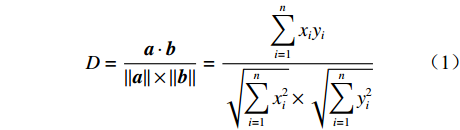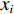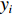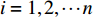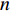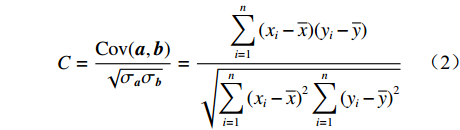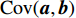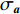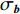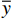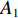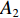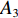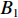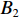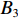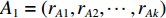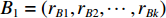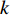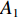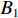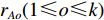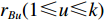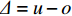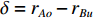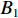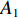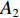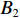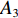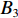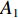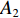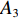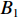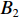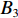Development of coal and rock identification device based on near-infrared spectroscopy
-
摘要: 目前近红外光谱煤岩识别都是在静态下采集光谱数据进行离线识别,无法适应放顶煤作业时需要实时识别输送机上高速移动煤岩的需求。针对该问题,基于近红外光谱技术研制了一种煤岩识别装置。该装置由数据采集与处理装置和光源探头一体化装置组成,通过光源探头一体化装置搜集煤岩反射光,利用数据采集与处理装置中改进的煤岩识别算法(余弦角算法和相关系数法)分析光谱数据,可在获取到煤岩光谱曲线后立即分析光谱信息并判断当前煤岩类别。为得到改进煤岩识别算法最佳特征波段与标准光谱库大小,通过实验得到了不同特征波段和标准光谱库大小对识别准确度的影响:1 300~1 500,1 800~2 000,2 100~2 300 nm特征宽度适用于大多数煤岩样本,标准光谱库大小与正确率正相关,识别时标准光谱库有必要增加曲线数量。为提高煤岩识别装置采集的光谱质量,在实验室模拟了煤岩与光源探头一体化装置的相对运动,探究了不同光谱采集参数对光谱质量的影响规律:积分时间主要参考光源的光照强度,当采集条件较好时积分时间设置为比下限略高5~10 ms最佳;考虑综放工作面对煤岩识别实时性要求高且放煤过程中刮板输送机上煤岩变化较快,积分次数设置为1最佳;平滑次数主要参考环境波动快慢,只需设置为可消除环境光变化即可。为提高煤岩识别装置在工作面煤流运动状态下识别的准确性,探究了改进余弦角算法与相关系数法在煤岩与光源探头一体化装置相对运动中识别的准确性,得到改进相关系数法是更适合在工作面使用的识别算法,正确率达到91.3%。煤矿现场煤岩识别试验结果表明,该装置在采集到1个放煤周期内放落煤岩的光谱曲线后,可通过改进识别算法立即分析光谱信息并准确判断当前煤岩类别,实现了放煤过程中煤岩实时识别。Abstract: The current near-infrared spectroscopy identification of coal and rock is to collect spectral data in a static state for offline identification. The technology cannot meet the need for real-time identification of high-speed moving coal and rock on conveyor during caving operation. In order to solve this problem, a coal and rock identification device is developed based on near-infrared spectroscopy technology. The device consists of a data acquisition and processing device, and a light source and probe integrated device. The light source and probe integrated device is used to collect the reflected light of coal and rock. The improved coal and rock identification algorithms (cosine angle algorithm and correlation coefficient method) in the data acquisition and processing device is used to analyze the spectrum data. The spectrum information can be analyzed immediately after obtaining a coal and rock spectrum curve. Then the current coal and rock type can be determined. In order to obtain the best characteristic band and standard spectral library size of the improved coal and rock identification algorithms, the effects of different characteristic bands and standard spectral library sizes on the identification accuracy are obtained through experiments. The characteristic widths of 1 300 -1 500 nm, 1 800-2 000 nm and 2 100-2 300 nm are suitable for most coal and rock samples. The size of the standard spectral library is positively correlated with the accuracy. It is necessary to increase the number of curves in the standard spectral library during identification. In order to improve the spectral quality collected by the coal and rock identification device, the relative motion of coal and rock and the light source and probe integrated device is simulated in the laboratory. The influence law of different spectral acquisition parameters on spectral quality is explored. The integration time mainly refers to the light intensity of the light source. When the acquisition conditions are good, the integration time should be set to be slightly higher than the lower limit by 5-10 ms. For the fully mechanized top coal caving face, the real-time requirement of coal and rock identification is high, and the coal and rock on the scraper conveyor change rapidly during the coal caving process. The integration number is set to one for the best. The smoothing times mainly refer to the speed of environmental fluctuation, which can be set to eliminate the change of ambient light. In order to improve the identification accuracy of coal and rock identification device in the coal flow movement state of working face, the identification accuracy of improved cosine algorithm and correlation coefficient method in the relative movement of coal and rock and light source and probe integrated device is explored. The improved correlation coefficient method is more suitable for the identification algorithm used in working face, and the accuracy rate is 91.3%. The results of the coal and rock identification test in coal mine show that after collecting the spectral curves of coal and rock in a coal drawing cycle, the device immediately analyzes the spectral information and determines the current coal and rock category by the improved identification algorithm. The device realizes the real-time identification of coal and rock in the coal drawing process.
-
0. 引言
综采放顶煤开采工艺是一种适用于厚煤层与特厚煤层开采的方法,可实现采煤、放煤平行作业,使工作面单产和工效均大幅度提高[1]。进行放煤作业时通常需要根据后部刮板输送机上放落煤岩的状态判断是否“关窗”,何时停止放煤是放煤作业的关键所在。以往都是工人凭借经验并通过视觉和听觉观察放煤口状况,主观判断停止时刻,并手动控制液压支架停止放煤。然而放煤过程中的大量粉尘与工作面高分贝噪声使得依靠人工目测和耳听很难得出准确的判断,常常导致过放和欠放,此外恶劣的环境严重影响工人的安全与身体健康。为了改善这一状况并适应综放工作面智能开采的需求,通过现代传感技术实时感知放煤过程中垮落的煤岩类别,利用客观真实的放煤数据判断“关窗”时刻,是解决放煤过程中资源采出率与煤炭含矸率这一矛盾的关键。目前国内外学者开展了大量煤岩识别技术研究工作,提出了许多识别方法。利用振动技术识别煤岩是应用较多的一种技术,文献[2]通过在放顶煤液压支架尾梁上安装振动传感器采集尾梁振动信号,利用煤矸冲击产生的信号进行煤岩识别。文献[3]采用煤矸识别传感器采集、分析、处理煤块和矸石撞击支架尾梁产生的振动信号,以能量值判断煤块和矸石的下落状态。文献[4]分析了振动信号的时域指标(峰峰值、方差和峰度指数),并根据时域特性识别煤岩。文献[5]基于固定在液压支架尾梁下的振动和声学传感器及信号处理技术,以煤岩冲击液压支架产生的独特振动和声学信号判断煤岩混合状态。但振动技术是通过液压支架间接识别煤岩类别的,不同液压支架振动模态不同,存在适应性不强等问题,不易推广。文献[6-7]根据煤矸不同的放射量确定阈值,进而识别煤岩类别,利用双能γ射线技术确定煤矸混合体中的矸石含量。该技术因不同工作面煤岩放射量不同,无法通过统一的阈值进行判断。文献[8]根据放煤口拍摄的图像,提出了基于图像灰度直方图和灰度均值的综放工作面煤岩性状识别方法。但图像识别方法只能得到煤岩的表面特性,当煤岩在外观上相似度较高时无法进行准确识别。为此,亟需引入一种能够通过煤岩物质成分进行煤岩识别的技术。
研究人员将光谱技术引入煤岩识别领域。近红外光谱属于分子振动光谱的倍频和主频吸收光谱[9-13],物质的反射和吸收光谱特征能够反映物质组成成分和结构等,是不同物质的“指纹”[14-15],能够从成分层面对物质进行识别,为煤岩识别提供了可能。文献[16-17]利用特征工程分别建立了辽宁铁法矿区与山西塔山矿区煤岩的光谱特征,并基于特征阈值进行煤岩分类。虽然通过人为观察光谱曲线而构建的特征针对性强,但对煤岩曲线多变的工况适应性较差,设置的阈值可能只适用于特定煤矿。文献[18-20]利用无监督的余弦角算法与相关系数法对不同矿区煤岩光谱进行识别。无监督识别算法虽然可以度量2个向量方向与长度的一致性,但是2个向量必须有相同的维度,且无法适应横向偏差。文献[21-23]利用近红外光谱建立随机森林等机器学习与宽度学习系统等深度学习分类算法辨别煤岩。基于深度学习的算法识别准确性高,但计算量大,单次识别时间长。以上这些研究都是在静态下采集光谱数据,然后进行离线识别,无法适应放顶煤作业时需要实时识别输送机上高速移动煤岩的需求。
本文基于近红外光谱技术研制了一种煤岩识别装置,该装置由数据采集与处理装置和光源探头一体化装置2个部分组成,通过光源探头一体化装置搜集煤岩反射光,利用数据采集与处理装置分析光谱数据,通过改进的煤岩识别算法,可在获取到煤岩光谱曲线后立即分析光谱信息并判断当前煤岩类别。实验结果证明了该装置在现场使用的可行性。
1. 煤岩识别装置研制
1.1 硬件系统
煤岩识别装置硬件组成如图1所示。数据采集与处理装置主要由嵌入式工控机、近红外光谱仪、继电器等组成。光源探头一体化装置由光源、准直镜头组成。嵌入式工控机配备Intel Cherry Trail Z8350四核处理器、4 GB DDR3内存和256 GB固态硬盘;近红外光谱仪采用AvaSpec−NIR512−2.5−HSC−EVO光谱仪,共有512个像元探测器,测量波长范围为1 000~2 500 nm,光谱分辨率为3.2 nm,杂散光小于1.0%,可将反射光转换为光谱数据。光源功率为400 W,波长范围为350~2 500 nm,光源通过角度调节可在距离光源0.7 m处汇聚成直径为65 mm的光斑。准直镜头的发射角为0.12°,可搜集距光源0.7 m处、直径为40 mm圆形区域内的反射光。继电器用于嵌入式工控机控制光源启停。煤岩识别装置的工作过程:嵌入式工控机控制光源照射到待测煤岩,准直镜头搜集待测煤岩的反射光,并经光纤传输到近红外光谱仪。近红外光谱仪将光信号转换为光谱数据并传输到嵌入式工控机。嵌入式工控机利用煤岩识别算法对得到的光谱数据进行处理,判断当前煤岩类别,并存储光谱曲线。
1.2 软件系统
煤岩识别装置识别流程如图2所示,主要包括3个步骤:光谱采集、煤岩识别和光谱存储。首先预设3个光谱采集参数,分别为积分时间(单次扫描时近红外光谱仪探测器暴露在光中的时间)、积分次数(形成单条光谱所需的扫描次数)与平滑次数(相邻像素取平均的窗口大小),获取缓存在近红外光谱仪中转换完成的波长及相应的辐射照度。然后判断是否已经获取校对数据,如果没有则完成黑校对(暗条件下的辐射照度)与白校对(光源完全反射的辐射照度),利用校对数据计算全反射光谱数据并在识别界面(图3)上显示。利用选择的煤岩识别算法结合标准光谱库中的光谱曲线,对比实时光谱曲线与标准光谱库中的光谱曲线,从而判别煤岩类别,并在界面输出识别结果。装置运行过程中会将采集的原始数据保存在数据库中,便于后续对装置结构与算法进行进一步优化。
1.2.1 标准光谱库
为实现无监督的煤岩识别算法,需要建立标准光谱库,通过计算实时光谱与标准光谱库中所有光谱的相似度,对比得到相似度最高值对应的标准光谱曲线,以该条标准光谱曲线对应的煤岩类别确定实时光谱所属的煤岩类别。为此从工作面获取了不同的煤岩试样创建标准光谱库,煤岩类型、外观特征、分布位置见表1,表1中包含了形态各异的烟煤试样与不同种类的岩石试样。从所有试样中选择其中26个最具代表性的煤岩,它们能够表征其余同类别试样的基本特征,采集它们的光谱曲线存储于标准光谱库中,结果如图4所示,其中煤炭11条、岩石15条。近红外光谱仪在边缘波段电流噪声较大,处理时只选取1 100~2 400 nm波段内数据。
表 1 煤岩类型、外观、分布Table 1. Type, appearance and distribution of coal and rock序号 样本类型 外观特征 分布位置 1 烟煤 灰黑色,密度较大,不易破碎 煤层 2 烟煤 亮黑色,分层结构明显,质地较坚硬 煤层 3 烟煤 暗黑色,条带状结构,局部有反光性 煤层 4 烟煤 暗黑色,层状结构,断口参差状 煤层 5 烟煤 暗黑色,质地较坚硬,易破碎 煤层 6 灰黑色炭
质泥岩深灰泛黑色,层理结构不明显,
粒径较小,易破碎煤层夹矸 7 灰白色高岭
质泥岩浅灰泛白色,断口光滑,硬度较高 煤层夹矸 8 深灰色砂
质泥岩深灰色,层理结构明显,易破碎,
透水性差煤层夹矸 9 深黑色炭
质泥岩整体呈深黑色,层理结构不明显,
致密块状,较坚硬直接顶 10 白色粉砂岩 断面呈白色,粗糙且有砂质感,
性脆,层理结构不明显,砂砾黏结性差直接顶 1.2.2 识别算法
本文采用余弦角算法和相关系数法进行煤岩识别,比较并选择2种算法中煤岩识别效果较好的方法推广到现场。余弦角算法是用向量空间中2个向量夹角的余弦值作为衡量2个向量间差异大小的度量[24],计算得到的广义余弦值越大,2条光谱的相似度越高。其计算公式为
$$ D = \frac{{\boldsymbol{a} \cdot \boldsymbol{b}}}{{||\boldsymbol{a}|| \times ||\boldsymbol{b}||}} = \frac{{\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n { {{x_i} {y_i}} } }}{{\sqrt {\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{ x_i^2}} } \times \sqrt {\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{ y_i^2}} } }} $$ (1) 式中:
$D$ 为2条光谱的广义余弦值;a,b分别为实时光谱向量和标准光谱向量;${x_i}$ 和${y_i}$ 分别为实时光谱向量和标准光谱向量第i ($i = 1,2, \cdots n$ ,$n$ 为波长数)个波长点处的反射率。相关系数法是用皮尔逊相关系数表示2个向量的相似度[21],计算公式为
$$ C = \frac{{{\rm{Cov}}({\boldsymbol{a}},{\boldsymbol{b}})}}{{\sqrt {{\sigma _{\boldsymbol{a}}}{\sigma _{\boldsymbol{b}}}} }} = \frac{{\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {({x_i} - \overline x )({y_i} - \overline y )} }}{{\sqrt {\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - \overline x )}^2}\displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({y_i} - \overline y )}^2}} } } }} $$ (2) 式中:
$C$ 为2条光谱的皮尔逊相关系数;${\rm{Cov}}({\boldsymbol{a}},{\boldsymbol{b}})$ 为实时光谱向量和标准光谱向量的协方差函数$ ; $ ${\sigma _{{\boldsymbol{a}}}}$ ,${\sigma _{\boldsymbol{b}}}$ 和$\overline x$ ,$\overline y$ 分别为实时光谱向量和标准光谱向量的标准差与均值。皮尔逊相关系数
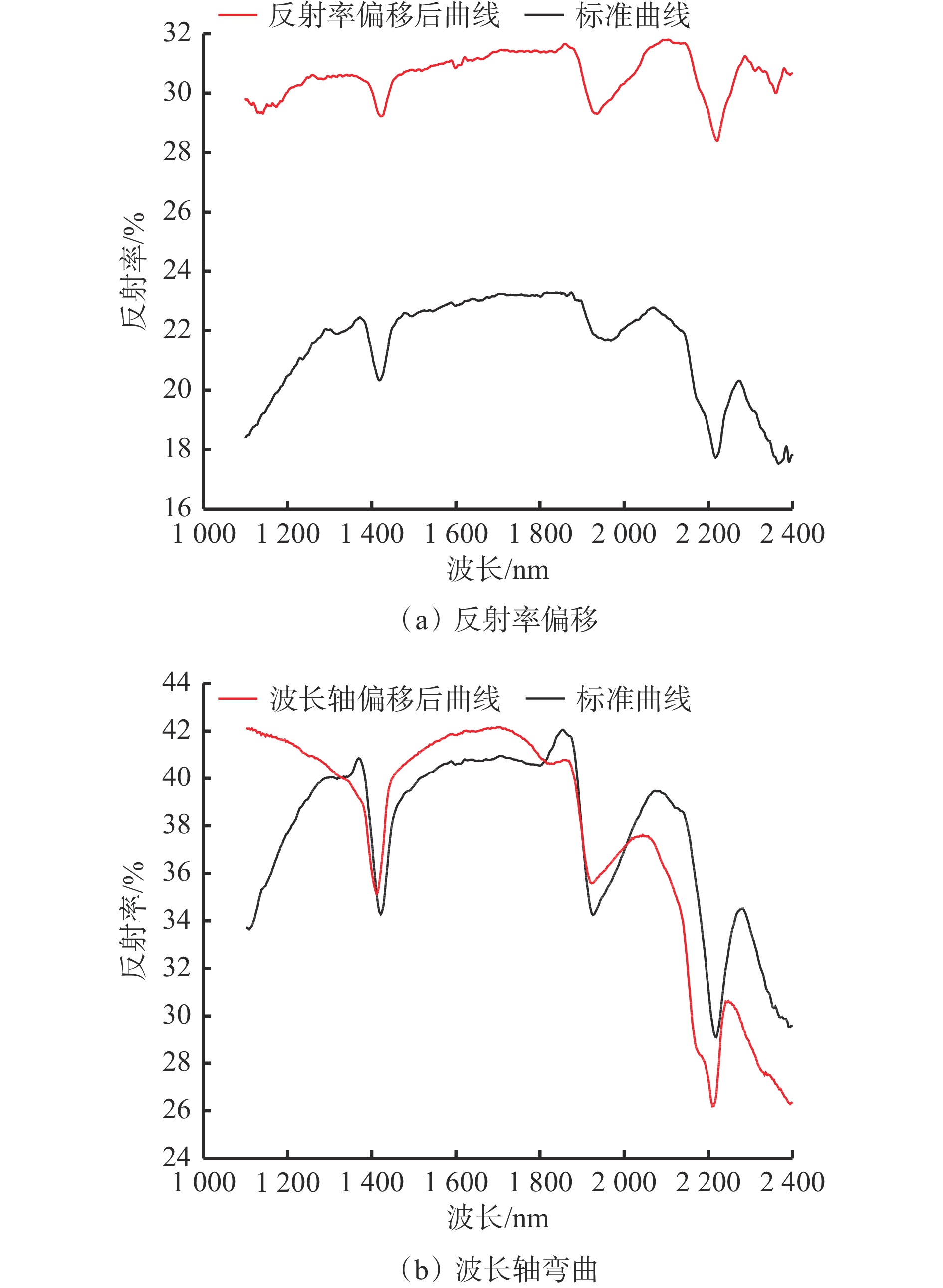
$C$ 为在−1.0~1.0,越接近0则相关性越低,靠近1或者−1相关性强。由于光谱采集时环境参数、光源寿命等都会对采集的光谱产生影响,会出现反射率偏移和波长轴弯曲的情况。反射率偏移是指相同种类煤岩在不同测量条件下波形相似但水平基线偏移。波长轴弯曲是指同种煤岩波形发生横向移动导致波谷之间不能完全对齐。为提高波形的关联性及识别的准确性,需要在降维的同时对细节误差进行修复。光谱波形的形变如图5所示。
从余弦角算法和相关系数法(式(1)和式(2))可看出,待比较的2个光谱向量波长数必须相同,如果同一种煤岩类别的光谱向量,其特征吸收谷不在同一个波长位置处,则这种度量方式将无法得到2个光谱向量形态的相似性。为解决上述问题,提高煤岩识别的准确性,对煤岩识别算法进行改进。改进算法本质上不改变最终计算形态相似性的方法,在计算形态相似性之前对比较的向量进行少量偏移,增大特征吸收谷处的重叠区域。改进算法在不同步骤所形成的光谱如图6所示。可看出改进算法识别后的标准光谱与实时采集光谱在特征吸收谷处重叠区域更多,为随后的计算打下了很好的基础。
具体计算过程如下:获取实时光谱与标准光谱库中任一光谱,对比前先进行分段插值,将原始光谱特征分为3段(1 400,1 900,2 200 nm附近),由于实际情况中光谱波长轴弯曲度为1~5 nm,有略小于光谱分辨率3.2 nm的部分,因此,对3段光谱数据分别进行线性插值,调整波长的分度值为1 nm,实时光谱分段后的3段数据分别记作
$A_1$ ,$A_2$ ,$A_3$ ,标准光谱库中用于对比的光谱分段后的3段数据分别记作$B_1$ ,$B_2$ ,$B_3$ 。设$A_1 = ({r_{A1}},{r_{A2}}, \cdots, {r_{Ak}})$ ,$B_1 = ({r_{B1}},{r_{B2}}, \cdots, {r_{Bk}})$ ($k$ 为分段后该段波形的维数)。对$A_1$ 和$B_1$ 进行搜索,找出其中最小值$ {r_{Ao}}(1 \leqslant o \leqslant k) $ 和${r_{Bu}}(1 \leqslant u \leqslant k)$ 。计算波长轴弯曲度$\varDelta = u - o$ ,将$B_1$ 循环移位$\varDelta$ 位,确保$A_1$ 与$B_1$ 中的最小值对应波长相同,然后将$B_1$ 中的所有数据减去$A_1 $ ,$B_1 $ 最小值的差值$\delta = {r_{Ao}} - {r_{Bu}}$ ,使$B_1$ 与$A_1$ 的最小值经偏移后相同,调整其水平基线在同一高度。对$A_2$ 与$B_2 $ 、$A_3$ 与$B_3 $ 做同样计算,随后将$A_1$ ,$A_2$ ,$A_3$ 及$B_1$ ,$B_2$ ,$B_3$ 分别合并为$\tilde A$ 和$\tilde B$ ,用余弦角算法或相关系数法依次计算出实时光谱与标准光谱库中所有标准光谱的余弦值或皮尔逊相关系数,排序找出最大余弦值或皮尔逊相关系数对应的标准光谱库中的光谱,该条光谱对应的煤岩类别即为当前光照区域内的煤岩类别。为验证改进算法的识别效果,利用煤岩识别装置采集不同试样光谱曲线,试样的类型、外观特征、分布位置与表1相同,得到如图7所示的102条光谱曲线,其中煤炭36条、岩石66条,分别用未改进与改进的识别算法对光谱曲线进行识别。
未改进与改进识别算法识别正确率见表2,可看出未改进识别算法误分波形概率较高,原因是余弦角算法与相关系数法识别时都必须维数相同且存在一一对应关系,受向量平移影响较大,波长轴弯曲会大幅降低正确率;改进算法正确率明显高于未改进算法,误分波形比例降低。
表 2 未改进算法与改进算法识别正确率比较Table 2. Identification accuracy comparison between unimproved algorithm and improved algorithm算法 余弦角算法 相关系数法 改进余弦角算法 改进相关系数法 正确率/% 72.55 77.45 95.1 95.1 为进一步提高识别算法的准确性,通过设置不同的识别波段与标准光谱库大小进行识别,确定最优的算法参数。
(1) 识别波段。不同的岩种在1 400,1 900,2 200 nm 附近形成的吸收谷宽度不同,因此,不同特征提取宽度也将影响识别正确率。为验证特征宽度对识别正确率的影响,分别采用波段1(1 250~1 550,1 750~2 050,2 050~2 350 nm),波段2(1 300~1 500,1 800~2 000,2 100~2 300 nm),波段3(1 350~1 450,1 850~1 950,2 150~2 250 nm)这3种宽度形式,用2种算法识别图7中的曲线,标准光谱库大小为26,试验结果见表3。
表 3 不同特征提取宽度下识别结果比较Table 3. Identification results comparison under different feature extraction width识别波段 标准光谱库大小/条 正确率/% 煤 岩 余弦角
算法相关系
数法波段1 11 15 93.12 87.25 波段2 11 15 96.08 94.12 波段3 11 15 93.14 93.14 结合表3与图7可看出,对于波段1,由于特征分布较分散并受近红外光谱仪性能影响,在曲线两端对光接收效果较差,造成信噪比较低而降低识别准确性;波段3虽然特征集中,提高了准确率,但是特征区域单一,对特征模糊的岩石识别易出现偏差;波段2的宽度适合于大多数煤岩样本,在该波段识别准确率最高,它兼顾了特征的分布特性与数据降维程度。
(2) 标准光谱库大小。标准光谱库中不同种类光谱的数量同样影响识别的准确性,但更多的光谱将降低识别的实时性,为探究标准光谱库大小对识别时间和正确率的影响,在2种识别算法下用4,13,20,26这4种不同大小的标准光谱库,以1 300~1 500,1 800~2 000,2 100~2 300 nm组合波段的形式识别图7中的光谱曲线,试验结果见表4。
表 4 不同大小标准光谱库识别结果比较Table 4. Identification results comparison of different sizes standard spectral library标准光谱库
大小/条不同种类条数 识别时间/s 正确率/% 煤 岩 余弦角算法 相关系数法 4 2 2 0.33 53.92 44.12 13 5 8 0.35 95.10 81.37 20 8 12 0.38 96.08 83.33 26 11 15 0.42 96.08 94.12 从表4可看出,标准光谱库大小与识别正确率正相关,由于图7中光谱曲线的煤岩种类较多,吸收谷宽度不同,当标准光谱库较小时,其他种类煤岩曲线会与当前曲线匹配得到最大值。识别时间对标准光谱库大小不敏感,增加标准光谱库中光谱数量对实时性影响不大。在实际应用中受多种因素影响,光谱变化较大,因此有必要增加标准光谱库中光谱曲线数量。为实现在较短时间内得到较高的准确性,标准光谱库大小为26比较合适。
2. 实验与测试
2.1 实验室实验
2.1.1 光谱采集参数确定
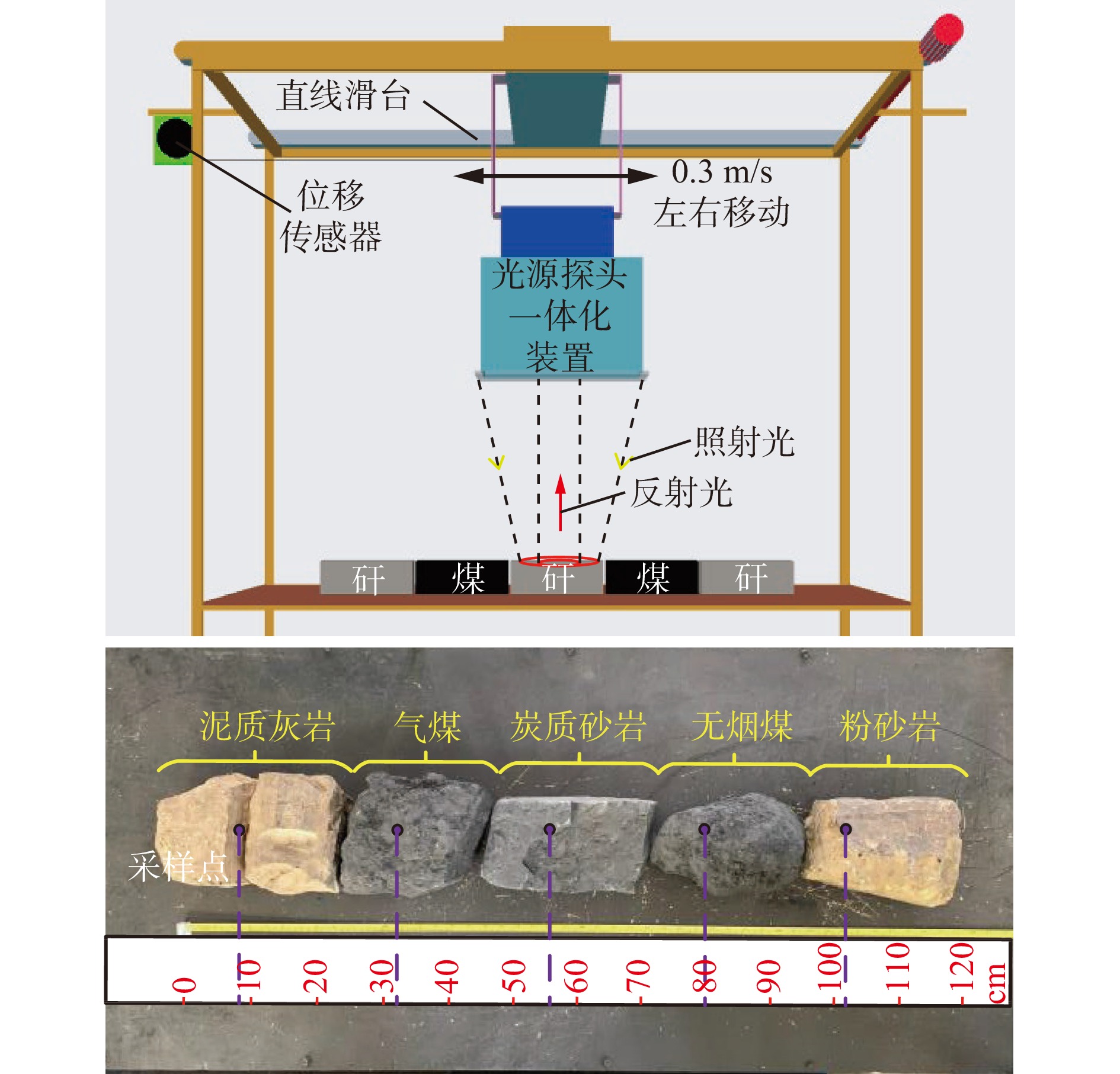
不同的光谱采集参数对于光谱质量有很大的影响,为了探究该影响规律,在实验室搭建了模拟试验台。为使最终光谱采集参数更具有泛化性,选择了5种能基本表征不同煤岩大类的试样:泥质灰岩、气煤、炭质砂岩、无烟煤和粉砂岩。模拟试验台与煤岩摆放实物如图8所示,模拟试验台采用滑台移动光源的方式,通过数控程序控制光源在样本上方0.6 m处以0.3 m/s的速度左右移动;采用直线滑台的电动机编码器检测光源移动距离,平台上间隔放置煤岩样本。
设置采集参数如下:采样积分时间为30 ms,积分次数为4,平滑次数为3。在每个煤岩试样上分别选择1个采样点,各采样点位置如图8所示,分别在90,330,560,800,1 020 mm。由于采集时光源是从左往右移动,为了使采集区域位于每种试样中心,采样点设置偏向于每种试样的左侧。实验时分别改变积分时间、积分次数、平滑次数,观察光谱曲线变化,并采用余弦角算法识别,光谱曲线上有●表示识别结果正确,有▲表示识别结果错误。
不同积分时间下获取的光谱曲线如图9所示。可看出积分时间为5 ms时,每个点采集的光谱曲线都不平滑,波动比较严重,吸收谷特别不明显,甚至被噪声覆盖,识别算法对积分时间为5 ms下的光谱数据无法准确判断。积分时间为30 ms时,每个点采集的光谱与预设点处相同,除炭质砂岩外,其他试样的吸收峰比较明显,炭质砂岩区域光谱曲线吸收谷非常弱,与煤炭在该段波长处的光谱曲线非常相似。积分时间为75 ms时,光谱曲线吸收谷特征有所减弱,此时近红外光谱仪已经接近饱和,无法吸收更多的光子。
积分时间越长,同一波长下获得的辐射照度越大,动态下采集距离变长,积分时间是5,30,75 ms时,实际采集距离分别为3,18,45 mm,实际采集距离是预设点之后的一段区域。积分时间增加导致探测区域增大,由于探测煤岩样本并不是均质且表面有高低变化,探测距离的增大会引入更多的噪声,进一步降低光谱数据的信噪比。动态采集中积分时间主要参考光源的光照强度,当光照强度较大时,可设置的积分时间最小值较小,但可设的最大值也较低。本实验中设置积分时间下限为10 ms,上限为75 ms。当低于下限或超过上限会出现波形丧失的情况,因此,煤岩识别装置安装位置处光照条件较好时,为实现更佳的识别效果和更好的实时性,积分时间设置为比下限略高5~10 ms最佳。
不同积分次数下获取的光谱曲线如图10所示。可看出积分次数为1时,各采集点得到的光谱曲线质量都很好,岩石的吸收谷明显且深度较大,各条曲线都能够正确识别。积分次数为3时,部分光谱曲线出现异变,炭质砂岩识别错误。积分次数为9时,岩石光谱曲线吸收谷略微变浅,识别准确性下降。积分是为了减少偶然变化影响,取多条光谱进行平均,因此动态采集过程中,积分次数越多,则采集距离越长。积分次数在1,3,9下采集距离分别是6,18,54 mm。采集距离增大同样会引入更多的噪声,进一步降低光谱数据的信噪比。综放工作面对煤岩识别的实时性要求高,且放煤过程中煤流速度较快,为提高煤岩识别装置识别频率,积分次数应越少越好,设置为1最佳。
不同平滑次数下获取的光谱曲线如图11所示。可看出平滑次数为0时,曲线全波段有细微锯齿状,但吸收谷明显,预设点处采集的煤岩光谱曲线基本能正确识别;平滑次数为3时的曲线明显优于0时,曲线上没有锯齿状波动,但在光谱特征不明显的炭质砂岩区域,本该是岩石的光谱曲线吸收谷消失;平滑次数为8时,由于平滑次数过大,吸收谷被当作噪声平滑掉一部分,但仍可进行正确的识别。
设置平滑次数是因为环境光、暗背景并非恒定不变,采集过程中环境光的改变会使曲线出现细微锯齿状,通过平滑可以消除锯齿。平滑次数并不影响曲线的采集距离。图11中平滑次数为0时得到的光谱曲线信噪比较低,平滑次数为3时光谱曲线质量更好。平滑次数主要参考环境波动快慢,只需设置为可消除环境光变化即可,过多的平滑次数会模糊吸收谷,降低识别的正确性。
2.1.2 动态下识别算法检验
选择表1中的不同样本顺序布置于试验台上,让光源探头一体化装置相对于煤岩试样以0.4 m/s的速度不断移动,动态采集煤岩光谱曲线,如图12所示,总计46条光谱曲线。利用改进的识别算法对采集到的光谱曲线进行识别,结果见表5。可看出余弦角算法在动态识别下正确率大幅下降,而相关系数法则能维持在较高的水平,原因可能是动态移动下采集的光谱特征被减弱,而相关系数法可消除量纲的特点起到了放大特征的作用。因此,综合考虑识别算法静态和动态识别特性,当将煤岩识别装置部署于工作面时,采用改进相关系数法。
表 5 动态采集下煤岩识别正确率Table 5. Accuracy of coal and rock identification under dynamic acquisition算法 改进余弦角算法 改进相关系数法 正确率/% 56.52 91.3 2.2 现场测试
2.2.1 煤岩识别装置现场安装
为验证该煤岩识别装置现场使用的可行性,选择在山西大同市某煤矿综放工作面进行现场试验。该综放工作面平均走向长为2 644.5 m,倾向长为230.5 m,煤层厚度为8.17~29.21 m,平均煤层厚度为15.76 m。煤为黑色、半亮型煤,煤层中含夹矸2~17 层,单层厚度为0.05~0.82 m,夹矸岩性多为炭质泥岩、高岭岩、粉砂岩等。煤岩识别装置样机如图13所示,装置现场安装如图14所示,将光源探头一体化装置安装于端头支架外侧,安装时光源照射方向垂直向下,使探照区域落在输送带的中线上,数据采集与处理装置放置于1号液压支架立柱间。光源探头一体化装置和数据采集与处理装置之间连接的电源线与光纤通过液压管道卡槽固定。
2.2.2 测试结果与分析
利用煤岩识别装置采集完整放煤过程中放落煤岩的光谱数据,结果如图15所示。综放工作面采集的光谱曲线受多种因素影响而存在波动,呈细微锯齿状,光谱数据信噪比较低,同时考虑工作面粉尘浓度大、环境湿度高等外界因素,加之顶板来压不稳定,光源受其扰动影响,反射率偏低。可看出400 s之前曲线较为平缓,没有明显的特征吸收谷,400~600 s时有吸收谷的曲线间歇性出现,600~850 s时曲线重新变得平滑,850 s后曲线全都是有吸收谷的形态。
图16为现场利用改进相关系数法得到的识别结果。可看出0~400 s时为完全放煤状态,400~600 s时存在夹矸现象,600~850 s又开始放煤,850 s以后放煤结束,矸石开始流出,识别结果与图15中观察到的光谱曲线变化一致,基本符合放煤−夹矸−放煤−全矸的放煤规律,这个结果从侧面说明改进的识别算法能够较为准确地对光谱曲线进行识别。
3. 结论
(1) 研制了一种近红外光谱煤岩识别装置。其由数据采集与处理装置和光源探头一体化装置组成,通过光源探头一体化装置搜集煤岩反射光,利用数据采集与处理装置分析光谱数据。利用煤岩识别装置内部署的改进识别算法,可在获取到煤岩光谱曲线后立即分析光谱信息并判断当前煤岩类别。该装置具有采集、识别和存储功能,可实现放煤过程中煤岩的实时识别。试验结果证明了该装置在现场使用的可行性。
(2) 通过对比原始识别算法与改进识别算法测试光谱的正确率,证明改进相关系数法可使实时光谱与标准光谱库光谱的特征吸收谷重叠区域更多,误分波形比例降低。探究了不同特征波段和标准光谱库大小对识别准确度的影响,认为1 300~1 500,1 800~2 000,2 100~2 300 nm特征宽度适用于大多数煤岩样本,标准光谱库大小与正确率正相关,采集动态光谱有必要增加标准光谱库中曲线数量,相关系数法相比于余弦角算法在动态识别中效果更好,识别正确率为91.3%。
(3) 通过探究不同光谱采集参数对光谱质量的影响规律,得到了光谱采集参数的设置准则:积分时间设置主要参考光源的光照强度,当采集条件较好时积分时间设置为比下限略高5~10 ms最佳;考虑综放工作面对煤岩识别的实时性要求高且放煤过程中刮板输送机上煤岩变化较快,积分次数设置为1最佳;平滑次数主要参考环境波动快慢,只需设置为可消除环境光变化即可。
-
表 1 煤岩类型、外观、分布
Table 1 Type, appearance and distribution of coal and rock
序号 样本类型 外观特征 分布位置 1 烟煤 灰黑色,密度较大,不易破碎 煤层 2 烟煤 亮黑色,分层结构明显,质地较坚硬 煤层 3 烟煤 暗黑色,条带状结构,局部有反光性 煤层 4 烟煤 暗黑色,层状结构,断口参差状 煤层 5 烟煤 暗黑色,质地较坚硬,易破碎 煤层 6 灰黑色炭
质泥岩深灰泛黑色,层理结构不明显,
粒径较小,易破碎煤层夹矸 7 灰白色高岭
质泥岩浅灰泛白色,断口光滑,硬度较高 煤层夹矸 8 深灰色砂
质泥岩深灰色,层理结构明显,易破碎,
透水性差煤层夹矸 9 深黑色炭
质泥岩整体呈深黑色,层理结构不明显,
致密块状,较坚硬直接顶 10 白色粉砂岩 断面呈白色,粗糙且有砂质感,
性脆,层理结构不明显,砂砾黏结性差直接顶 表 2 未改进算法与改进算法识别正确率比较
Table 2 Identification accuracy comparison between unimproved algorithm and improved algorithm
算法 余弦角算法 相关系数法 改进余弦角算法 改进相关系数法 正确率/% 72.55 77.45 95.1 95.1 表 3 不同特征提取宽度下识别结果比较
Table 3 Identification results comparison under different feature extraction width
识别波段 标准光谱库大小/条 正确率/% 煤 岩 余弦角
算法相关系
数法波段1 11 15 93.12 87.25 波段2 11 15 96.08 94.12 波段3 11 15 93.14 93.14 表 4 不同大小标准光谱库识别结果比较
Table 4 Identification results comparison of different sizes standard spectral library
标准光谱库
大小/条不同种类条数 识别时间/s 正确率/% 煤 岩 余弦角算法 相关系数法 4 2 2 0.33 53.92 44.12 13 5 8 0.35 95.10 81.37 20 8 12 0.38 96.08 83.33 26 11 15 0.42 96.08 94.12 表 5 动态采集下煤岩识别正确率
Table 5 Accuracy of coal and rock identification under dynamic acquisition
算法 改进余弦角算法 改进相关系数法 正确率/% 56.52 91.3 -
[1] 于斌,徐刚,黄志增,等. 特厚煤层智能化综放开采理论与关键技术架构[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):42-53. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.5050 YU Bin,XU Gang,HUANG Zhizeng,et al. Theory and its key technology framework of intelligentized fully-mechanized caving mining in extremely thick coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):42-53. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.5050
[2] 马英. 基于尾梁振动信号采集的煤矸识别智能放煤方法研究[J]. 煤矿开采,2016,21(4):40-42. MA Ying. Intelligent coal caving with gangue identification based on tail beam vibration signal collection[J]. Coal Mining Technology,2016,21(4):40-42.
[3] 魏文艳. 综采工作面放顶煤自动控制系统[J]. 工矿自动化,2015,41(7):10-13. WEI Wenyan. Automatic control system of top coal caving on fully-mechanized coal mining face[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2015,41(7):10-13.
[4] XUE Guanghui,LIU Ermeng,ZHAO Xinying,et al. Coal-rock character recognition in fully mechanized caving faces based on acoustic pressure data time domain analysis[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2015,789/790:566-570. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.789/790.566
[5] SONG Qingjun,JIANG Haiyan,ZHAO Xieguang,et al. An automatic decision approach to coal-rock recognition in top coal caving based on MF-Score[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications,2017,20(4):1307-1315. DOI: 10.1007/s10044-017-0618-7
[6] 张宁波,鲁岩,刘长友,等. 综放开采煤矸自动识别基础研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2014,34(4):532-536. ZHANG Ningbo,LU Yan,LIU Changyou,et al. Basic study on automatic detection of coal and gangue in the fully mechanized top coal caving mining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2014,34(4):532-536.
[7] 张宁波,刘长友,陈现辉,等. 综放煤矸低水平自然射线的涨落规律及测量识别分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(5):988-993. ZHANG Ningbo,LIU Changyou,CHEN Xianhui,et al. Measurement analysis on the fluctuation characteristics of low level natural radiation from gangue[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2015,40(5):988-993.
[8] 朱世刚. 综放工作面煤岩性状识别方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京) , 2014. ZHU Shigang. Study on coal and rock character recognition method in fully mechanized caving faces[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing, 2014.
[9] 褚小立,史云颖,陈瀑,等. 近五年我国近红外光谱分析技术研究与应用进展[J]. 分析测试学报,2019,38(5):603-611. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2019.05.016 CHU Xiaoli,SHI Yunying,CHEN Pu,et al. Research and application progresses of near infrared spectroscopy analytical technique in China in past five years[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2019,38(5):603-611. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2019.05.016
[10] 张玲,邱芳萍,于健. 现代近红外光谱技术[J]. 长春工业大学学报,2003, 24(4): 23-25. ZHANG Ling,QIU Fangping,YU Jian. Modern near-infrared spectroscopic techniques[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Technology,2003, 24(4): 23-25.
[11] PASQUINI C. Near infrared spectroscopy:fundamentals,practical aspects and analytical applications[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society,2003,14(2):198-219. DOI: 10.1590/S0103-50532003000200006
[12] XIU Liancun, ZHENG Zhizhong, CHEN Chunxia, et al. Mineral identification and geological mapping using near-infrared spectroscopy analysis[C]// IEEE International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing (PIC), 2018: 119-123.
[13] 宋亮,刘善军,毛亚纯,等. 基于可见光−近红外光谱的煤种分类方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(10):1473-1476. SONG Liang,LIU Shanjun,MAO Yachun,et al. Coal classification based on visible and near-infrared spectrum[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science),2017,38(10):1473-1476.
[14] 杨恩,王世博,葛世荣. 典型块状煤的可见−近红外光谱特征研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2019,39(6):1717-1723. YANG En,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong. Study on the visible and near-infrared spectra of typical of lump coal[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2019,39(6):1717-1723.
[15] 杨恩,王世博,葛世荣. 典型煤系岩石的可见−近红外光谱特征研究[J]. 工矿自动化,2019,45(3):45-51. YANG En,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong. Research on visible-near infrared spectrum features of typical coal measures rocks[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2019,45(3):45-51.
[16] 宋亮,刘善军,虞茉莉,等. 基于可见−近红外和热红外光谱联合分析的煤和矸石分类方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(2):416-422. SONG Liang,LIU Shanjun,YU Moli,et al. A classification method based on the combination of visible near-infrared and thermal infrared spectrum for coal and gangue distinguishment[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2017,37(2):416-422.
[17] 王赛亚,王世博,葛世荣,等. 综放工作面煤岩近红外光谱特征与机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(8):3024-3032. WANG Saiya,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong,et al. Study on near-infrared spectrum characteristics and mechanism of and rock in mechanized caving face[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2020,45(8):3024-3032.
[18] 向阳,王世博,葛世荣,等. 粉尘环境下典型煤岩近红外光谱特征及识别方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(11):3430-3437. XIANG Yang,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong,et al. Study on near-infrared spectrum features and identification methods of typical coal-rock in dust environment[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(11):3430-3437.
[19] 韦任,徐良骥,孟雪莹,等. 基于高光谱特征吸收峰的煤岩识别方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(6):1942-1948. WEI Ren,XU Liangji,MENG Xueying,et al. Coal and rock identification method based on hyper spectral feature absorption peak[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021,41(6):1942-1948.
[20] 周悦,王世博,葛世荣,等. 不同探测距离与角度下典型煤岩近红外光谱特征与定性分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(9):2737-2742. ZHOU Yue,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong,et al. Near infrared spectral characteristics and qualitative analysis of typical coal-rock under different detection distances and angle[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(9):2737-2742.
[21] 杨恩,王世博,葛世荣,等. 基于反射光谱的煤岩感知实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(12):3912-3920. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0051 YANG En,WANG Shibo,GE Shirong,et al. Experimental study on coal-rock perception based on reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(12):3912-3920. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.0051
[22] 徐良骥,孟雪莹,韦任,等. 基于可见光−近红外光谱的煤岩识别方法实验研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2022,42(7): 2135-2142. XU Liangji,MENG Xueying,WEI Ren,et al. Experimental research on coal-rock identification method based on visible-near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2022,42(7): 2135-2142.
[23] ZOU Liang,YU Xinhui,LI Ming,et al. Nondestructive identification of coal and gangue via near-infrared spectroscopy based on improved broad learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2020,69(10):8043-8052.
[24] 张昊. 基于高光谱的煤岩识别技术研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017: 35-36. ZHANG Hao. Study on identification technology of coal and rock based on hyper-spectrum[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017: 35-36.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李雄,沈良,田亚锋,尹家宽,王立阳,杨东晨,慕礼洋,朱益军. 基于EMD与DCNN混合智能煤岩识别方法研究. 煤矿机械. 2024(01): 58-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李嘉豪,司垒,王忠宾,魏东,顾进恒. 综放工作面煤矸识别技术及其应用. 仪器仪表学报. 2024(01): 1-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 许献磊,陈令洲,彭苏萍,梁鹏,赵禹深. 矿井煤岩界面节点式雷达快速动态探测系统及实验研究. 煤炭学报. 2024(04): 1964-1975 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈瀑,杨健,褚小立,李敬岩,许育鹏,刘丹. 近五年我国近红外光谱分析技术的研究与应用进展. 分析化学. 2024(09): 1213-1224 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李一鸣. 基于小波包多尺度模糊熵和加权KL散度的煤岩智能识别. 工矿自动化. 2023(04): 92-98 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: