A method for constructing a knowledge graph of unsafe behaviors in coal mines
-
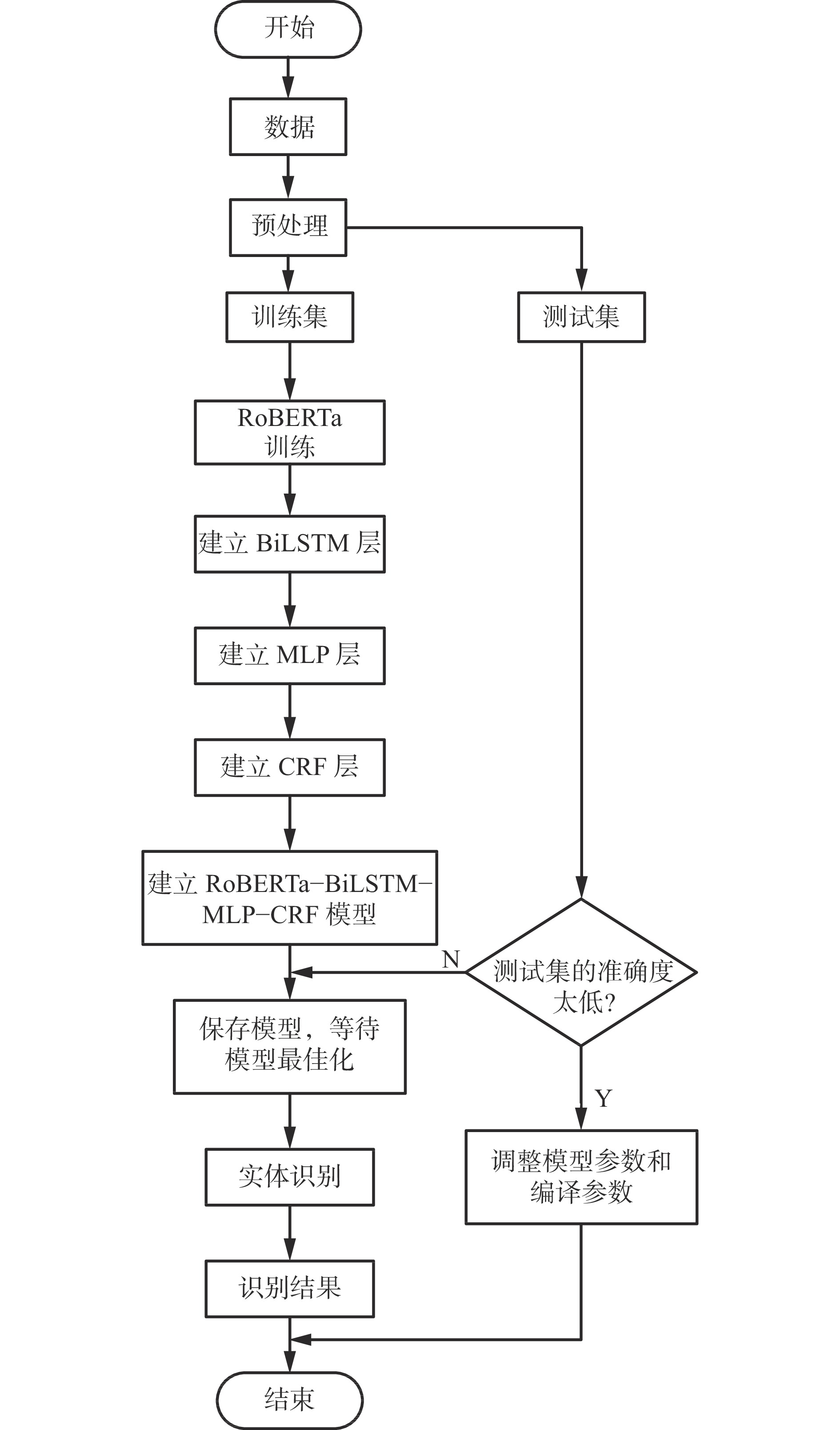
摘要: 虽然知识图谱已广泛应用于各个领域,但在煤矿安全方面,尤其在煤矿井下不安全行为方面的研究较少。构建了一种自底向上的煤矿井下不安全行为知识图谱。首先,采用传统机器学习和深度学习算法相结合的方法进行命名实体识别,采用RoBERTa进行词语向量化,采用双向长短时记忆网络(BiLSTM)对向量进行标注,提高网络模型对上下文特征的捕捉能力,通过多层感知机(MLP)解决煤矿井下不安全行为数据集数据量不足的问题,采用条件随机场(CRF)模型解决前面存在的单词关系不识别问题,并捕获全文信息和预测结果。其次,根据语句的结构特点,设计了基于知识“实体−关系−实体”三元组的依存句法树结构,对井下不安全行为领域的知识资源进行知识抽取与表示。最后,构建面向井下不安全行为的知识图谱。实验结果表明:① RoBERTa−BiLSTM−MLP−CRF模型对于导致结果、违反性行为、错误性行为及粗心性行为4类实体类别具有较好的识别效果,其准确率分别为86.7%,80.3%,80.7%,77.4%。② 在相同的数据集下,RoBERTa−BiLSTM−MLP−CRF模型训练的准确率、召回率、F1值较RoBERTa−BiLSTM−CRF模型分别提高了1.6%,1.5%,1.6%。Abstract: Although knowledge graphs have been widely applied in various fields, there is relatively little research on coal mine safety, especially in the area of unsafe behavior underground. A bottom-up knowledge graph of unsafe behaviors in coal mines has been constructed. Firstly, a combination of traditional machine learning and deep learning algorithms is used for named entity recognition. RoBERTa is used for word vectorization. The bidirectional long short term memory network (BiLSTM) is used to annotate the vectors, improving the network model's capability to capture contextual features. To solve the problem of insufficient data volume in the dataset of unsafe behaviors in coal mines, a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) is used. The conditional random field (CRF) model is adopted to solve the problem of unrecognized word relationships and capture full-text information and prediction results. Secondly, based on the structural characteristics of the statements, a dependency syntax tree structure based on the knowledge "entity - relationship - entity" triplet is designed to extract and represent knowledge resources in the field of unsafe behavior underground. Finally, a knowledge graph of unsafe behaviors underground is constructed. The experimental results show that the RoBERTa-BiLSTM-MLP-CRF model has good recognition performance for four types of entity categories: results, violating behavior, erroneous behavior, and careless behavior, with accuracy rates of 86.7%, 80.3%, 80.7%, and 77.4%, respectively. ② Under the same dataset, the accuracy, recall, and F1 value of the RoBERTa-BiLSTM-MLP-CRF model training are improved by 1.6%, 1.5%, and 1.6%, respectively, compared to the RoBERTa-BiLSTM-CRF model.
-
表 1 实体待预测标签
Table 1. Entity to be predicted labels
实体类型 开始标签 中间或结尾标签 遗忘性行为 B−forget I−forget 粗心性行为 B−careless I−careless 错误性行为 B−error I−error 违反性行为 B−violate I−violate 关联因素影响性行为 B−factor I− factor 导致后果 B−cause I−cause 表 2 实体相似度计算实例
Table 2. Example of entity similarity calculation
实体1 实体2 Sconsine SJarccard 粉尘瓦斯爆炸 粉尘瓦斯事故 0.67 0.50 违章指挥 违章命令 0.67 0.60 不安全动作 不安全行为 0.60 0.43 安全培训 安全训练 0.67 0.60 表 3 基于Neo4j的知识存储方案
Table 3. Neo4j-based knowledge storage solutions
类型 作用 对象范围 节点 描述知识实体 井下扒车、穿化纤衣入井等 标签 描述知识概念类 违章指挥、违规操作等 边 描述实体关系 包含关系、关联关系等 表 4 实体类型识别效果
Table 4. Entity type identification effect
% 实体类别 P R F1 遗忘性行为 63.5 67.4 65.4 粗心性行为 77.4 84.1 80.6 错误性行为 80.7 83.1 81.9 违反性行为 80.3 83.7 82.0 关联因素影响性行为 73.0 76.0 74.5 导致后果 86.7 90.0 88.3 表 5 模型对比结果
Table 5. Model contrast results
% 模型 P R F1 BiLSTM−CRF 71.2 74.8 73.0 BERT−BiLSTM−CRF 74.9 79.1 77.0 RoBERTa−BiLSTM−CRF 75.6 79.1 77.3 RoBERTa−BiLSTM−MLP−CRF 77.2 80.6 78.9 -
[1] 黄辉,张雪. 煤矿员工不安全行为研究综述[J]. 煤炭工程,2018,50(6):123-127.HUANG Hui,ZHANG Xue. Review of research on unsafe behavior of miners[J]. Coal Engineering,2018,50(6):123-127. [2] GUARINO N,WELTY C. Evaluating ontological decisions with OntoClean[J]. Communications of the ACM,2002,45(2):61-65. doi: 10.1145/503124.503150 [3] HORROCKS,IAN,PATEL-SCHNEIDER,et al. SWRL:a semantic web rule language combining OWL and RuleML[J]. W3C Member Submission,2004,21(79):1-31. [4] BORDES A,USUNIER N,GARCIA-DURAN A,et al. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[C]. Neural Information Processing Systems,South Lake Tahoe,2013:1-9. [5] WANG Zhen,ZHANG Jianwen,FENG Jianlin,et al. Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes[C]. The 28th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,2014. [6] 刘文聪,张春菊,汪陈,等. 基于BiLSTM−CRF的中文地质时间信息抽取[J]. 地球科学进展,2021,36(2):211-220.LIU Wencong,ZHANG Chunju,WANG Chen,et al. Geological time information extraction from Chinese text based on BiLSTM-CRF[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2021,36(2):211-220. [7] 吴闯,张亮,唐希浪,等. 航空发动机润滑系统故障知识图谱构建及应用[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报:1-14[2023-05-22].https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0434.WU Chuang,ZHANG Liang,TANG Xilang,et al. Construction and application of fault knowledge graph for aero-engine lubrication system[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics:1-14[2023-05-22]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0434. [8] SHAO Zhou,YUAN Sha,WANG Yongli,et al. ELAD:an entity linking based affiliation disambiguation framework[J]. IEEE Access,2020,8:70519-70526. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986826 [9] FANG Yuan,CHANG Mingwei. Entity linking on microblogs with spatial and temporal signals[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics,2014,2:259-272. doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00181 [10] SIMONE F,ANSALDI S,AAGNELLO P,et al. Industrial safety management in the digital era:constructing a knowledge graph from near misses[J]. Computers in Industry,2023,146. DOI: 10.1016/j.compind.2022.103849. [11] 尉桢楷,程梦,周夏冰,等. 基于类卷积交互式注意力机制的属性抽取研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2020,57(11):2456-2466.WEI Zhenkai,CHENG Meng,ZHOU Xiabing,et al. Convolutional interactive attention mechanism for aspect extraction[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2020,57(11):2456-2466. [12] 刘峤,李杨,段宏,等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2016,53(3):582-600.LIU Qiao,LI Yang,DUAN Hong,et al. Knowledge graph construction techniques[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development,2016,53(3):582-600. [13] HOCHREITER S,SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation,1997,9(8):1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [14] SEKI K. On cross-lingual text similarity using neural translation models[J]. Journal of Information Science,2020,27:315-321. [15] 李红霞,樊欣怡. 人因视角下国内煤矿安全领域研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(1):181-186.LI Hongxia,FAN Xinyi. Status and development trend of coal mine safety research from the perspective of human factors[J]. Coal Engineering,2022,54(1):181-186. [16] BENGIO Y,DUCHARME RVINCENT P. A neural probabilistic language model[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2003,3:1137-1155. [17] PENNINGTON J,SOCHER R,MANNING C. Glove:global vectors for word representation[C]. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing,Doha,2014:1532-1543. [18] PETERS M E,NEUMANN M,LYYER M,et al. Deep contextualized word representations[C]. Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics,New Orleans,2018:2227-2237. [19] DEVLIN J,CHANG Mingwei,LEE K,et al. BERT:pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Lingristics,Jill Burstein,2019:4171-4186. [20] XU Wencong,HU Yue,LI Jianxun. A data-driven Dir-MUSIC method based on the MLP model[J]. IET Science,Measurement & Technology,2022(6):367-376. [21] 王智广,文红英,鲁强,等. 地质领域开放式实体关系联合抽取[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2021,42(4):996-1005.WANG Zhiguang,WEN Hongying,LU Qiang,et al. Joint extraction of open entity relation in geological field[J]. Computer Engineering and Design,2021,42(4):996-1005. [22] 赵晓娟,贾焰,李爱平,等. 多源知识融合技术研究综述[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(3):459-473.ZHAO Xiaojuan,JIA Yan,LI Aiping,et al. A survey of the research on multi-source knowledge fusion technology[J]. Journal of Yunnan University(Natural Sciences Edition),2020,42(3):459-473. [23] 乔骥,王新迎,闵睿,等. 面向电网调度故障处理的知识图谱框架与关键技术初探[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(18):5837-5849.QIAO Ji,WANG Xinying,MIN Rui,et al. Framework and key technologies of knowledge-graph-based fault handling system in power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(18):5837-5849. [24] 曹现刚,张梦园,雷卓,等. 煤矿装备维护知识图谱构建及应用[J]. 工矿自动化,2021,47(3):41-45.CAO Xiangang,ZHANG Mengyuan,LEI Zhuo,et al. Construction and application of knowledge graph for coal mine equipment maintenance[J]. Industry and Mine Automation,2021,47(3):41-45. -





 下载:
下载: