Network hole coverage reconstruction algorithm for post-disaster coal mine Internet of things
-
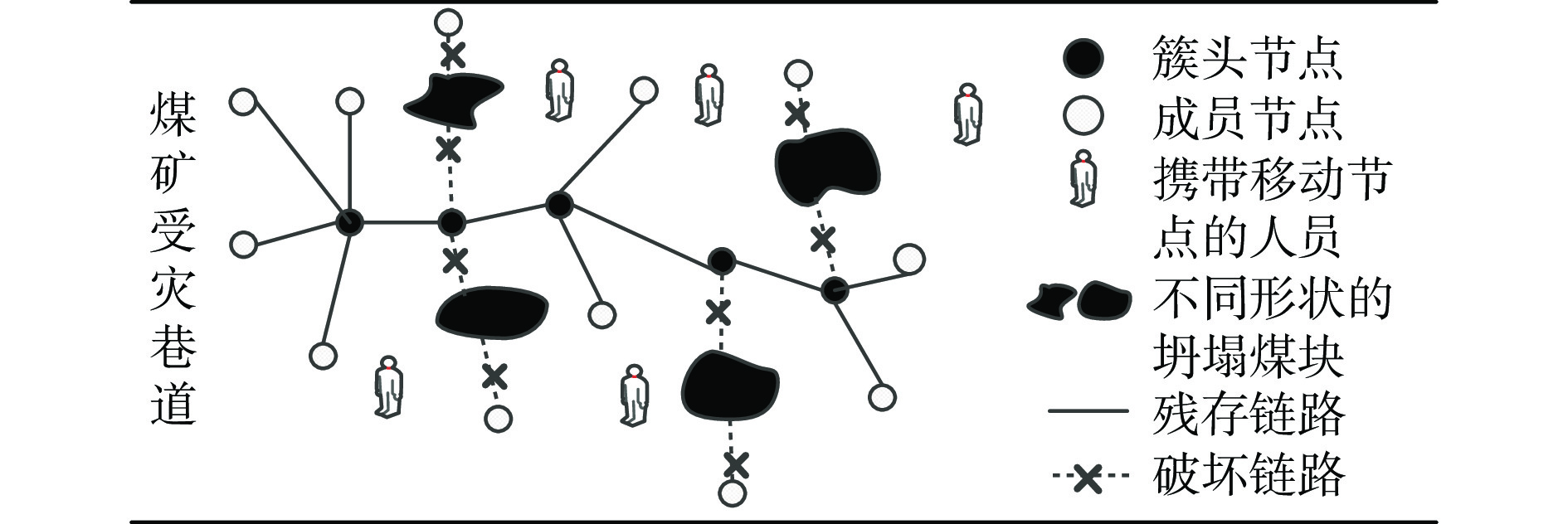
摘要: 灾后煤矿物联网因部分节点损毁或障碍物遮挡,会导致网络空洞问题,阻碍网络连通。现有网络空洞覆盖算法未考虑井下灾后地理环境因素,且未对修复后的网络进行优化,无法满足灾后煤矿物联网重构需求。针对该问题,提出了一种煤矿物联网灾后有障碍物情况下的网络空洞覆盖重构算法−NHCRA−O。建立了灾后煤矿物联网模型和节点感知模型,采用Delaunay三角剖分对网络中残存节点及障碍物角点进行区域划分,通过节点感知模型判断区域内是否存在网络空洞;计算Delaunay三角形质心位置,利用质心和Delaunay三角形顶点之间的距离确定虚拟修复节点位置;对虚拟修复节点和移动节点进行可视化判断,并基于距离因子和能量因子计算二者优先级,通过预剪枝操作删除部分计算结果来提高算法收敛速度,根据可视化判断结果和节点优先级进行虚拟修复节点和移动节点双向匹配,从而确定移动节点最终位置,完成网络空洞修复;融合剩余能量因子、节点连通度和方向介数计算节点优先级,根据优先级选举簇头节点,其他成员节点就近入簇,实现网络重构。采用Matlab2016a软件对NHCRA−O的节点匹配效率、网络覆盖效率和网络生存时间进行仿真研究,结果表明:NHCRA−O完成移动节点与虚拟修复节点匹配的次数较Gale−Shapley算法减少31.4%,网络覆盖率较C−V算法和PSO算法高且移动节点平均移动距离短,NHCRA−O重构的网络生存时间明显高于SEP算法和LEACH算法重构的网络。Abstract: Due to the damage of some nodes or obstacles in the post-disaster coal mine Internet of things, network hole would appear to hinder network connectivity. The existing network hole coverage algorithm does not consider the geographical environment factors after the underground disaster, and does not optimize the repaired network. Therefore, the algorithm cannot meet the reconstruction requirements of the post-disaster coal mine Internet of things. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a network hole coverage reconstruction algorithm with obstacles, NHCRA-O, for post-disaster coal mine Internet of things. The post-disaster coal mine Internet of things model and the node perception model are established. Delaunay triangulation is used to divide residual nodes and corner points of obstacles in the network. The node perception model is used to judge whether there is a network hole in the area. The centroid position of the Delaunay triangle is calculated. The distance between the centroid and the vertex of the Delaunay triangle is used to determine the virtual repair node position. The virtual repair node and mobile node are visualized, and the priority of both is calculated based on distance factor and energy factor. The pre-pruning operation is used to delete some calculation results to improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. According to the visual judgment result and node priority, the virtual repair node and the mobile node are matched in both directions. Therefore, the final position of the mobile node is determined and the network hole repair is completed. The node priority is calculated by fusing the residual energy factor, node connectivity and directional betweenness. The cluster head node is elected according to the priority, and other member nodes join the cluster nearby to realize network reconstruction. Matlab2016a software is used to simulate the node matching efficiency, network coverage efficiency and network time-to-live of NHCRA-O. The results show that the number of times that NHCRA-O completes the matching of mobile nodes with virtual repair nodes is 31.4% less than that of Gale-Shapley algorithm. The network coverage is higher than the C-V algorithm and the PSO algorithm, and the average moving distance of the mobile nodes is shorter. The network time-to-live reconstructed by NHCRA-O is significantly longer than that reconstructed by SEP algorithm and LEACH algorithm.
-
-
表 1 网络空洞覆盖重构仿真参数
Table 1 Simulation parameters of network hole coverage and reconstruction
参数 值 参数 值 监测区域/(m×m) $ 150\times 100 $ 最小误警率 0.05 静态节点数 20 节点感知半径/m 10 移动节点数 30 节点通信半径/m 20 节点初始能量/J 1 能量阈值/J 0.3 信号衰减指数 4 仿真时间/s 1 000 自由空间功率放大
系数/$(\mathrm{p}\mathrm{J}\cdot \mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}^{-1}\cdot { {\rm{m} } }^{-2})$10 多径衰落空间功率放
大系数/$( \mathrm{p}\mathrm{J}\cdot \mathrm{b}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}^{-1}\cdot { {\rm{m} } }^{-4})$0.0013 -
[1] 丁恩杰,赵志凯. 煤矿物联网研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 工矿自动化,2015,41(5):1-5. DING Enjie,ZHAO Zhikai. Research advances and prospects of mine Internet of things[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2015,41(5):1-5.
[2] FOROOSHANI A E,BASHIR S,MICHELSON D G,et al. A survey of wireless communications and propagation modeling in underground mines[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials,2013,15(4):1524-1545.
[3] 胡青松,杨维,丁恩杰,等. 煤矿应急救援通信技术的现状与趋势[J]. 通信学报,2019,40(5):163-179. HU Qingsong,YANG Wei,DING Enjie,et al. State-of-the-art and trend of emergency rescue communication technologies for coal mine[J]. Journal on Communications,2019,40(5):163-179.
[4] 周非,郭浩田,杨伊. 一种改进的虚拟力重定位覆盖增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报,2020,42(9):2194-2200. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT190662 ZHOU Fei,GUO Haotian,YANG Yi. An improved virtual force relocation coverage enhancement algorithm[J]. Joural of Electronics & Informaton Technology,2020,42(9):2194-2200. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT190662
[5] CHEN Wenbai,WU Xibao,LU Yang. An improved path planning method based on artificial potential field for a mobile robot[J]. Cybernetics and Information Technologies,2015,15(2):181-191. DOI: 10.1515/cait-2015-0037
[6] KHAN M U,LI S,WANG Q,et al. CPS oriented control design for networked surveillance robots with multiple physical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems,2016,35(5):778-791. DOI: 10.1109/TCAD.2016.2524653
[7] 史进,董瑶,白振东,等. 移动机器人动态路径规划方法的研究与实现[J]. 计算机应用,2017,37(11):3119-3123. SHI Jin,DONG Yao,BAI Zhendong,et al. Research and implementation of mobile robot path planning method[J]. Journal of Computer Applications,2017,37(11):3119-3123.
[8] 李国进,陈武,易丐. 基于改进人工势场法的移动机器人导航控制[J]. 计算技术与自动化,2017,36(1):52-56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6199.2017.01.011 LI Guojin,CHEN Wu,YI Gai. Navigation control of mobile robot based on improved artificial potential field method[J]. Computing Technology and Automation,2017,36(1):52-56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6199.2017.01.011
[9] 孙梦娜,杨如民,余成波. 导航系统中多目标路径平滑化规划的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2017,53(18):17-23. DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1706-0195 SUN Mengna,YANG Rumin,YU Chengbo. Research on multi-objective path-smoothing planning in navigation system[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications,2017,53(18):17-23. DOI: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1706-0195
[10] MAHBOUBI H, SHARIFI F, AGHDAM A G, et al. Distributed coordination of a network of nonidentical agents with limited communication capabilities in the presence of fixed obstacles[C]//Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Washington, 2013: 5398-5403.
[11] LO S H. Delaunay triangulation of non-convex planar domains[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,1989,28(11):2695-2707. DOI: 10.1002/nme.1620281113
[12] 胡楠,吴成东,于晓升,等. 基于C−V模型的网络覆盖空洞探测与修复算法[J]. 控制与决策,2016,31(8):1424-1428. HU Nan,WU Chengdong,YU Xiaosheng,et al. Network coverage holes detecting and healing algorithm based on C-V model[J]. Control and Decision,2016,31(8):1424-1428.
[13] 李中捷,谢东朋. 基于多对一Gale−Shapley算法的D2D通信资源分配[J]. 计算机应用研究,2019,36(8):2500-2503. LI Zhongjie,XIE Dongpeng. Resource allocation for D2D communication based on many-to-one Gale-Shapley algorithm[J]. Applications Research of Computer,2019,36(8):2500-2503.
[14] AFSAR M M,TAYARANI N M. Clustering in sensor networks:a literature survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications,2014,46:198-226. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnca.2014.09.005
[15] HEINZELMAN W R, CHANDRAKASAN A, BALAKRISHNAN H. Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, 2000: 10-12.
[16] 曾建潮,崔志华. 一种保证全局收敛的PSO算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2004,41(8):1333-1338. ZENG Jianchao,CUI Zhihua. A guaranteed global convergence particle swarm optimizer[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2004,41(8):1333-1338.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 曹帅,董立红,邓凡,高峰. 基于YOLOv7-SE的煤矿井下场景小目标检测方法. 工矿自动化. 2024(03): 35-41 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 杨艳红,钟宝江,田宏伟. DS-YOLOv4-tiny救援机器人目标检测模型. 计算机仿真. 2022(01): 387-393 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 武慧挺,周海晶,董仕涛. 煤矿救援机器人嵌入式实时操作系统设计和分析. 煤炭技术. 2022(02): 213-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 马艾强,姚顽强,蔺小虎,张联队,郑俊良,武谋达,杨鑫. 面向煤矿巷道环境的LiDAR与IMU融合定位与建图方法. 工矿自动化. 2022(12): 49-56 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 韩利强. 基于5G技术控制的煤矿救援机器人的设计. 煤矿安全. 2021(06): 168-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郑伟,杨晓辉,吕中宾,任聪,吴合风,王超. 基于改进YOLOv4输电线关键部件实时检测方法. 科学技术与工程. 2021(24): 10393-10400 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载:







