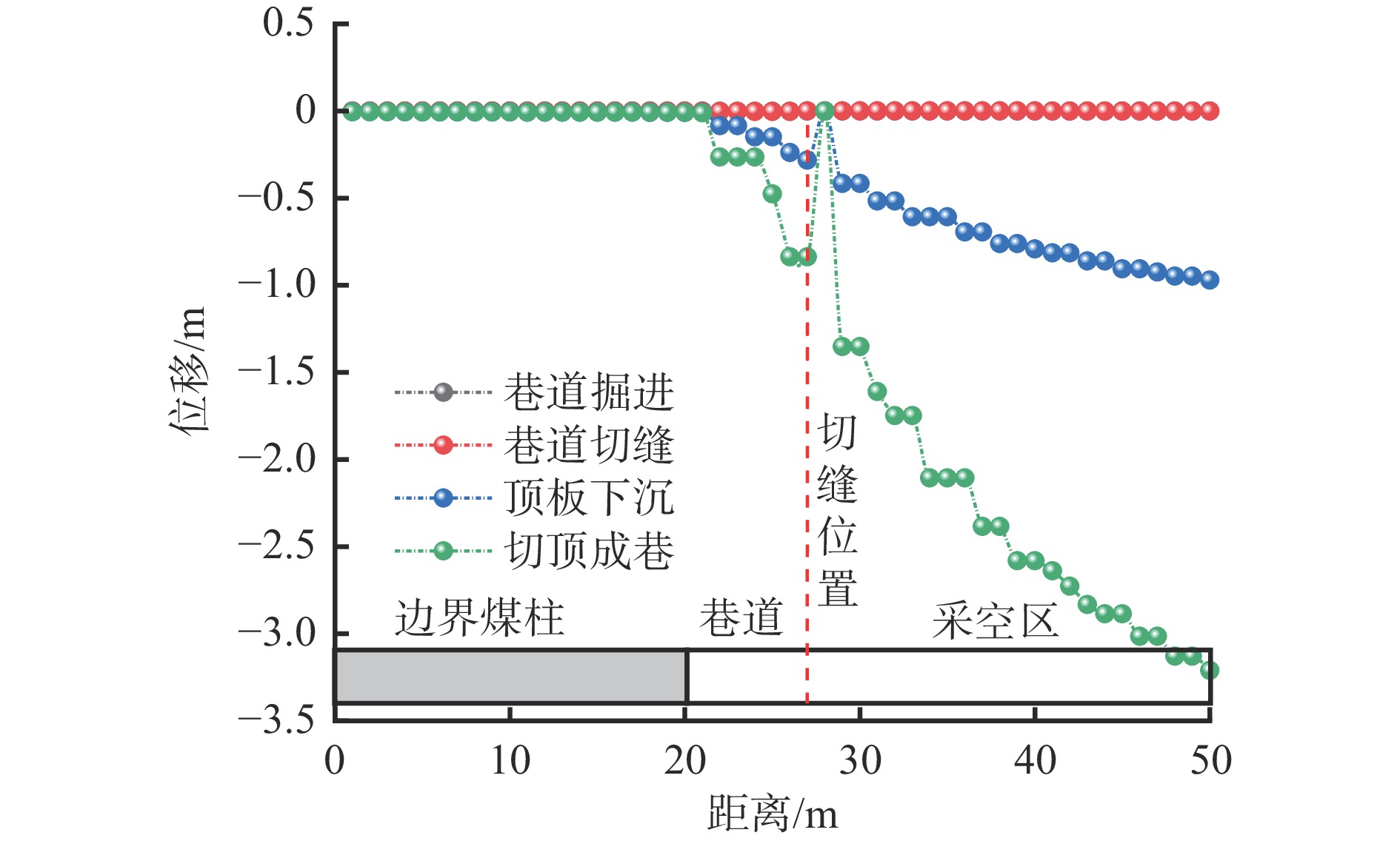
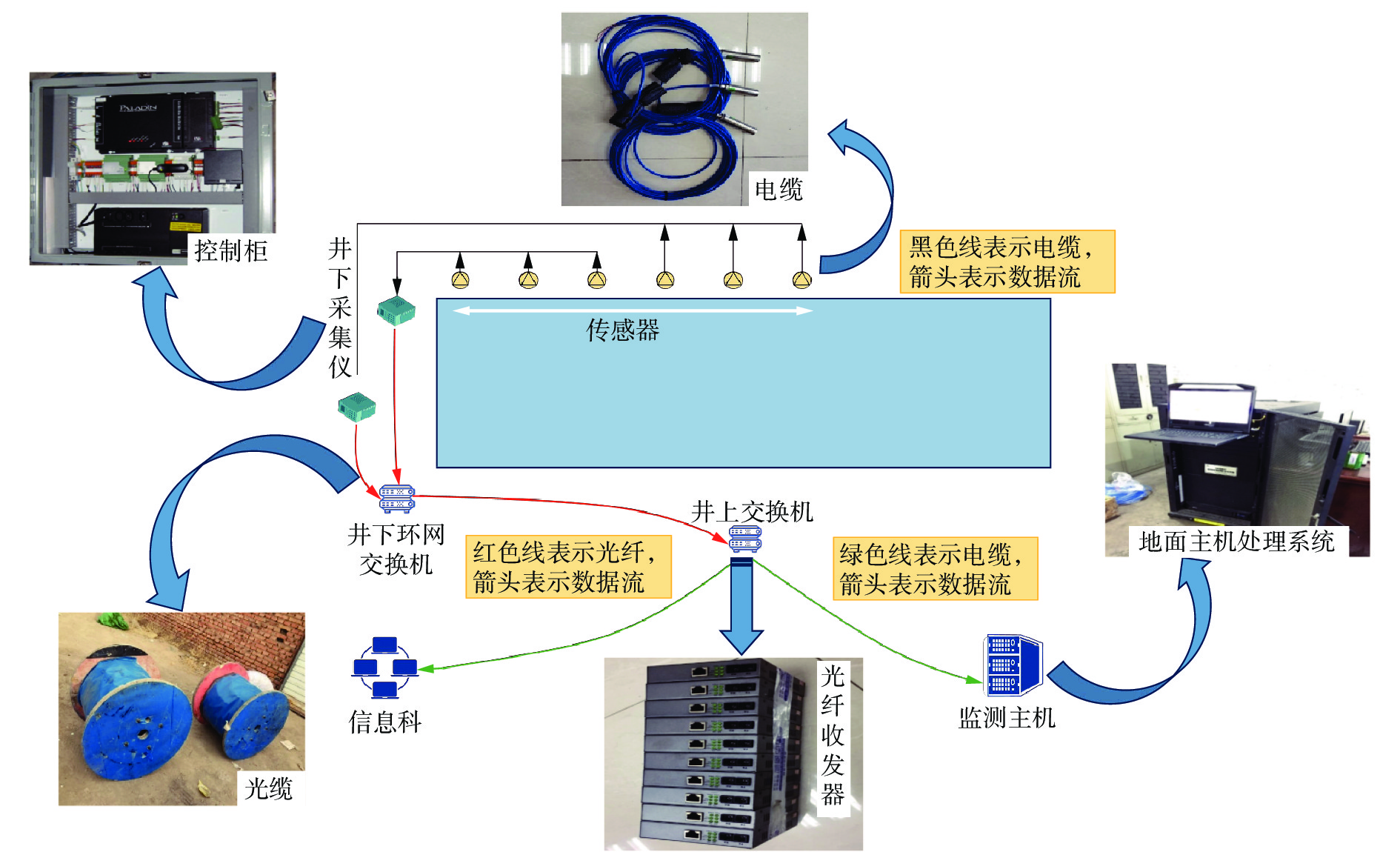
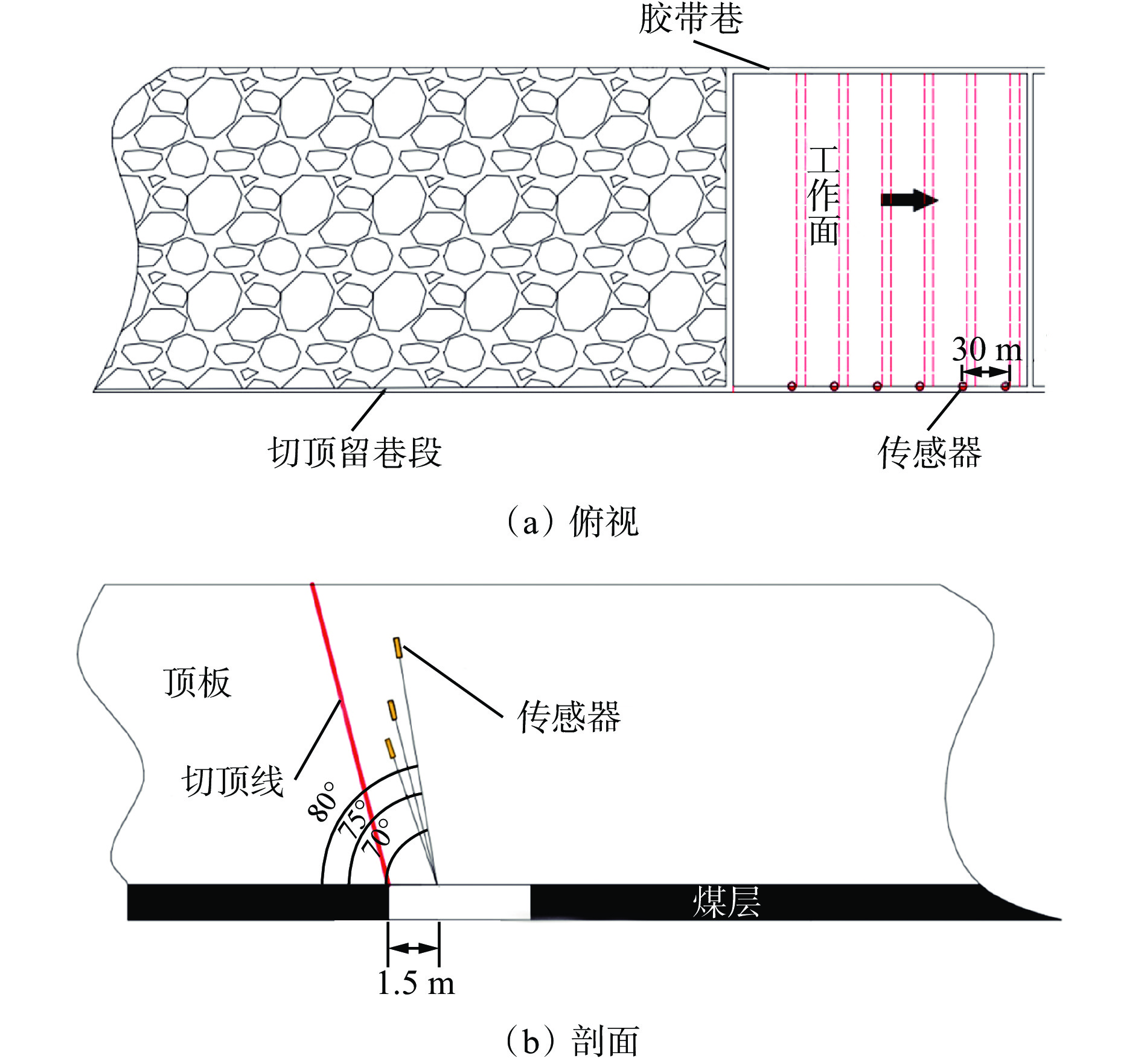
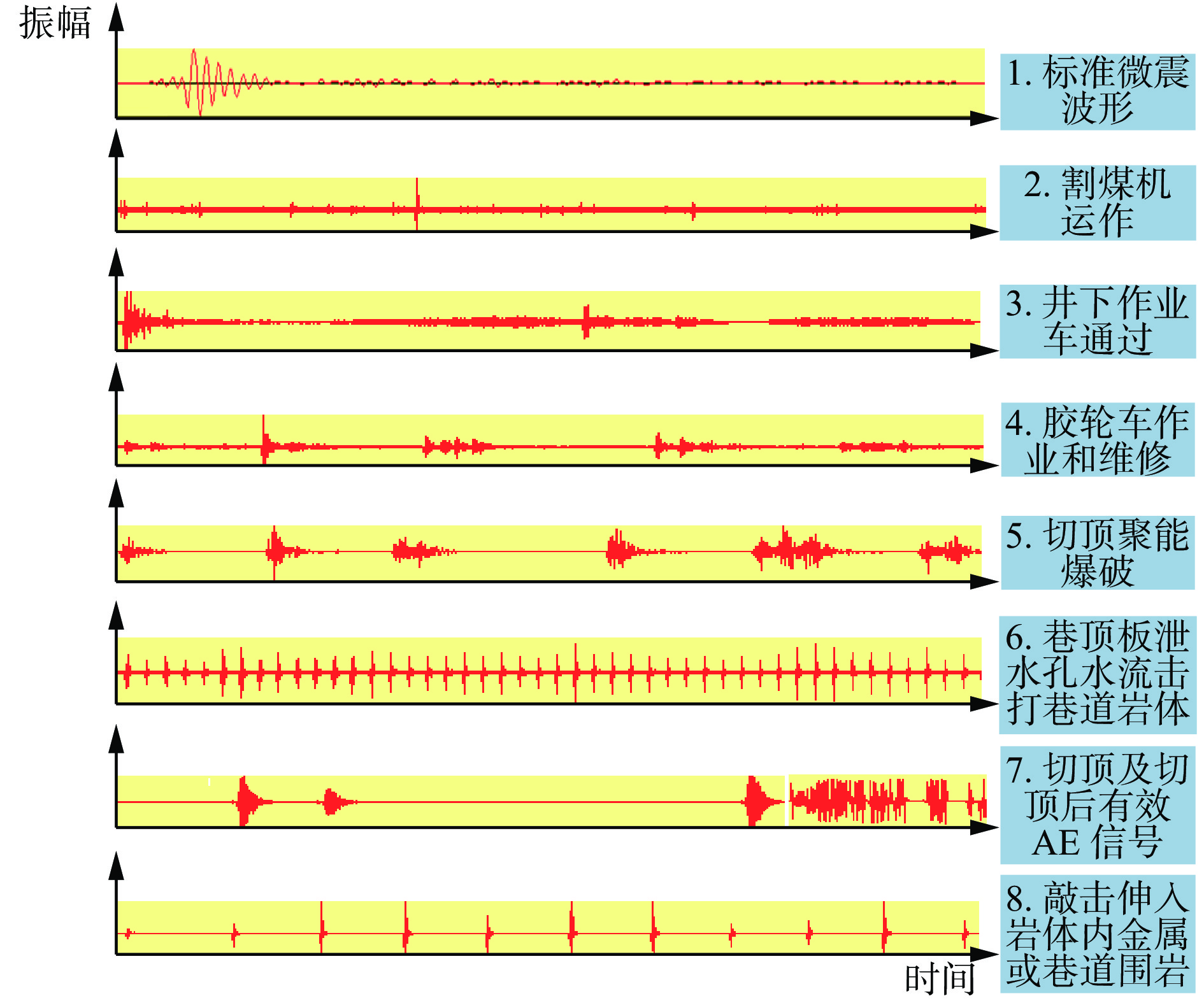
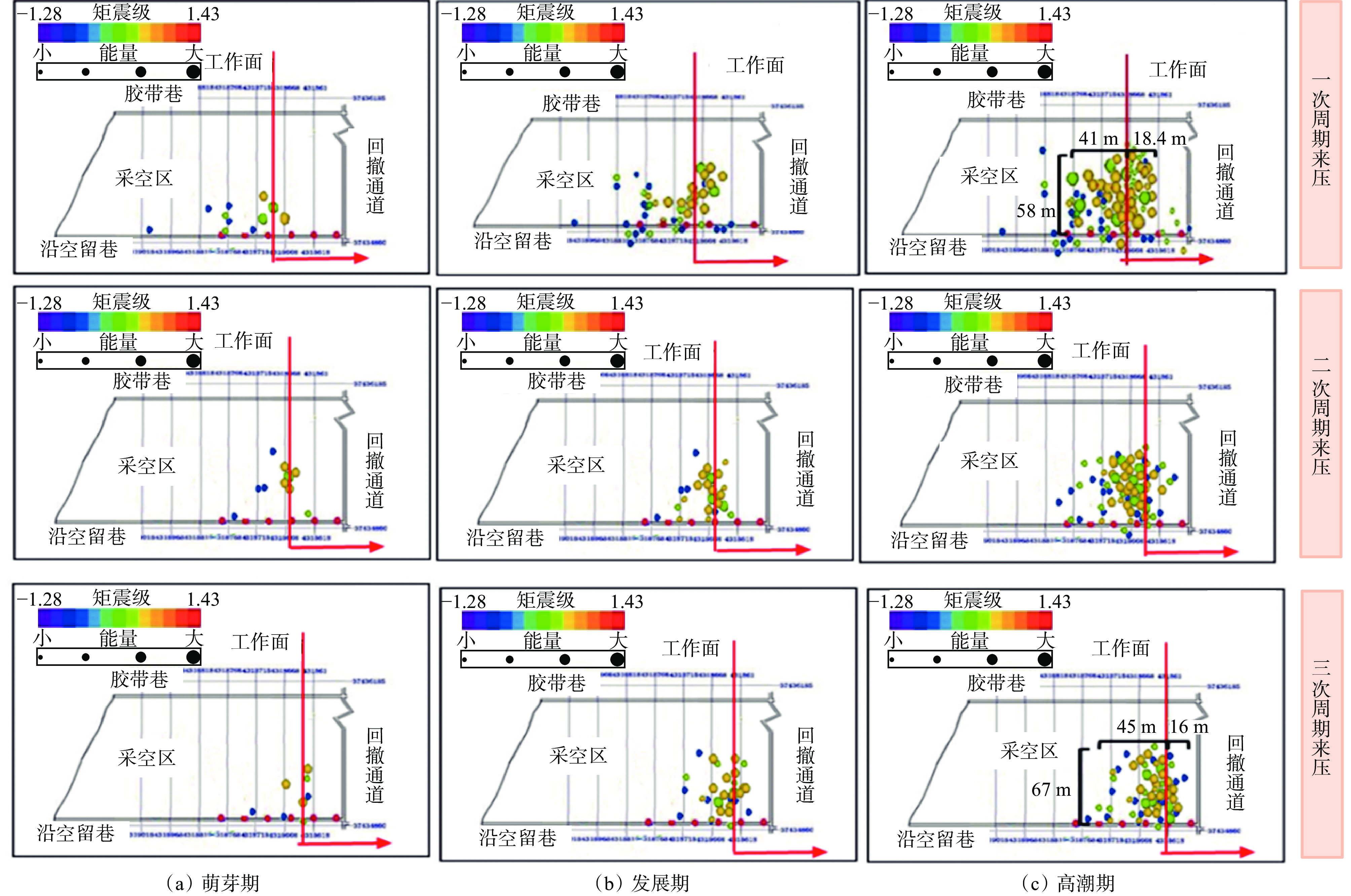
摘要: 为进一步研究无煤柱切顶留巷技术开采后的覆岩破坏规律,以柠条塔煤矿S1201−Ⅱ工作面为工程背景,采用物理相似模拟与数值模拟的研究手段,结合现场微震监测技术建立了微震波形数据库,研究了随工作面持续开采,无煤柱切顶留巷不同阶段的覆岩采动裂隙演化及应力空间展布特征,得出了工作面覆岩周期性破断规律。研究结果表明:工作面发生初次来压时的覆岩裂隙发育高度为57.6 m,切顶前中部裂隙带发育高度为95.5~96.1 m,裂采比为23.8~24.0,边缘侧裂隙发育高度为105.9~106.4 m,裂采比为26.4~26.6。切顶后工作面两侧裂隙带最终发育高度为104.3~105.2 m,裂采比为26.1~26.3,工作面中部裂隙带由于上覆岩层的不断压实弥合,最终发育高度为94.3~95.2 m,裂采比为23.6~23.8。当巷道分别处于掘进、切缝阶段,顶板位移基本没有产生改变;当其进入顶板下沉、切顶成巷阶段,顶板位移不断增大。切顶卸压完成后,巷道侧支承压力峰值增大,表明切缝之后的工作面跨度进一步增大,倾向支承压力不断增大;工作面顶板卸压效果显著,顶板产生大范围应力释放现象。在该工作面布置了微震监测系统,发现微震事件的周期性产生与工作面周期来压有强关联性,其发展过程可划分为萌芽期—发展期—高潮期,进一步综合得出覆岩的周期性破断演化规律。Abstract: In order to further study the failure law of overburden after the mining of non-pillar gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting technology, taking the S1201-II working face of Ningtiaota Coal Mine as the engineering background, physical similarity simulation and numerical simulation research methods are used. Combined with on-site microseismic monitoring technology, a microseismic waveform data library is established. With continuous mining of the working face, the evolution of overburden mining induced cracks and stress spatial distribution features at different stages of non-pillar gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting are studied. The periodic crack law of the overburden in the working face has been obtained. The research results show that the height of the overburden cracks during the initial pressure on the working face is about 57.6 m, the height of the middle crack zone before cutting is 95.5-96.1 m, the crack mining ratio is 23.8-24.0, the height of the edge side cracks is 105.9-106.4 m, and the crack mining ratio is 26.4-26.6 m. After the roof cutting, the final development height of the crack zone on both sides of the working face is about 104.3-105.2 m, with a crack mining ratio of 26.1-26.3. Due to the continuous compaction and closure of the overburden layer, the final development height of the crack zone in the middle of the working face is 94.3-95.2 m, with a crack mining ratio of 23.6-23.8. When the roadways are in the excavation and cutting stages respectively, there is basically no change in the displacement of the roof. When it enters the sinking and roadway formation stage, the displacement value of the roof continuously increases. After the completion of roof cutting and pressure relief, the peak support pressure on the side of the roadway increases, indicating that the span of the working face further increases after the cutting seam, and the inclined support pressure continues to increase. The pressure relief effect of the working face roof is significant, and the roof produces a large-scale stress release phenomenon. A microseismic monitoring system is installed in the working face, and it is found that there is a strong correlation between the periodic occurrence of microseismic events and the periodic pressure of the working face. The development process can be divided into the budding stage, development stage, and climax stage. Further comprehensive analysis can be conducted to obtain the periodic crack evolution law of the overburden.
-
-
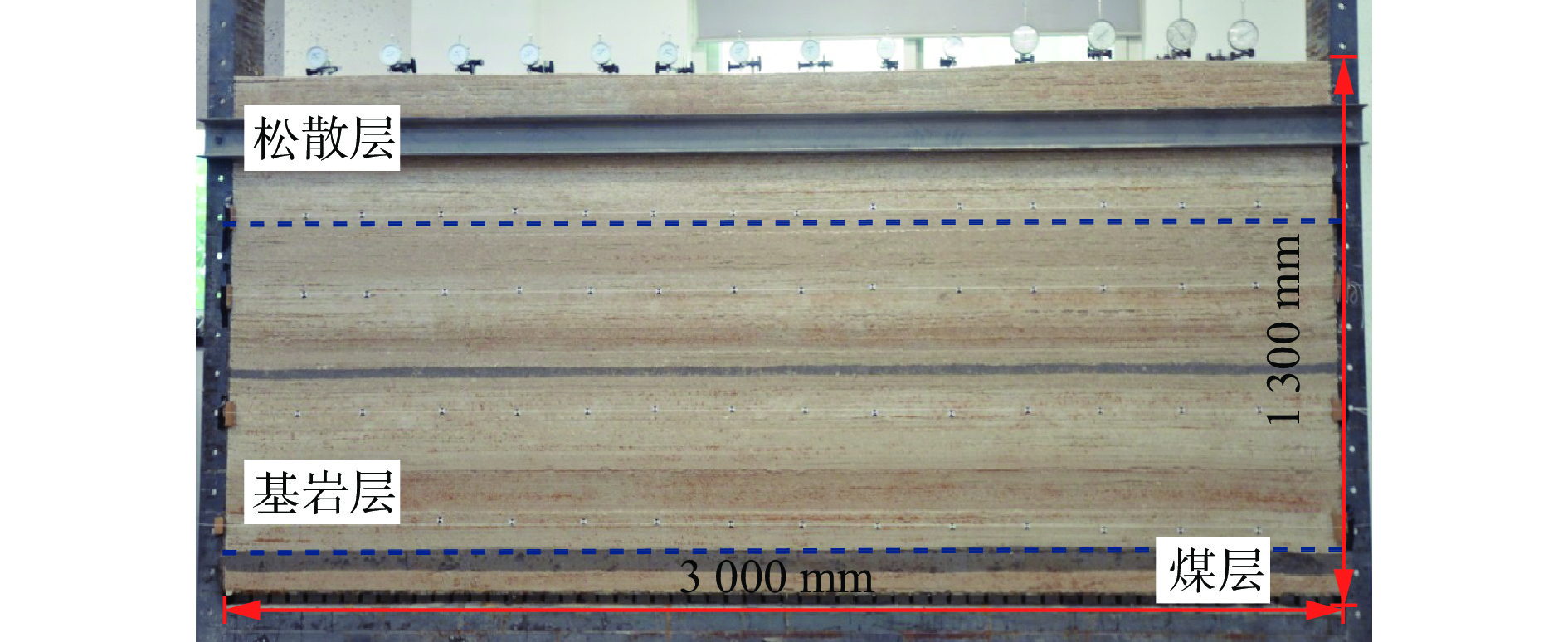
表 1 模拟实验相似材料配比方案
Table 1 Simulation experiment for similar material matching scheme
岩层 厚度/cm 材料质量/kg 河砂 石膏 大白粉 粉煤灰 细粒砂岩 6 8.40 0.48 0.72 — 砂质泥岩 2 8.64 0.29 0.67 — 细粒砂岩 8 8.40 0.48 0.72 — 粗粒砂岩 2 8.64 0.29 0.67 — 粉砂岩 16 8.53 0.21 0.86 — 中粒砂岩 14 8.64 0.29 0.67 — 细粒砂岩 6 8.40 0.48 0.72 — 1−2上煤 3 1.96 0.10 0.49 1.96 粉砂岩 11 8.53 0.21 0.86 — 细粒砂岩 9 8.40 0.48 0.72 — 中粒砂岩 19 8.64 0.29 0.67 — 2−2煤 4 1.96 0.10 0.49 1.96 粉砂岩 16 8.53 0.21 0.86 — 表 2 煤岩体物理力学参数
Table 2 Mechanical parameters of coal and rock
岩石 密度/
(kg·m-3)体积模
量/MPa剪切模
量/MPa抗拉强
度/MPa黏聚
力/MPa内摩擦
角/(°)细砂岩 2 420 4 167 2 869 1.8 3.5 37 中粒砂岩 2 550 3 435 3 876 1.9 3.9 37.5 煤层 1 350 2 381 1 163 0.6 1.3 32.9 粉砂岩 2 530 3 372 3 816 1.7 4.5 20.4 细粒砂岩 2 640 9 302 9 137 2.1 4.2 28 表 3 周期来压步距和周期来压强度统计
Table 3 Statistical of the periodic weighting step and pressure strength
来压时简( 年−月−日) 工作面上端头侧 工作面中部 工作面下端头侧 来压强度/MPa 来压步距/m 来压强度/MPa 来压步距/m 来压强度/MPa 来压步距/m 2018−12−12 29.24 15.0 38.6 17.3 39.2 15.6 2018−12−15 31.6 16.3 36.9 14.8 36.4 17.4 2018−12−17 28.6 15.8 38.6 18.9 37.4 21.3 2018−12−19 29.3 20.3 37.7 26.0 36.5 22.9 2018−12−22 32.6 22.7 37.4 25.0 37.5 23.0 2018−12−24 35.7 24.0 37.5 24.7 38.9 24.7 2018−12−26 39.8 24.8 38.2 23.1 34.9 15.7 2018−12−28 34.7 19.6 38.1 17.0 35.6 21.4 2019−01−02 35.0 15.6 39.5 18.2 36.8 16.9 2019−01−04 37.6 17.0 37.9 18.9 37.6 15.4 2019−01−06 36.4 15.0 36.8 17.3 34.8 15.6 -
[1] 何满潮,宋振骐,王安,等. 长壁开采切顶短壁梁理论及其110工法——第三次矿业科学技术变革[J]. 煤炭科技,2017(1):1-9,13. HE Manchao,SONG Zhenqi,WANG An,et al. Theory of longwall mining by using roof cuting shortwall team and 110 method-the third mining science and technology reform[J]. Coal Science & Technology Magazine,2017(1):1-9,13.
[2] 张国锋,何满潮,俞学平,等. 白皎矿保护层沿空切顶成巷无煤柱开采技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2011,28(4):511-516. ZHANG Guofeng,HE Manchao,YU Xueping,et al. Research on the technique of no-pillar mining with gob-side entry formed by advanced roof caving in the protective seam in Baijiao Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2011,28(4):511-516.
[3] 赵萌烨,黄庆享,朱磊,等. 无煤柱切顶沿空留巷顶板“短砌体—铰接”结构及支撑阻力研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(增刊1):84-93. ZHAO Mengye,HUANG Qingxiang,ZHU Lei,et al. Research on roof structure and support resistance of gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting and non-pillar mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2021,46(S1):84-93.
[4] 华心祝. 我国沿空留巷支护技术发展现状及改进建议[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2006,34(12):78-81. HUA Xinzhu. Development status and improved proposals on gob-side entry retaining support technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2006,34(12):78-81.
[5] 王亚军,何满潮,张科学,等. 无煤柱自成巷开采巷道矿压显现特征及控制对策[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(4):677-685. WANG Yajun,HE Manchao,ZHANG Kexue,et al. Strata behavior characteristics and control countermeasures for the gateroad surroundings in innovative non-pillar mining method with gateroad formed automatically[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2018,35(4):677-685.
[6] 朱珍,何满潮,王琦,等. 柠条塔煤矿自动成巷无煤柱开采新方法[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2019,48(1):46-53. ZHU Zhen,HE Manchao,WANG Qi,et al. An innovative non-pillar mining method for gateroad formation automatically and its application in Ningtiaota Coal Mine[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2019,48(1):46-53.
[7] 何满潮,马资敏,郭志飚,等. 深部中厚煤层切顶留巷关键技术参数研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(3):468-477. HE Manchao,MA Zimin,GUO Zhibiao,et al. Key parameters of the gob-side entry retaining formed by roof cutting and pressure release in deep medium-thickness coal seams[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2018,47(3):468-477.
[8] 迟宝锁,周开放,何满潮,等. 大采高工作面切顶留巷支护参数优化研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(8):128-133. CHI Baosuo,ZHOU Kaifang,HE Manchao,et al. Optimization research on supporting parameters of roof cutting entry retaining with large mining height face[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2017,45(8):128-133.
[9] WANG Qi,HE Manchao,YANG Jun,et al. Study of a no-pillar mining technique with automatically formed gob-side entry retaining for longwall mining in coal mines[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2018,110:1-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.07.005
[10] HE Manchao,GONG Weili,WANG Jiong,et al. Development of a novel energy-absorbing bolt with extraordinarily large elongation and constant resistance[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences. 2014,67:29-42.
[11] 唐文胜,张国锋,刘小强,等. 异形断面短臂梁卸压效应模拟分析[J]. 中国高新技术企业,2016(9):162-163. TANG Wensheng,ZHANG Guofeng,LIU Xiaoqiang,et al. Simulation analysis of pressure relief effect of special short arm beam[J]. China High-Tech Enterprises,2016(9):162-163.
[12] 金龙. 厚煤层综放工作面安全高效开采技术及应用[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2020. JIN Long. Technology and application of safe and efficient mining in fully mechanized caving face of thick coal seam[D]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2020.
[13] 顾有富,王慧芹. 切顶卸压沿空留巷技术在土城矿的应用[J]. 能源与节能,2013(1):6-7. GU Youfu,WANG Huiqin. Application of top cutting pressure-relief gob-side entry retaining technology in Tucheng Mine[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation,2013(1):6-7.
[14] 刘衍利,黎卫兵,黄星源. 切顶卸压爆破技术在沿空留巷中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2014,45(6):132-135. LIU Yanli,LI Weibing,HUANG Xingyuan. The application of roof cutting and pressure relief blasting technology in gob-side entry retaining[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2014,45(6):132-135.
[15] 宋润权,谢家鹏. 切顶卸压技术在工作面及沿空巷道维护中的应用[J]. 煤炭科技,2012(3):52-54. SONG Runquan,XIE Jiapeng. Application of roof cutting and pressure unloading technology in the maintenance of working face and along the empty roadway[J]. Coal Science & Technology Magazine,2012(3):52-54.
[16] 蔡洪林,尹贤坤,汤朝均,等. 切顶卸压沿空留巷无煤柱开采技术研究与应用[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2012,39(5):15-18. CAI Honglin,YIN Xiankun,TANG Chaojun,et al. Research and application of coal pillar mining technology for cutting pressure discharge along the empty lane[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection,2012,39(5):15-18.
[17] 吴海波,赵凯. 微震监测技术在复杂地质煤矿开采优化及顶板控制中的应用[J]. 现代矿业,2023,39(9):14-17,22. WU Haibo,ZHAO Kai. Application of microseismic monitoring technology in mining optimization and roof control of complex geological coal mine[J]. Modern Mining,2023,39(9):14-17,22.
[18] 李浩荡,蓝航,杜涛涛,等. 宽沟煤矿坚硬厚层顶板下冲击地压危险时期的微震特征及解危措施[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(增刊1):6-11. LI Haodang,LAN Hang,DU Taotao,et al. Micro-seismic characteristic and danger-relief method in rock-burst danger period of mining face under hard and thick roof of Kuangou Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2013,38(S1):6-11.
[19] 孔令海,李峰,欧阳振华,等. 采动覆岩裂隙分布特征的微震监测研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(1):109-113,143. KONG Linghai,LI Feng,OUYANG Zhenhua,et al. Study on microseismic monitoring and measuring of fracture distribution features in mining overburden strata[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2016,44(1):109-113,143.
[20] 孔令海,王永仁,李少刚. 房柱采空区下回采工作面覆岩运动规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(5):26-29. KONG Linghai,WANG Yongren,LI Shaogang. Analysis on overburden strata movement law of coal mining face under goaf of room and pillar mining face[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2015,43(5):26-29.
[21] 李鸿昌. 压力的相似模拟实验[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,1988. LI Hongchang. A similar simulation experiment for the pressure[M]. Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology Press,1988.



 下载:
下载: